HTTP/HTTPS Data Forwarding
Introduction
The figure below shows the subscription and push process.

Before pushing HTTPS messages to an application, the platform must verify the application authenticity. Therefore, the application CA certificate must be loaded to the platform. (You can create a commissioning certificate during commissioning and replace it with a commercial certificate during commercial use to avoid security risks.)
Push mechanism: After receiving a push message from the platform, the application returns a 200 OK message. If the application does not respond within 15 seconds or returns a non-200 response code (500, 501, 502, 503, or 504), the message push fails and the message will be discarded. If the platform fails to push the message for 10 times in a row, IoTDA adds the host address of the subscription URL to the blocklist and messages to push will be stacked on the platform for one day or until the stack size of data become 1 GB. To retain only the latest data, see Data Forwarding Stack Policies. Then, the platform attempts to push messages to the host address in the blocklist every 3 minutes. If the push fails, the platform keeps the blocklist. If the push succeeds, the platform removes the host address from the blocklist. After the host address is removed from the blocklist, the latest messages are pushed only after all stacked messages are pushed based on the maximum flow control value. The default flow control value is 800 TPS per second. For details about the customized configuration, see Data Forwarding Flow Control Policies.
Subscribing to Data
After connecting to IoTDA, an application calls an API to subscribe to data.
- For details on how to configure HTTP or HTTPS subscriptions on the console, see Configuring HTTP/HTTPS Subscription and Loading the CA Certificate.
- For details on how to subscribe to data through APIs, see Calling APIs, Creating a Rule Trigger Condition, Creating a Rule Action, and Modifying a Rule Trigger Condition.
Format of Pushed Data
For details on the format of data pushed by the platform to applications after data subscription is created, see Data Transfer APIs.
In the HTTP message header, the value of Content-Type is application/json, and the character set is UTF-8.
Loading the CA Certificate
If HTTPS is used, you must load the push certificate by following the instructions provided in this section. Then create a subscription task on the console by following the instructions provided in Configuring HTTP/HTTPS Subscription.
- If the application cancels the subscription and then re-subscribes the data again (with the URL unchanged), the CA certificate must be loaded to the platform again.
- If a subscription type (URL) is added, you must load the CA certificate corresponding to the URL to the platform. Even if the CA certificate used by the new URL is the same as that used by the original URL, the CA certificate must be loaded again.
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose Rules > Server Certificates. Click Upload Certificate, configure parameters based on the following table, and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Certificate Name
Used to distinguish different certificates and can be customized.
CA Certificate
A CA certificate from the application can be applied for and purchased in advance.
NOTE:You can create a commissioning certificate during commissioning. For security reasons, you are advised to replace the commissioning certificate with a commercial certificate during commercial use.
- In the navigation pane, choose , locate the target certificate, click
 to obtain the certificate ID, which is used as a parameter in the API Creating a Rule Action.
Figure 1 Server certificate - Obtaining the certificate ID
to obtain the certificate ID, which is used as a parameter in the API Creating a Rule Action.
Figure 1 Server certificate - Obtaining the certificate ID
Creating a Commissioning Certificate
A commissioning certificate, or a self-signed certificate, is used for authentication when the client accesses the server through HTTPS. When the platform uses HTTPS to push data to an application, the platform authenticates the application. This section uses the Windows operating system as an example to describe how to use OpenSSL to make a commissioning certificate. The generated certificate is in PEM format and the suffix is .cer.
The table below lists common certificate storage formats.
|
Storage Format |
Description |
|---|---|
|
DER |
Binary code. The suffix is .der, .cer, or .crt. |
|
PEM |
Base64 code. The suffix is .pem, .cer, or .crt. |
|
JKS |
Java certificate storage format. The suffix is .jks. |
The commissioning certificate is used only for commissioning. During commercial use, you must apply for certificates from a trusted CA. Otherwise, security risks may occur.
- Download and install OpenSSL.
- Open the CLI as user admin.
- Run cd c:\openssl\bin (replace c:\openssl\bin with the actual OpenSSL installation directory) to access the OpenSSL view.
- Generate the private key file ca_private.key of the CA root certificate.
openssl genrsa -passout pass:123456 -aes256 -out ca_private.key 2048
- aes256: cryptographic algorithm
- passout pass: private key password
- 2048: key length
- Use the private key file of the CA root certificate to generate the ca.csr file to be used in 6.
openssl req -passin pass:123456 -new -key ca_private.key -out ca.csr -subj "/C=CN/ST=GD/L=SZ/O=Huawei/OU=IoT/CN=CA"
Modify the following information based on actual conditions:
- C: country, for example, CN
- ST: region, for example, GD
- L: city, for example, SZ
- O: organization, for example, Huawei
- OU: organization unit, for example, IoT
- CN: common name (the organization name of the CA), for example, CA
- Create the CA root certificate ca.cer.
openssl x509 -req -passin pass:123456 -in ca.csr -out ca.cer -signkey ca_private.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
Modify the following information based on actual conditions:
- passin pass: The value must be the same as the private key password set in 4.
