Preventing Malicious Traffic
Attacks and malicious traffic will result in a bill higher than your normal expenditures. This high bill cannot be waived or refunded. To reduce such risks, set defenses and notifications.
Stopping Losses Promptly
If your domain name has been attacked or traffic has been stolen, you can use usage capping and request rate limiting to prevent further losses, analyze attack behavior, and set protection policies.
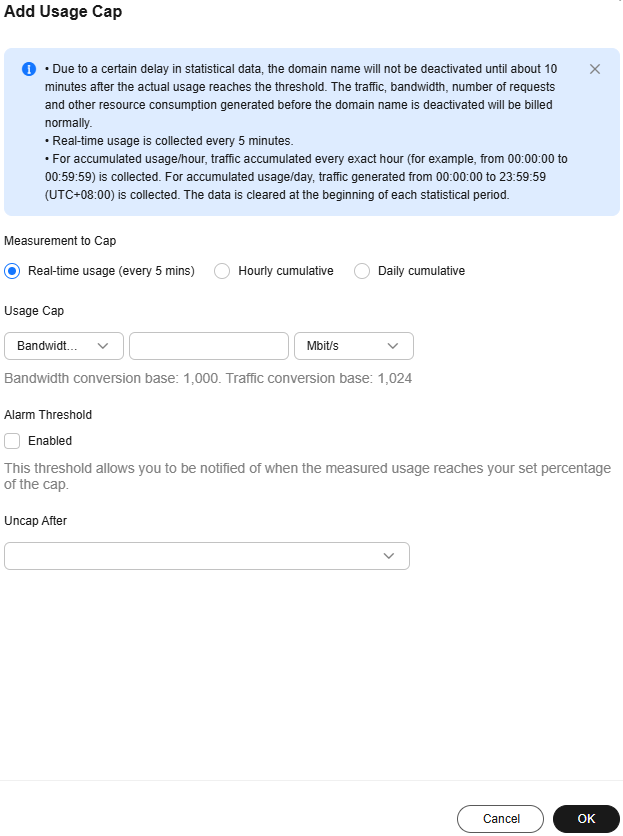
- Set a usage cap for a domain name. When the bandwidth or traffic usage reaches the threshold, CDN will be disabled for the domain name to prevent high bills caused by traffic theft or malicious attacks.
Figure 1 Adding a usage cap
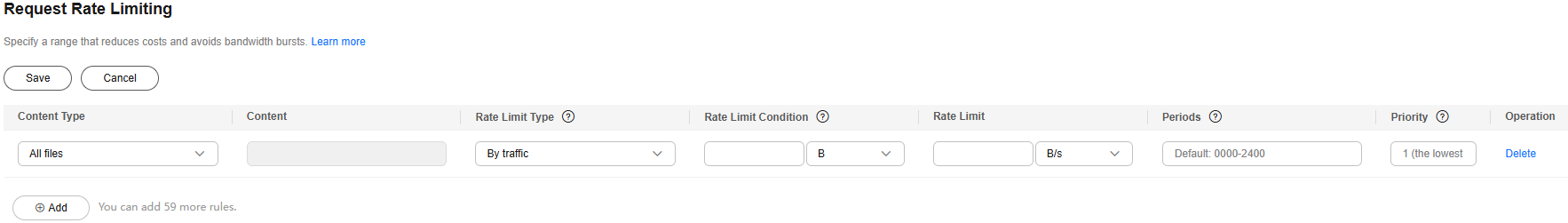
- Limit downlink rates of user requests to CDN PoPs to control the total request bandwidth and reduce the risk of sudden spikes in bandwidth use.
Figure 2 Setting request rate limiting
Analyzing Attack Behaviors
After a domain name is attacked, analyze the attack time and attacker information to harden security configurations.
- Determine the attack period by selecting a statistical period and dimension and analyzing high bills. For details about how to export bills, see Bills.
- Analyze offline logs in the attack period, check HTTP request information, identify abnormal IP addresses and anti-leeching information, and set protection rules accordingly. For details, see Analyzing Malicious Access Addresses Through Logs.
- Download and analyze custom operations reports such as popular URL, popular referer, and popular UA reports. These reports are available if you have customized them for the domain name before an attack. For details, see Operations Reports.

Set operations reports beforehand. If attacks cause a high bill before you configure them, you have to rely on offline logs for past data analysis.
Resolving Issues
- After analyzing attack behavior, extract the corresponding attack IP addresses, referers, or user agents. Then use CDN's basic access control to filter out these attack sources.
