Gateways and Child Devices
Overview
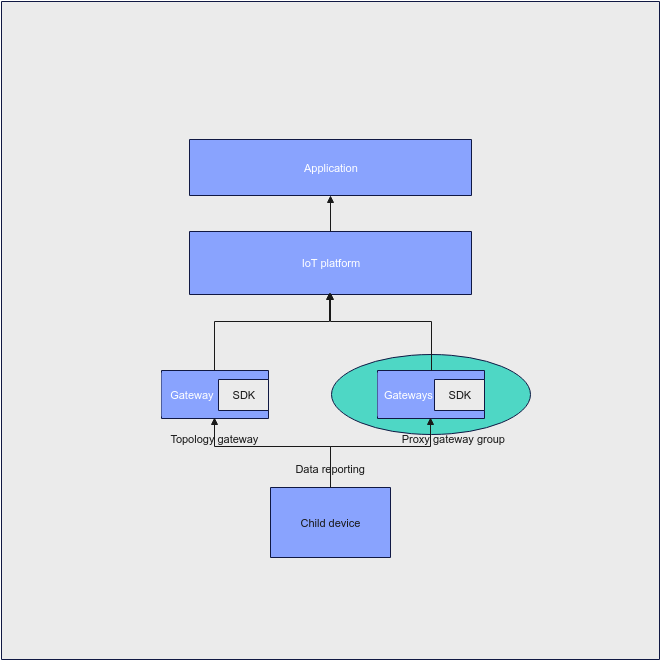
IoT devices can connect to IoTDA in two modes.
- Directly connected devices: Devices directly connect to the platform using specified protocols.
- Indirectly connected devices: Devices that do not support the TCP/IP protocol stack cannot directly communicate with the platform and need to use gateways as media for data forwarding. Devices directly connected to the platform through MQTT can be used as gateways.
The following figure shows the relationship between directly connected devices and indirectly connected devices.
Service Flow
You can use the APIs provided by IoT device SDKs to connect gateways and child devices to the platform. API names of SDKs vary depending on the language. For details, see IoT Device SDK (Java), IoT Device SDK (C), IoT Device SDK (C#), IoT Device SDK (Android), and IoT Device SDK Tiny (C).
|
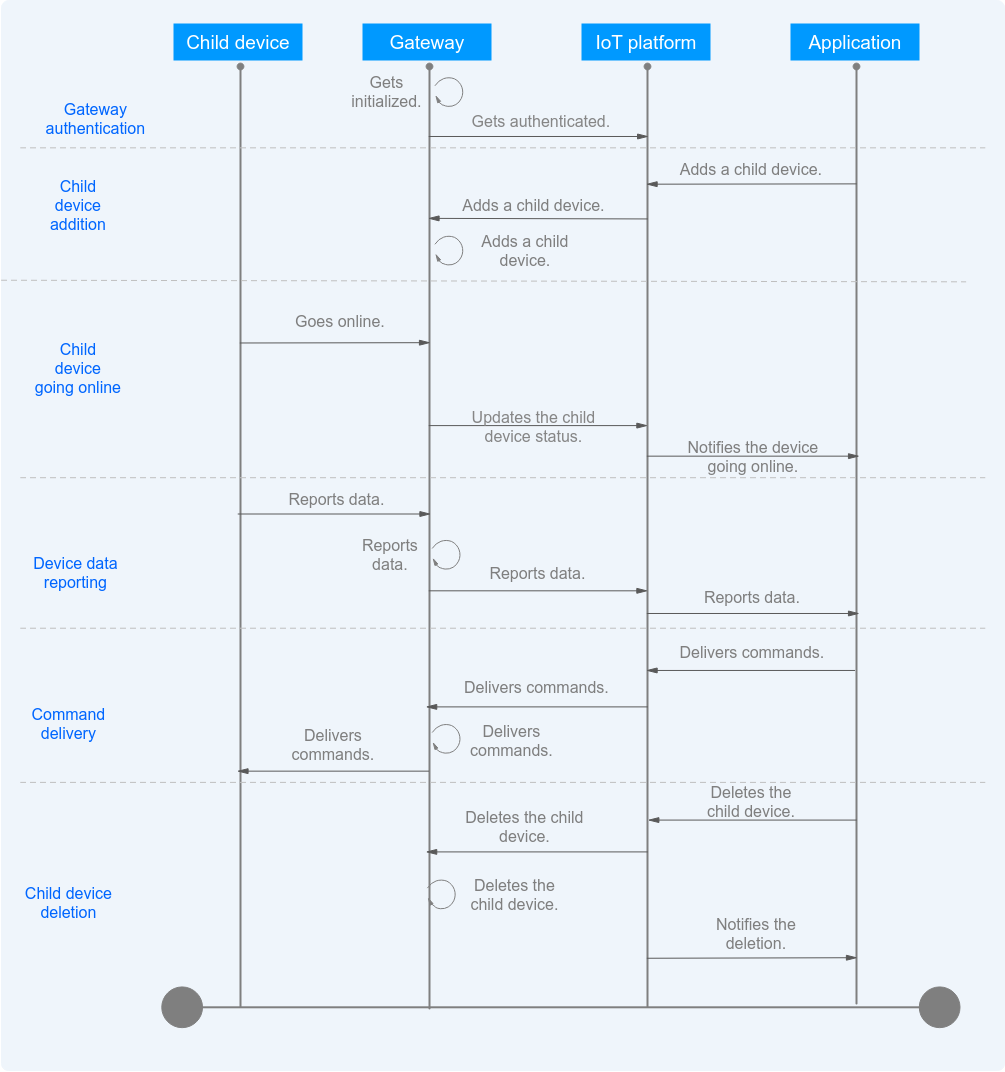
Child Device Management Process at the Application Side |
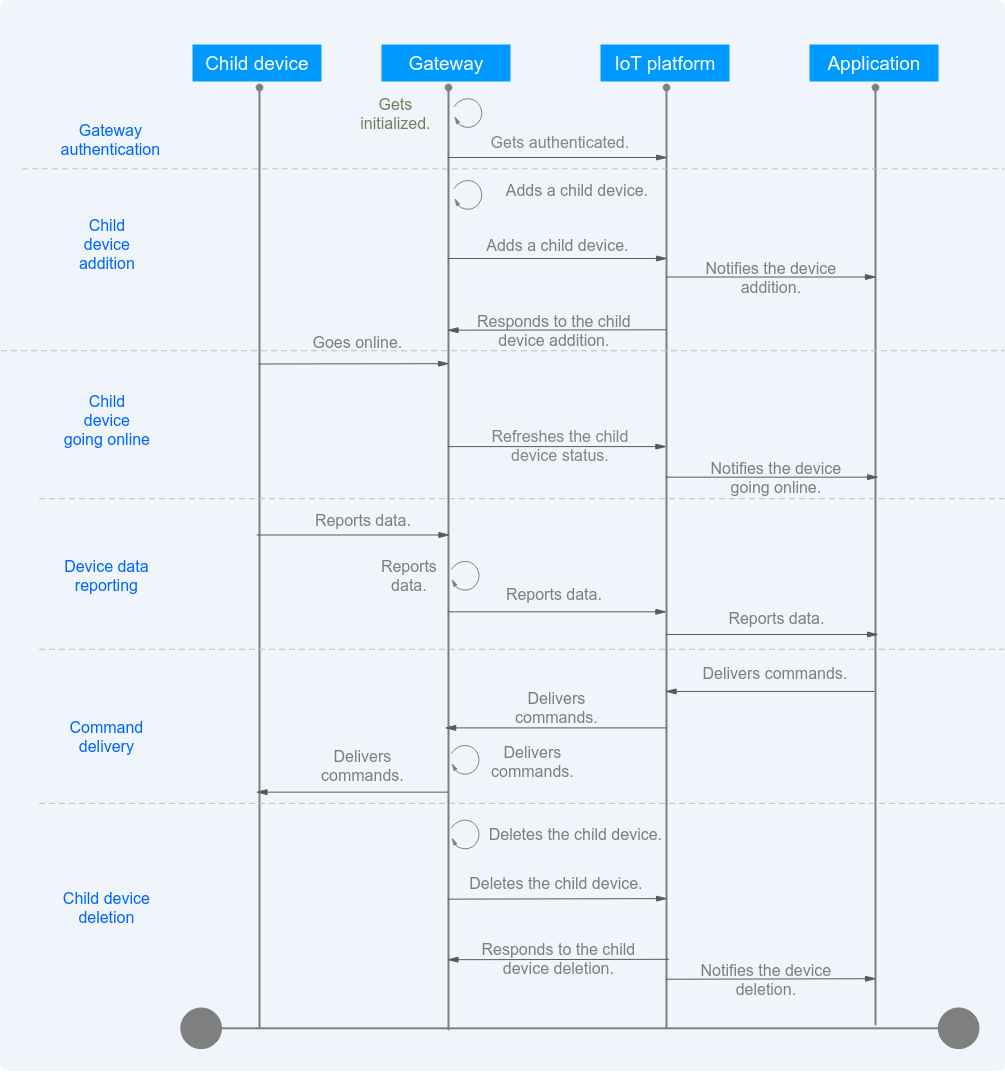
Child Device Management Process at the Gateway Side |
|---|---|
|
Figure 2 Child device management process at the application side
|
Figure 3 Child device management process at the gateway side
|
|
1. A user uploads the product model of a gateway to the platform and registers the gateway. |
|
|
2. The gateway calls the authentication API to go online. |
|
|
3. The user uploads the product model of a child device to the platform. |