- days: validity period of the certificate.
- Generate the private key file for the application.
openssl genrsa -passout pass:123456 -aes256 -out server_private.key 2048
- Generate the .csr file for the application.
openssl req -passin pass:123456 -new -key server_private.key -out server.csr -subj "/C=CN/ST=GD/L=SZ/O=Huawei/OU=IoT/CN=appserver.iot.com"
Modify the following information based on actual conditions:
- C: country, for example, CN
- ST: region, for example, GD
- L: city, for example, SZ
- O: organization, for example, Huawei
- OU: organization unit, for example, IoT
- CN: common name. Enter the domain name or IP address of the application.
- Use the CA private key file ca_private.key to sign the file server.csr and generate the server certificate file server.cer.
openssl x509 -req -passin pass:123456 -in server.csr -out server.cer -sha256 -CA ca.cer -CAkey ca_private.key -CAserial ca.srl -CAcreateserial -days 3650
- (Optional) If you need a .crt or .pem certificate, proceed this step. The following uses the conversion from server.cer to server.crt as an example. To convert the ca.cer certificate, replace server in the command with ca.
openssl x509 -inform PEM -in server.cer -out server.crt
- In the bin folder of the OpenSSL installation directory, obtain the CA certificate (ca.cer/ca.crt/ca.pem), application server certificate (server.cer/server.crt/server.pem), and private key file (server_private.key). The CA certificate is loaded to the platform, and the application server certificate and private key file are loaded to the application.
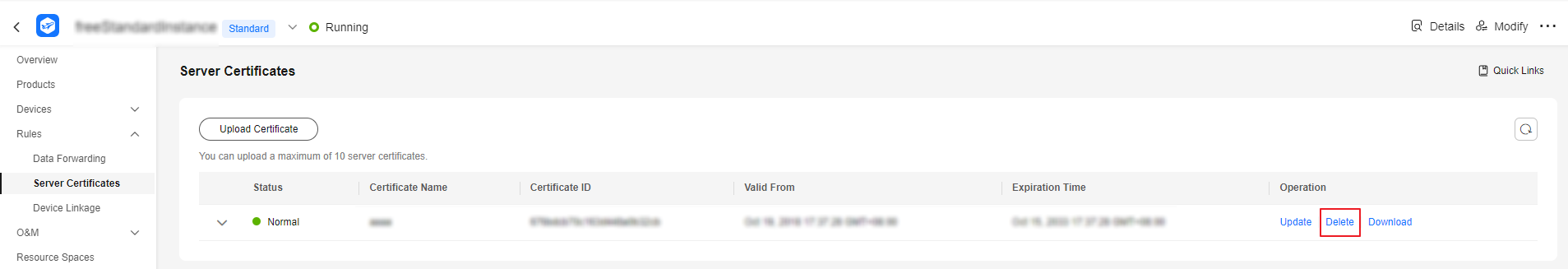
Deleting a Certificate
You can delete a server certificate that is no longer used.
After a server certificate is deleted, the push to the application server may fail. Back up related data before the deletion.
Configuring HTTP/HTTPS Subscription
This section describes how to configure HTTP or HTTPS subscription on the console.
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose , and click Create Rule.
- Set the parameters based on the table below and click Create Rule.
Table 1 Parameters for creating a rule Parameter
Description
Rule Name
Name of the rule to be created.
Description
Description of the rule.
Data Source
- Device: Device information, such as device addition, deletion, and update, will be forwarded. When Data Source is set to Device, quick configuration is not supported.
- Device property: A property value reported by a device in a resource space will be forwarded. Click Quick Configuration on the right and select the product, property, and service data to forward.
- Device message: A message reported by a device in a resource space will be forwarded. Click Quick Configuration on the right and select data of a specified topic to forward. Select the product to which the topic belongs and enter the topic name. You can use a custom topic on the product details page or a preset topic.
- Device message status: The status of device messages exchanged between the device and platform will be forwarded. For details on the device message status, see Message Delivery Status. When Data Source is set to Device message status, quick configuration is not supported.
- Device status: The status change of a directly or an indirectly connected device in a resource space will be forwarded. Click Quick Configuration on the right to forward information about devices whose status is Online, Offline, or Abnormal to other services. For details on the status of devices directly connected to the platform, see Device Management.