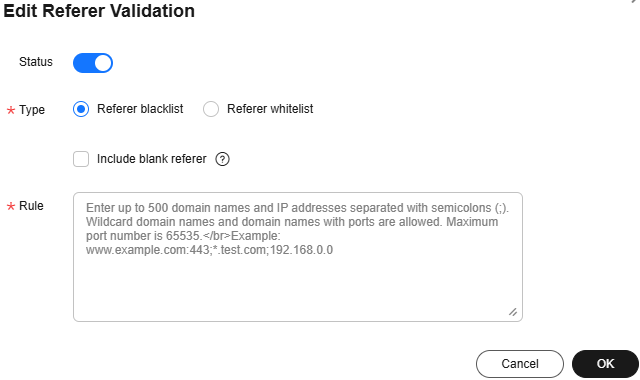
- Attackers forge the Referer request header to mimic a valid requested source. Use referer validation to block requests from these malicious referers. Set a referer blacklist or whitelist to allow valid referer requests and reject unauthorized third-party websites from accessing your resources.
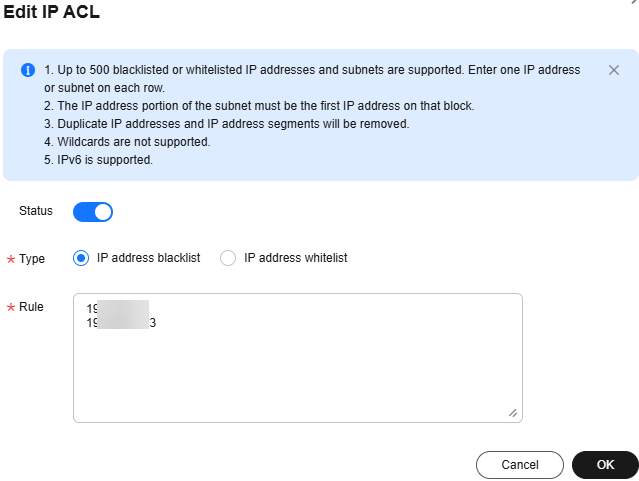
- Set an IP blacklist and add the IP addresses to it to filter them out.
- Attackers forge the User-Agent field to send a large number of requests to bypass security check. The User-Agent field may contain empty or random values. Set a User-Agent blacklist to filter out suspicious User-Agent fields. Set a User-Agent blacklist or whitelist to filter out requests with blank user agents.
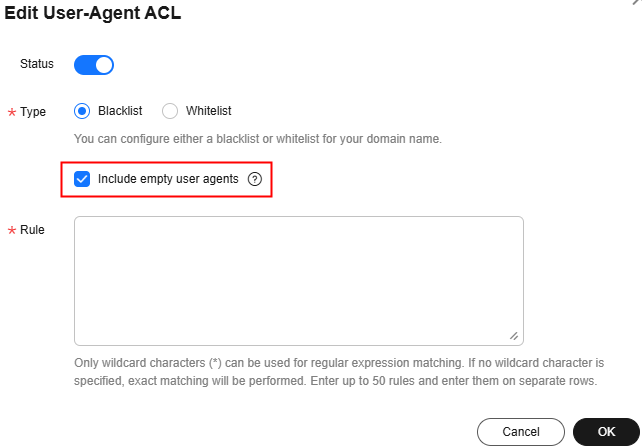
- Attackers forge the Referer request header to mimic a valid requested source. Use referer validation to block requests from these malicious referers. Set a referer blacklist or whitelist to allow valid referer requests and reject unauthorized third-party websites from accessing your resources.
- Enable Edge Security (EdgeSec). EdgeSec is a security service Huawei Cloud deploys on CDN edge PoPs. Its features include anti-DDoS, CC attack protection, WAF, and bot behavior analysis. Set security rules as required to fully protect your domain names.
Follow-Up Protection

Cloud Eye monitoring is free of charge on CDN. If you configure alarms on Cloud Eye, SMN will charge you for alarm notifications sent to you. For details about SMN pricing, see SMN Pricing Details.
Limit the IP address frequency to restrict the number of queries per second (QPS) for a URL sent from a single IP address to a single PoP. This helps you defend against CC attacks and malicious theft and reduce the risk of high bills.
Set a bandwidth threshold. When the bandwidth of client requests reaches the threshold, CDN alerts you, helping you identify attacks promptly and prevent excess billing caused by bandwidth theft or attacks.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





