Working with Global Accelerator to Accelerate Cross-Border Access
Prerequisites
- You have prepared a domain name based on Notes and Constraints.
- You have enabled CDN.
Scenarios
When resources requested by clients are not cached on CDN PoPs, PoPs pull them from the origin server. If the service area you selected for the domain name and the origin server are in different countries, PoPs will encounter slow or failed origin pull due to cross-border network issues. For example, if your domain's service area is outside the Chinese mainland but the origin server is in the Chinese mainland, all client requests are scheduled to PoPs outside the Chinese mainland. This causes cross-border origin pull when no cache hits. As a result, origin pull slows down or may fail.
To address these challenges and accelerate both dynamic and static content access across borders, consider using Huawei Cloud Global Accelerator with CDN.
Solution Overview
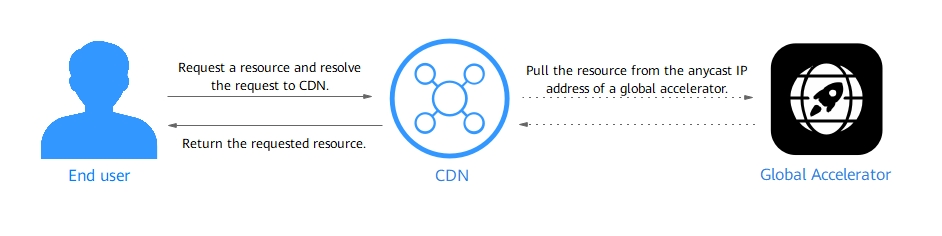
When a user initiates an access request, CDN checks whether the requested content is cached on the PoP with the fastest response speed. If yes, the PoP returns the resource to the user. If no, the PoP pulls content from Global Accelerator, which enables cross-border access and returns the resource to the PoP. The PoP then returns the resource to the user and caches it.
Resource Cost and Planning
This practice assumes that the acceleration domain name is www.example.com and its service area is outside the Chinese mainland. The origin server (IP address: 192.168.1.1) is in the Chinese mainland.
|
Resource |
Description |
Quantity |
Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Global accelerator |
You are billed based on how long each global accelerator is retained in your account.
|
1 |
For details, see Global Accelerator Pricing Details. |
|
Global accelerator data transmission |
You are billed by the GBs used by your global accelerators.
|
Per actual use |
|
|
Record set added to the public zone |
A record set with Line set to Default and Value set to the CNAME provided by CDN |
1 |
Free |
|
CDN acceleration domain name |
Service Area: Outside Chinese mainland Origin server type: IP address Origin server address: the anycast IP address allocated by the global accelerator |
1 |
For details, see CDN Pricing Details. |
Flowchart
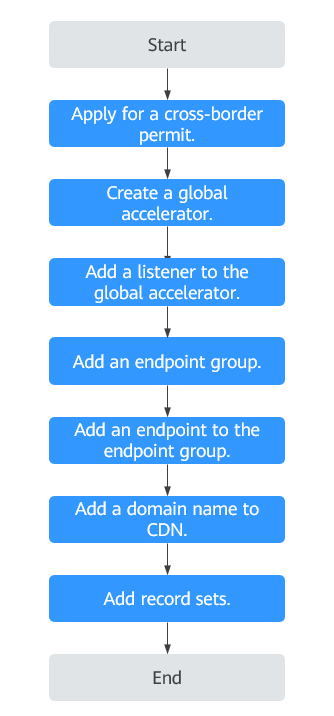
Step 1: Apply for a Cross-Border Permit
In accordance with the laws and administrative regulations of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) of the People's Republic of China, only China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom are allowed for cross-border network communications, and a cross-border permit is required if you carry out business activities outside the Chinese mainland.
- Log in to the Cross-border Permits page.
- Click Request a Cross-Border Permit.
The Cross-Border Service Application System page is displayed.