- Batch task: The batch task status will be forwarded. When Data Source is set to Batch Task, quick configuration is not supported.
- Product: Product information, such as product addition, deletion, and update, will be forwarded. When Data Source is set to Product, quick configuration is not supported.
- Asynchronous command status of the device: Status changes of asynchronous commands to devices using LwM2M over CoAP will be forwarded. For details on the asynchronous command status of devices, see Asynchronous Command Delivery. When Data Source is set to Asynchronous command status of the device, quick configuration is not supported.
- Run log: Service run logs of MQTT devices will be forwarded. When Data Source is set to Run log, quick configuration is not supported.
Trigger
After you select a data source, the platform automatically matches trigger events.
Resource Space
You can select a single resource space or all resource spaces. If All resource spaces is selected, quick configuration is not supported.
- Under Set Forwarding Target, click Add. On the displayed page, set the parameters based on the table below and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Forwarding Target
Select Third-party application (HTTP push).
Push URL
Enter the URL for IoTDA to push messages to the application. For example, if the URL is https://www.example.com:8443/example/, set Domain/IP and Port to www.example.com:8443 in Loading the CA Certificate.
- If the push URL uses HTTP, the CA certificate is not required.
- If the push URL uses HTTPS, upload the CA certificate. For details about how to upload a certificate, see Loading the CA Certificate.
Token
Used for signature authentication. The value can contain 3 to 32 characters, including letters and digits. When pushing data to the user server, the platform signs the token and assembles the signature information into the header.
Certificate ID
This configuration is valid only for the HTTPS server. It is used as the truststore certificate for the client to verify the compliance of the commercial certificate of the server. This configuration is unavailable for non-compliant certificates such as self-signed certificates and certificates with incomplete certificate chains.
Certificate Domain Name
To enable SNI, configure corresponding certificate and domain name on the server in advance.
- After the rule is defined, click Enable Rule to start forwarding data to the HTTP or HTTPS message queue.
Token-based Platform Authentication for HTTP/HTTPS Push
If you select Authentication and enter the token when adding the Third-party application (HTTP push) forwarding target, the platform will add the following parameters to the header of the HTTP or HTTPS request:
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
timestamp |
Timestamp when the platform pushes data. |
|
nonce |
Random number generated by the platform. |
|
signature |
Signature consisting of token, timestamp, and nonce. |
Signature rules:
- Sort token, timestamp, and nonce in alphabetical order.
- Encrypt the sorted string using SHA-256.
- After receiving the pushed message, you can encrypt timestamp and nonce in the header and token based on rules and compare the obtained value with the signature in the header to determine whether the message is from the platform.
Java example for signature verification:
- Add the dependency. Use a specific version based on the actual service requirements.
<dependency> <groupId>commons-codec</groupId> <artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId> <version>${commons.version}</version> </dependency> - Obtain the signature information from the request header and use the commons-codec dependency package for signature.
public boolean checkSignature(String nonce, String timestamp, String signature, String token) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(token); if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(nonce)) { list.add(nonce); } if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(timestamp)) { list.add(timestamp); } Collections.sort(list); StringBuilder signatureBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (String s : list) { signatureBuilder.append(s); } String serverSignature = DigestUtils.sha256Hex(signatureBuilder.toString()); if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serverSignature) && serverSignature.equals(signature)) { return true; } return false; } - For example, the token is set to aaaaaa in a request, and the header contains the following parameters:
nonce: 8b9b796d388d49bba43adaa53aaf5bc4 timestamp: 1675654743514 signature: 2ff821fb8a976ede7d06434395ec8c25e4100bff8b3d12d8099ef7e30b58bd4c
The string after sorting is 16756547435148b9b796d388d49bba43adaa53aaf5bc4aaaaaa. The string encrypted using SHA-256 is 2ff821fb8a976ede7d06434395ec8c25e4100bff8b3d12d8099ef7e30b58bd4c.
After a token is created, you need to configure a new token each time you modify the forwarding target. Otherwise, the token does not take effect.
Platform Authentication
As a server, if an application needs to authenticate the platform, the platform CA certificate must be loaded on the application. For details, see Obtaining Resources.
FAQ
- How Do I Obtain the Access Addresses and Certificates of the Old and New Domain Names?
- How Do I Obtain the Callback URL When Calling the Subscription API?
- Can a Domain Name Be Used in a Callback URL?
- What Do I Do If Message Push Fails After Subscription?
- Why Does the Application Receive Multiple Push Messages After a Device Reports a Piece of Data?
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





