C Demo Usage Guide
Overview
This topic uses C as an example to describe how to connect a device to the platform over MQTTS or MQTT and how to use platform APIs to report properties and subscribe to a topic for receiving commands.
The code snippets in this document are only examples and are for trial use only. To put them into commercial use, obtain the IoT Device SDKs of the corresponding language for integration by referring to Obtaining Resources.
Prerequisites
- You have installed the Linux operating system (OS) and GCC (4.8 or later).
- You have obtained OpenSSL (required in MQTTS scenarios) and Paho library dependencies.
- You have obtained the device access address from the IoTDA console. For details, see Platform Connection Information.
- You have created a product and a device on the IoTDA console. For details, see Creating a Product, Registering an Individual Device, and Registering a Batch of Devices.
Preparations
- Compiling the OpenSSL library
- Visit the OpenSSL website (https://www.openssl.org/source/), download the latest OpenSSL version (for example, openssl-1.1.1d.tar.gz), upload it to the Linux compiler (for example, to the /home/test directory), and run the following command to decompress the package:
tar -zxvf openssl-1.1.1d.tar.gz
- Generate a makefile.
Run the following command to access the OpenSSL source code directory:
cd openssl-1.1.1d
Run the following configuration command:./config shared --prefix=/home/test/openssl --openssldir=/home/test/openssl/ssl
In this command, prefix is the installation directory, openssldir is the configuration file directory, and shared is used to generate a dynamic-link library (.so library).
If an exception occurs during the compilation, add no-asm to the configuration command (indicating that the assembly code is not used).
./config no-asm shared --prefix=/home/test/openssl --openssldir=/home/test/openssl/ssl

- Generate library files.
Run the following command in the OpenSSL source code directory:
make depend
Run the following command for compilation:
make
Install OpenSSL.
make install
Find the lib directory in home/test/openssl under the OpenSSL installation directory.
The library files libcrypto.so.1.1, libssl.so.1.1, libcrypto.so, and libssl.so are generated. Copy these files to the lib folder of the demo and copy the content in /home/test/openssl/include/openssl to include/openssl of the demo.

Note: Some compilation tools are 32-bit. If these tools are used on a 64-bit Linux computer, delete -m64 from the makefile before the compilation.
- Visit the OpenSSL website (https://www.openssl.org/source/), download the latest OpenSSL version (for example, openssl-1.1.1d.tar.gz), upload it to the Linux compiler (for example, to the /home/test directory), and run the following command to decompress the package:
- Compiling the Eclipse Paho library file
- Visit https://github.com/eclipse/paho.mqtt.c to download the source code paho.mqtt.c.
- Decompress the package and upload it to the Linux compiler.
- Modify the makefile.
- Run the following command to edit the makefile:
vim Makefile
- Search for the target string.
/DOXYGEN_COMMAND =
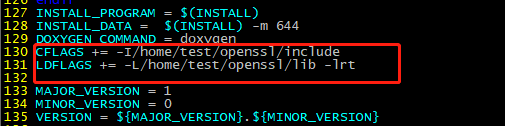
- Add the following two lines (customized OpenSSL header files and library files) under /DOXYGEN_COMMAND =doxygen:
CFLAGS += -I/home/test/openssl/include LDFLAGS += -L/home/test/openssl/lib -lrt
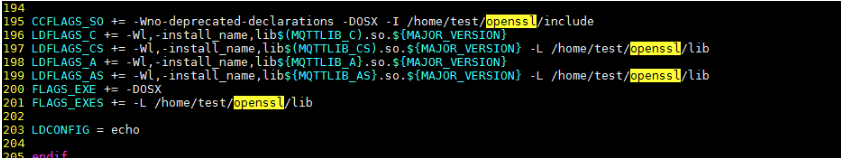
- Replace the OpenSSL addresses of CCFLAGS_SO, LDFLAGS_CS, LDFLAGS_AS and FLAGS_EXES with the actual ones.
- Run the following command to edit the makefile:
- Start the compilation.
- Run the following command:
make clean
- Run the following command:
make
- Run the following command:
- After the compilation is complete, you can view the libraries that are compiled in the build/output directory.
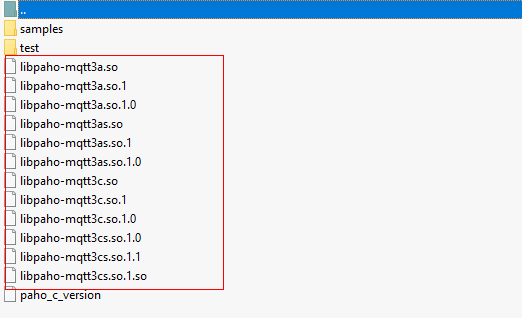
- Copy the Paho library file.