|
|
4. After the gateway authentication is successful, an application calls the API for creating a device. (The device information entered in the API request must be consistent with that defined in the product model). After the child device is added, the user can view it on the console. For details, see Viewing a Child Device. The user can also add child devices on the console. For details, see Adding a Child Device on the Platform. |
4. After the gateway authentication is successful, the gateway calls the API described in Platform Notifying a Gateway of New Child Device Connection. (The device information entered in the API request must be consistent with that defined in the product model). After the processing is complete, the platform sends the processing result to the gateway through the API described in Platform Responding to a Request for Adding Child Devices. |
|
5. The status of the newly added child device is still displayed as Inactive on the console. This is because the gateway has not reported the latest status of the child device to the platform. Call the API described in Gateway Updating Child Device Status after the child device is added or before the child device reports data.
NOTE:
The status of a child device indicates whether the child device is connected to the gateway, and the gateway reports the status to the platform for status updates. If the gateway cannot report the status of a child device, the child device status is not updated on the platform. For example, after a child device connects to the platform through a gateway, the child device status is displayed as online. If the gateway is disconnected from the platform, the gateway can no longer report the child device status and the platform will consider the child device online. |
|
|
6. The gateway calls the API described in Gateway Reporting Device Properties in Batches to report the data of the child device. The parameters in the API request are the information about the gateway and the child device. |
|
|
7. The gateway subscribes to a topic for command delivery, and receives and processes commands delivered by the application or platform. |
|
|
8. The application calls the API for deleting a device to command the gateway to delete the child device. The gateway deletes the device upon receiving the command. |
8. The gateway calls the API described in Gateway Requesting for Deleting Child Devices. After receiving the request, the platform processes the data and sends the result to the device through the API described in Platform Responding to a Request for Deleting Child Devices. |
Switching Device Gateways
You can switch the gateways of child devices as required in multiple ways.
- Individual operation: On the device details page, click Switch Gateway. On the displayed page, select the target gateway and click OK. The gateway of the current device is switched.