Figure 1 Applying for a cross-border permit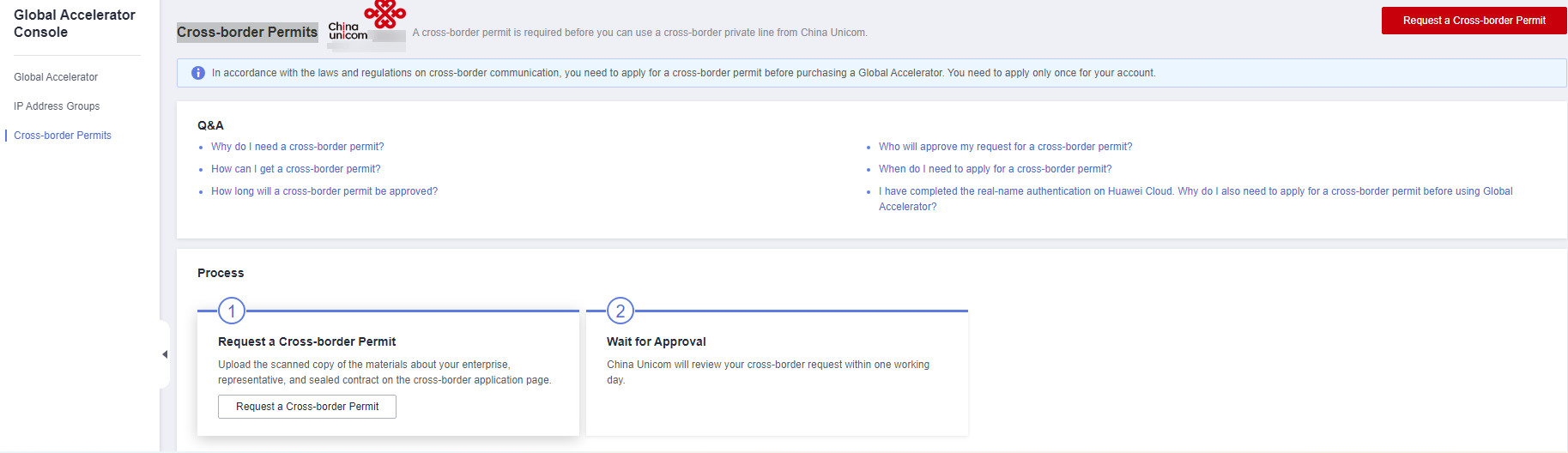
- On the application page, set related parameters and upload related materials.
- Click Submit.
Step 2: Buy a Global Accelerator
To use Global Accelerator for faster access, you first need to create a global accelerator.
- Log in to the Global Accelerator console.
- On the Global Accelerator page, click Buy Global Accelerator.
Figure 2 Buying a global accelerator
- Set parameters. Select Outside the Chinese mainland for Applicability. For other parameters, see Table 2.
Figure 3 Creating a global accelerator
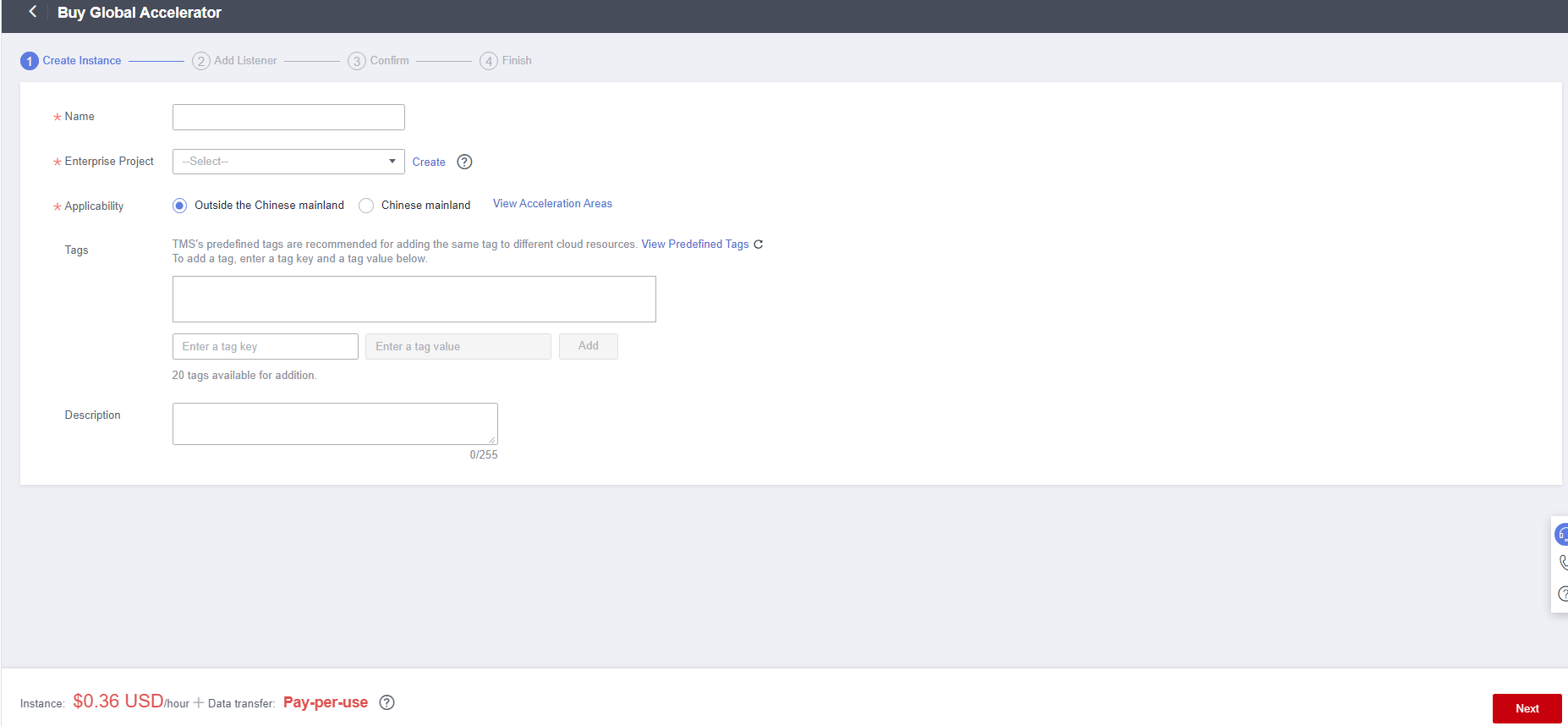
Table 2 Parameters for creating a global accelerator Parameter
Description
Name
Name of the global accelerator you want to create.
Use only letters, digits, and hyphens (-).
Enter 1 to 64 characters.
Enterprise Project
An enterprise project allows you to group cloud resources for easier resource and member management.
You can use an existing enterprise project or create one.
Applicability
Area where the global accelerator will be used.
There are two options: Outside the Chinese mainland and Chinese mainland. Outside the Chinese mainland is selected by default.
Outside the Chinese mainland is recommended for this practice.
IP Address Type
Type of the IP address used by the global accelerator.
If you selected Chinese mainland for Applicability, you can select IPv4 or IPv4+IPv6.
Default value: IPv4.
IP Address Pool
The IP address pool that will assign a static IP address to your global accelerator as an access point. This parameter is only available when IP Address Type is set to IPv4.
You can select the Huawei Cloud IP address pool or use your own public IP addresses.
- By default, the system assigns a static IP address from the Huawei Cloud IP address pool to your accelerator.
- To bring your own IP addresses to Huawei Cloud Global Accelerator, submit a service ticket.
Assignment Method
The way you would like an IP address to be assigned to the global accelerator when you choose to use your own public IP addresses.
There are two options: Auto or Manual.
IP Address
This parameter is available only when Assignment Method is set to Manual.
Enter the IP address of the global accelerator.
Tags
Identifiers of the global accelerator. Each tag consists of a key and a value. You can add 20 tags for a global accelerator.
NOTE:If you have created a predefined tag in TMS, you can select the corresponding tag key and value.
For details about predefined tags, see Predefined Tag Overview.
If you have configured tag policies for Global Accelerator, you need to add tags to your accelerators based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, global accelerators may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
Description
Supplementary information about the global accelerator.
Enter up to 255 characters.
- Click Next.
Step 3: Add a Listener to the Global Accelerator
You need to configure a listener for your global accelerator. A listener checks for connection requests and distributes traffic to endpoints based on specific policies.