Currently, only libpaho-mqtt3as is used in the SDK. Copy the libpaho-mqtt3as.so and libpaho-mqtt3as.so.1 files to the lib folder of the demo. Go back to the Paho source code directory, and copy MQTTAsync.h, MQTTClient.h, MQTTClientPersistence.h, MQTTProperties.h, MQTTReasonCodes.h, and MQTTSubscribeOpts.h in the src directory to the include/base directory of the demo.
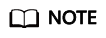
Some Paho versions have the MQTTExportDeclarations.h header file. You are advised to add all MQTT-related header files to the folder.
Importing Sample Code
- Download the sample code quickStart(C).
- Copy the code to the Linux runtime environment. The following figure shows the code file hierarchy.
Description of the directories:
- src: source code directory
mqtt_c_demo: core source code of the demo
util/string_util.c: utility resource file
- conf: certificate directory
rootcert.pem is used by the device to verify the platform identity when the device connects to the platform. For a non-basic edition instance, copy the content of the c/ap-southeast-1-device-client-rootcert.pem file in the certificate file to the conf/rootcert.pem file.
- include: header files
base: dependent Paho header files
openssl: dependent OpenSSL header files
util: header files of the dependent tool resources
- lib: dependent library file
libcrypto.so*/libssl.so*: OpenSSL library file
libpaho-mqtt3as.so*: Paho library file
- Makefile: Makefile
- src: source code directory
Establishing a Connection
To connect a device or gateway to the platform, upload the device information to bind the device or gateway to the platform.
- Set parameters.
char *uri = "ssl://iot-mqtts.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com:8883"; int port = 8883; char *username = "********"; //deviceId char *password = "********";
Note: MQTTS uses port 8883 for access. If MQTT is used for access, the URL is tcp://Domain name space:1883 and the port is 1883. For details about how to obtain the domain name space, see Platform Connection Information. The default heartbeat interval is 120 seconds. To change it, modify the keepAliveInterval parameter. For details about the heartbeat interval range, see Constraints.
- Start the connection.
- Add -lm to the end of the 15th line in Makefile and run the make command for compilation. Delete -m64 from the makefile in a 32-bit OS.
- Run export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib/ to load the library file.
- Run ./MQTT_Demo.o.
//connect int ret = mqtt_connect(); if (ret != 0) { printf("connect failed, result %d\n", ret); }
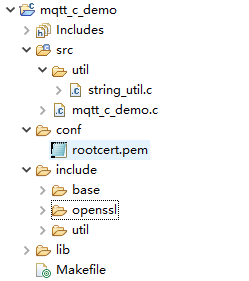
- If the connection is successful, the message "connect success" is displayed. The device is also displayed as Online on the console.
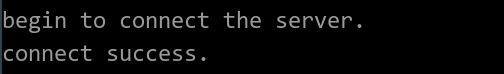 Figure 1 Device list - Device online status
Figure 1 Device list - Device online status
If the connection fails, the mqtt_connect_failure function executes backoff reconnection. The example code is as follows:
void mqtt_connect_failure(void *context, MQTTAsync_failureData *response) { retryTimes++; printf("connect failed: messageId %d, code %d, message %s\n", response->token, response->code, response->message); // Backoff reconnection int lowBound = defaultBackoff * 0.8; int highBound = defaultBackoff * 1.2; int randomBackOff = rand() % (highBound - lowBound + 1); long backOffWithJitter = (int)(pow(2.0, (double)retryTimes) - 1) * (randomBackOff + lowBound); long waitTImeUntilNextRetry = (int)(minBackoff + backOffWithJitter) > maxBackoff ? (minBackoff + backOffWithJitter) : maxBackoff; TimeSleep(waitTImeUntilNextRetry); //connect int ret = mqtt_connect(); if (ret != 0) { printf("connect failed, result %d\n", ret); } }
Subscribing to a Topic
Only devices that subscribe to a specific topic can receive messages about the topic published by the broker. For details on the preset topics, see Topics.
Subscribe to a topic.
//subscribe
char *cmd_topic = combine_strings(3, "$oc/devices/", username, "/sys/commands/#");
ret = mqtt_subscribe(cmd_topic);
free(cmd_topic);
cmd_topic = NULL;
if (ret < 0) {
printf("subscribe topic error, result %d\n", ret);
}
If the subscription is successful, the message "subscribe success" is displayed in the demo.