Figure 4 Device - Gateway switching
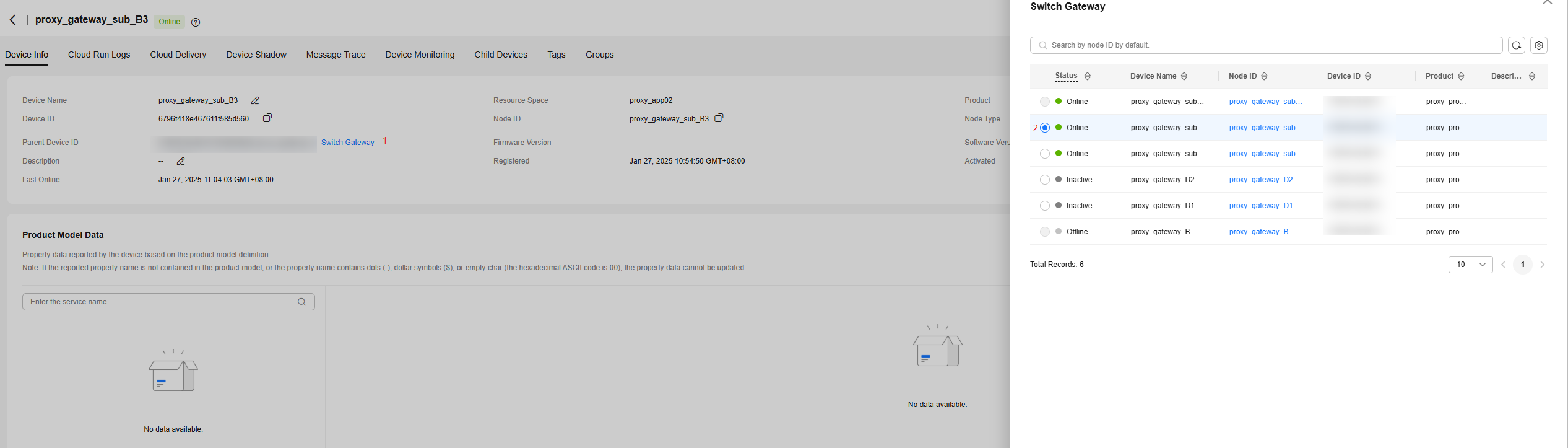
- Batch operation: On the device details page, click the Child Devices tab. Select the target child devices and click Switch Gateway. On the displayed page, select the target gateway and click OK.
Figure 5 Child devices - Gateway switching
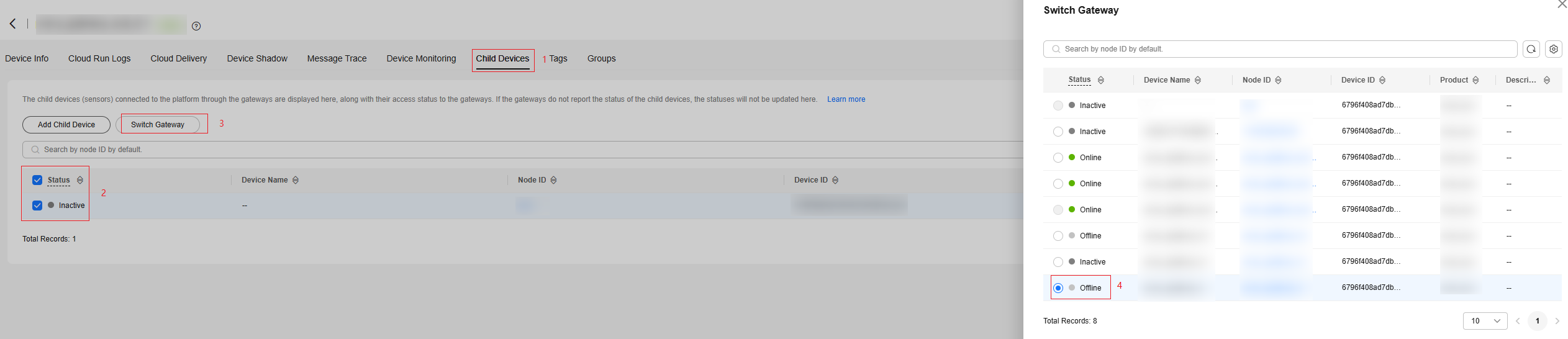
- API calling: Call the API for creating a batch task to migrate a batch of devices to a specified gateway.
{ "app_id":": "Resource space ID", "task_name": "Task name", "task_type": "changeGateway",// Task type. The value is fixed to changeGateway. "targets":["66bd9bbbfae9e821c15413df_asdasd4"],// ID of the target device "document": {"gateway_id":"6396e6ab78242f16ee80b6f1_wbxtest10824"}// Device ID of the target gateway }
Connecting a Gateway to the Platform
Connect a gateway to the platform by integrating the gateway with the SDK. For details, see Indirectly Connecting to the Platform.
Adding a Child Device on the Platform
- Method 1: After the gateway is connected to the platform, call the API for creating a device to connect the child device to the platform.