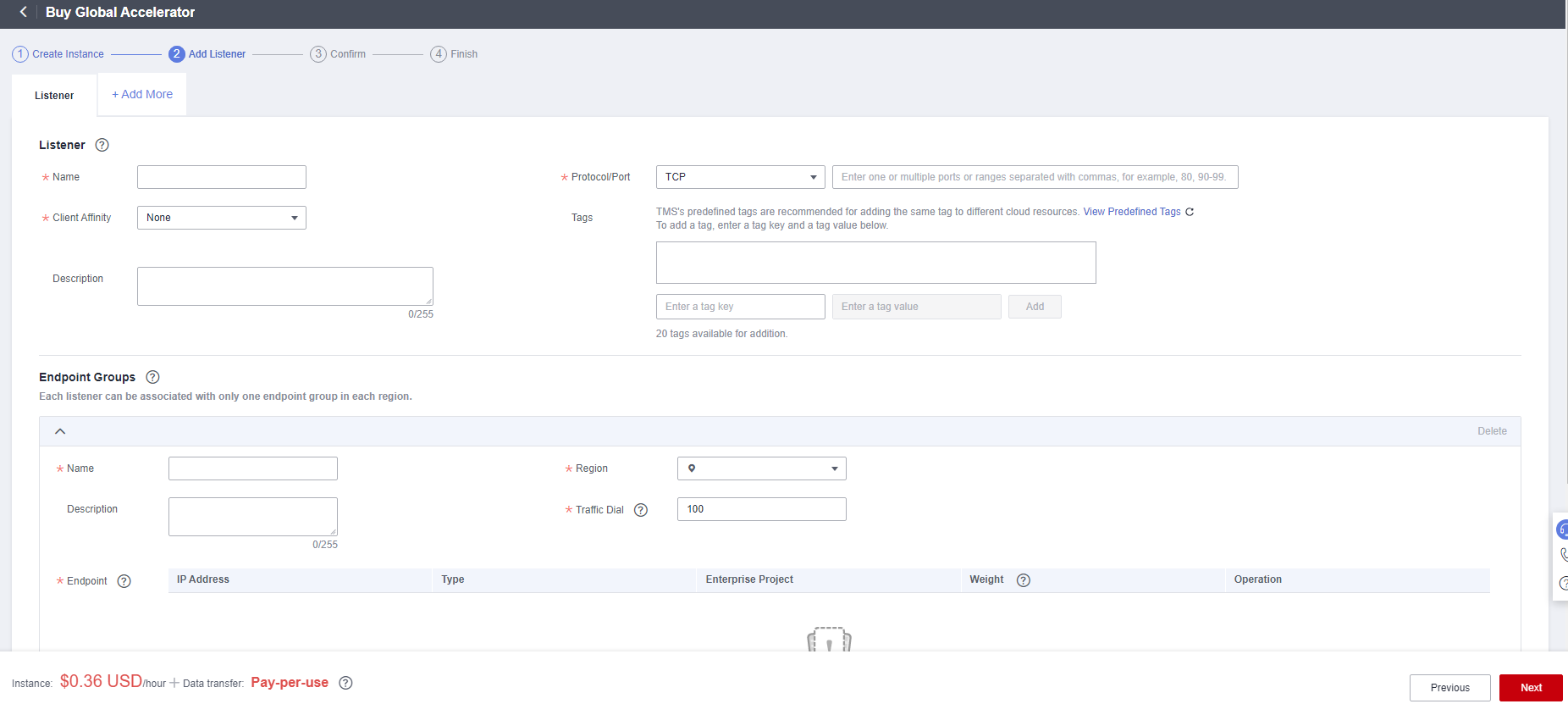
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
Name of the listener. Use only letters, digits, and hyphens (-). Enter 1 to 64 characters. |
|
Protocol |
Protocol used by the listener to receive requests from clients. Select TCP or UDP. |
|
Port Ranges |
Ports or port ranges used by the listener to receive requests from clients. The port range is 1 to 65535. Use a hyphen (-) to separate the start and end ports. You can enter one or more ports or port ranges separated by commas (,). Example: 1-10,11-50,51,52-200 |
|
Client Affinity |
How requests are routed. Select None or Source IP address. TCP and UDP support only Source IP address. Source IP address: The source IP address of each request is calculated using the consistent hashing algorithm to obtain a unique hashing key, and all backend servers are numbered. The system allocates the client to a particular server based on the generated key. This allows requests from the same IP address to be forwarded to the same backend server. |
|
Tags |
Identifiers of the listener. Each tag consists of a key and a value. You can add up to 20 tags to each listener.
NOTE:
If you have created a predefined tag in TMS, you can select the corresponding tag key and value. For details about predefined tags, see Predefined Tag Overview. If you have configured tag policies for Global Accelerator, you need to add tags to your listeners based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, listeners may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies. |
|
Description |
Supplementary information about the listener. Enter up to 255 characters. |
Step 4: Associate an Endpoint Group with the Listener
Associate an endpoint group with the listener in the CN East-Shanghai1 region and add an endpoint to this endpoint group as instructed by Table 4.
|
Type |
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Endpoint Groups |
Name |
Name of the endpoint group.
|
|
Region |
Region where the endpoint group will be used. Select CN East-Shanghai1 for this practice. |
|
|
Description |
Supplementary information about the endpoint group. Enter up to 255 characters. |
|
|
Traffic Dial |
The percentage of traffic directed to each endpoint group. If you increase the traffic dial, more requests will be distributed to this endpoint group. If you set the traffic dial to 0, no requests will be distributed to this endpoint group. Value range: 0 to 100
NOTE:
If a listener has multiple endpoint groups, traffic will be first distributed to the endpoint group with the lowest latency based on the traffic dial value you set. Then, the rest of the traffic will be distributed to other endpoint groups. |
|
|
Endpoint |
A single point of contact for clients. Global Accelerator distributes incoming traffic across healthy endpoints. Enter the actual origin server address (192.168.1.1 in this practice). |
|
|
Health Check |
Health Check |
Whether to enable health check. If you disable health check, requests may be forwarded to unhealthy endpoints. |
|
Protocol |
The health check protocol can be TCP or UDP. Default value: TCP |
|
|
Port Ranges |
Port used for health checks. Value range: 1 to 65535 |
|
|
Advanced Settings |
||
|
Interval (s) |
Maximum amount of time between two consecutive health checks, in seconds. Value range: 1 to 60 |
|
|
Timeout (s) |
How long to wait for a response before a health check times out. Value range: 1 to 60 |
|
|
Maximum Retries |
Maximum number of health check retries allowed. Value range: 1 to 10 |
|
Step 5: Add a Domain Name to CDN
- Log in to the CDN console.
- In the navigation pane, choose .
- On the Domains page, click Add Domain Names and specify domain parameters.
- Domain Name: www.example.com
- Service Area: Outside Chinese mainland
- Service Type: Website
- Origin Server Settings
- Origin Protocol: HTTP
- Type: IP address
- Address: the anycast IP address of the global accelerator
- Origin ports: same as the frontend ports set in Step 3: Add a Listener to the Global Accelerator
- Host Header: the acceleration domain name by default
Figure 5 Adding a domain name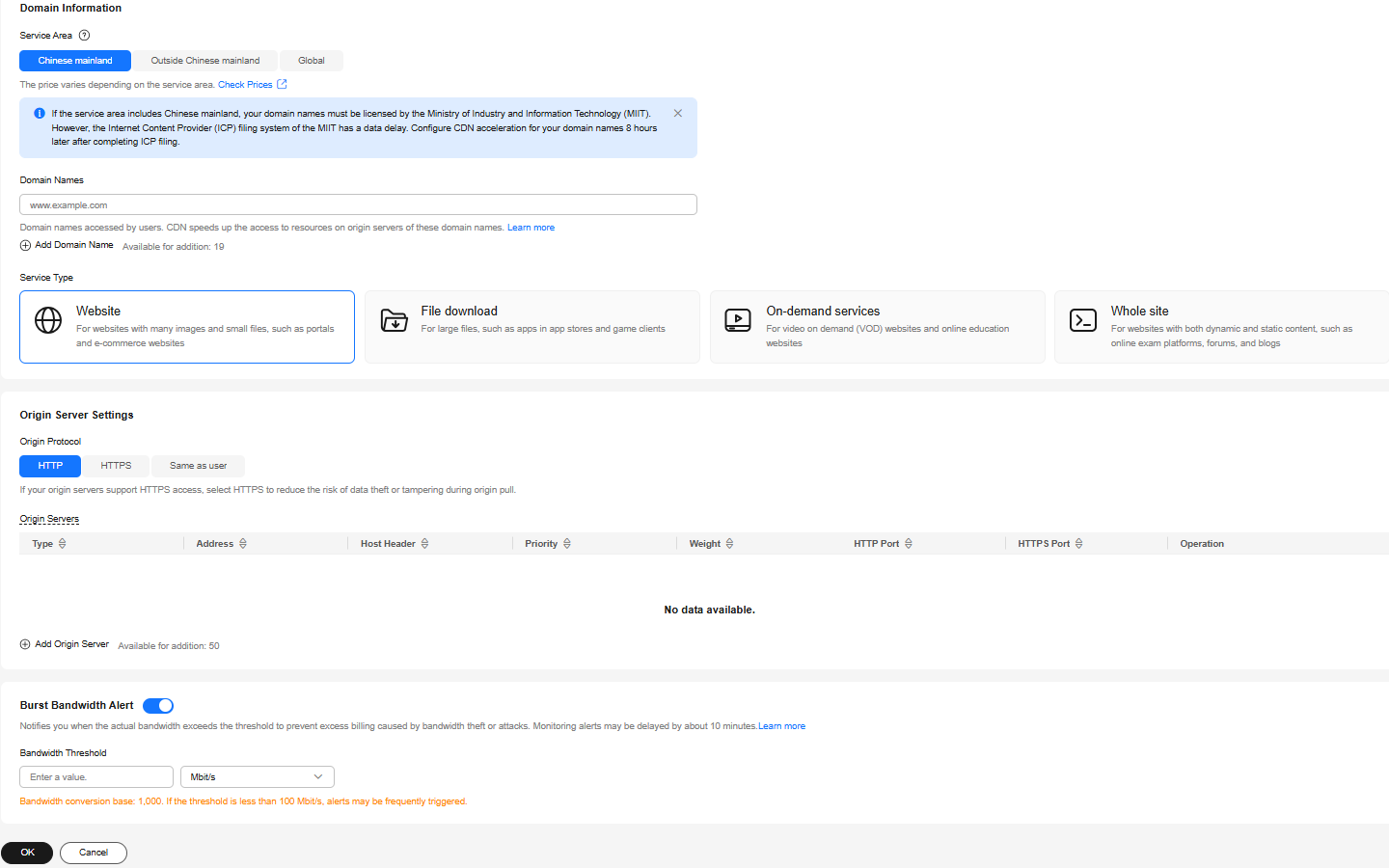
For details about other parameters, see Adding a Domain Name.
Step 6: Add a Record Set
After the domain name is added, CDN automatically generates a CNAME for the domain name. The CNAME cannot be accessed directly. You must add it to your domain's DNS records. Then requests for your domain name will be redirected to CDN PoPs for acceleration.
This section uses Huawei Cloud DNS as an example.
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- On the Public Zones page, click the target domain name.
The Record Sets page is displayed.
- In the upper right corner of the page, click Add Record Set.
- Add a CNAME record for the domain name as prompted. Retain the default values for the parameters not listed in the following table.
- Click OK.
- Check whether the CNAME record has taken effect.
Open the command line interface that comes with Windows and run the following command:
nslookup -qt=cname Acceleration domain name
In this practice, the acceleration domain name is www.example.com. If the CNAME generated by CDN is displayed, the CNAME configuration has taken effect.
Verification
You can run the curl command on a Windows PC in the area where acceleration is required to check whether the access is accelerated.
curl -o /dev/null -s -w "time_connect: %{time_connect}\ntime_starttransfer: %{time_starttransfer}\ntime_total: %{time_total}\n" "http[s]://<Website domain name>[:<Port>]"

- Port: the port for end users to access the website.
- time_connect: the time taken to establish a connection, in seconds. It is from the time when a TCP connection request is initiated to the time when the connection is established.
- time_starttransfer: the time taken from the start until the first byte was just about to be transferred, in seconds.
- time_total: the total time in seconds, that the full operation lasted.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