Reporting Properties
Devices can report their properties to the platform. For details, see Reporting Device Properties.
//publish data
char *payload = "{\"services\":[{\"service_id\":\"parameter\",\"properties\":{\"Load\":\"123\",\"ImbA_strVal\":\"456\"}}]}";
char *report_topic = combine_strings(3, "$oc/devices/", username, "/sys/properties/report");
ret = mqtt_publish(report_topic, payload);
free(report_topic);
report_topic = NULL;
if (ret < 0) {
printf("publish data error, result %d\n", ret);
}
If the property reporting is successful, the message "publish success" is displayed in the demo.
The reported properties are displayed on the device details page.
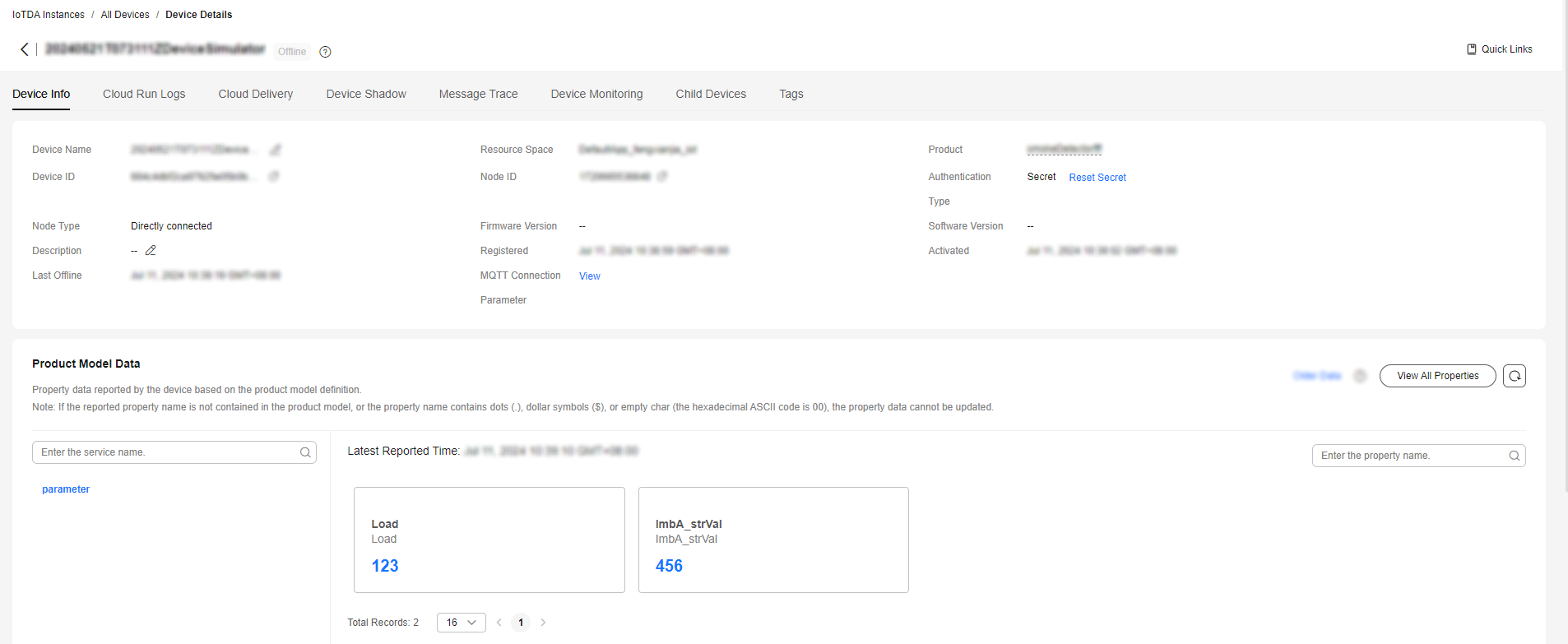
If the latest data is not displayed on the device details page, check whether the services and properties reported by the device are the same as those in the product model.
Receiving a Command
After subscribing to a command topic, you can deliver a synchronous command on the console. For details, see Command Delivery to an Individual MQTT Device.
If the command delivery is successful, the command received is displayed in the demo:

The code for receiving commands in the demo is as follows:
//receive message from the server
int mqtt_message_arrive(void *context, char *topicName, int topicLen, MQTTAsync_message *message) {
printf( "mqtt_message_arrive() success, the topic is %s, the payload is %s \n", topicName, message->payload);
return 1; // cannot return 0 here, otherwise the message will not update or something wrong would happen
}
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