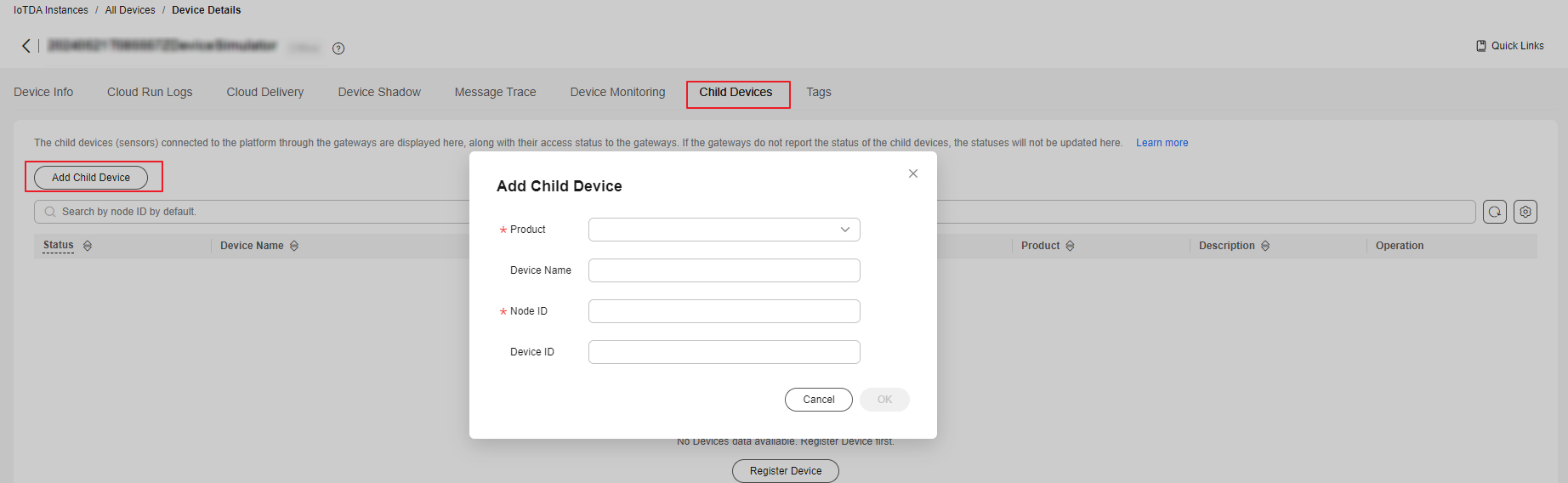
- Method 2: Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card. In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices. On the device list, click a gateway to access its details page. On the Child Devices tab page, click Add Child Device.
Figure 6 Device - Adding a child device
Viewing a Child Device
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose . In the device list, click View in the row of a gateway to access its details.
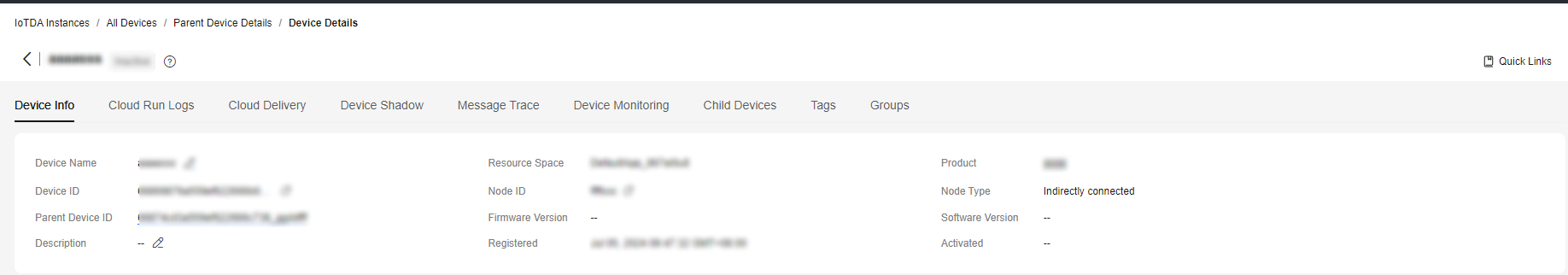
- On the Child Devices tab page, view the status, device ID, and node ID of the child devices connected to the platform through the gateway.
- Click View in the row of a child device to view its details.
Figure 7 Device - Child device details
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot