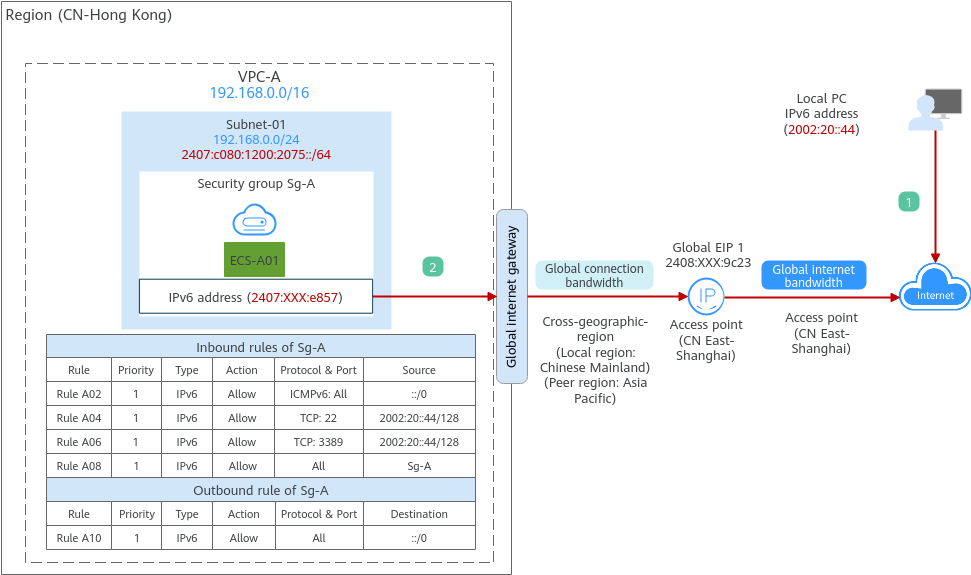
Using a Global EIP to Enable Cross-Region Communications on an IPv6 Network
You can use a global EIP and an ECS to enable Internet access and cloud communications on an IPv6 network across regions.
A global EIP requires a global connection bandwidth for private network communications and a global internet bandwidth for Internet access. To enable an ECS to communicate with the Internet through a global EIP, you also need to bind a global internet gateway to the global EIP.
Figure 1 shows the IPv6 network architecture in this example. The network communication requirements are as follows:
- The local PC (IPv6 address: 2002:20::44) can remotely log in to ECS-A01 across regions.
- ECS-A01 can access the Internet across regions.
Operation Process
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Before using cloud services, sign up for a HUAWEI ID and enable Huawei Cloud services. |
|
|
Create a VPC and an ECS.
|
|
|
Step 2: Create a Global Internet Gateway and Add an IPv6 Route |
Create a global internet gateway in the VPC of the ECS and add a route with the destination 0::0/0 to the route table of the selected VPC to direct traffic to the global internet gateway. |
|
Assign a global EIP (G-EIP1) with a global internet bandwidth. You can add the global EIP to an existing global internet bandwidth or purchase one. |
|
|
Step 4: Bind the Global EIP to an ECS and a Global Internet Gateway |
Bind the global EIP to the ECS and then to a global connection bandwidth. You can add the global EIP to an existing global connection bandwidth or purchase one. |
|
Test ECS connectivity using an IPv6 address:
|
Preparations
Before creating resources, such as global EIPs and global internet gateways, you need to sign up for a HUAWEI ID and enable Huawei Cloud services.
If you already have a HUAWEI ID, skip this part.
Step 1: Create a VPC and an ECS
- Create a VPC with a subnet.
- Go to the page for creating a VPC.
- On the Create VPC page, set parameters as needed.
In this example, you need to create a VPC and subnet, and enable IPv6 for this subnet.
Figure 2 Setting a subnet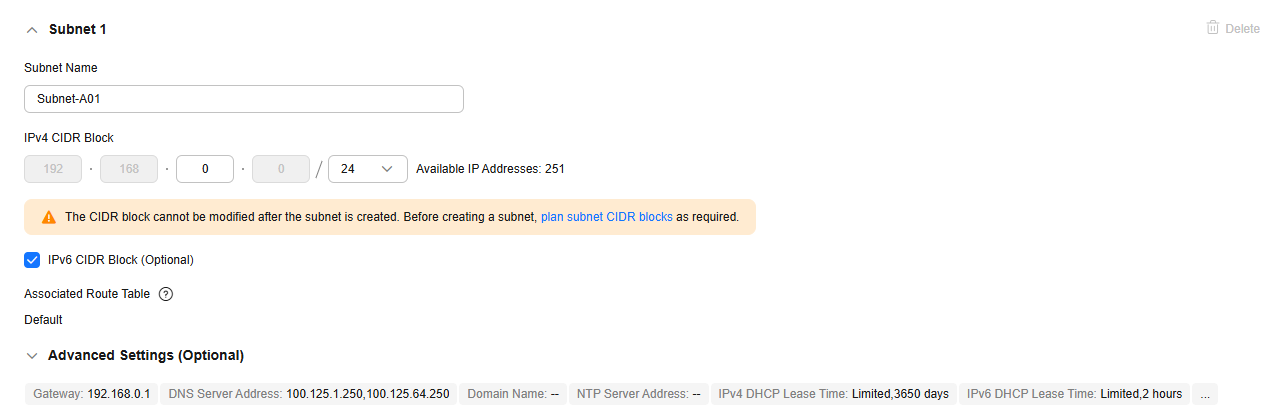
Table 1 VPC parameters Parameter
Example Value
Description
Region
CN-Hong Kong
The region where the VPC is created. Select the region nearest to you to ensure the lowest possible latency. The VPC, ECS, and EIP used in this example must be in the same region.
The region cannot be changed after the VPC is created.
Name
VPC-A
The VPC name.
The name can be modified after the VPC is created.
IPv4 CIDR Block
192.168.0.0/16
The IPv4 CIDR block of the VPC. You are advised to select from the following CIDR blocks:- 10.0.0.0/8–24: The IP address ranges from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255, and the netmask ranges from 8 to 24.
- 172.16.0.0/12–24: The IP address ranges from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255, and the netmask ranges from 12 to 24.
- 192.168.0.0/16–24: The IP address ranges from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255, and the netmask ranges from 16 to 24.
The CIDR block cannot be changed after the VPC is created.
Enterprise Project
default
The enterprise project by which resources are centrally managed. Select an existing enterprise project for the VPC.
The enterprise project cannot be changed after the VPC is created.
Monitor subnet IP address usage
No configuration is required.
Configure it as required. If this option is enabled, Cloud Eye will monitor the IPv4 address usage of all subnets in the current VPC.
This parameter can be changed after the VPC is created.
This parameter is available only in certain regions. You can check the regions on the console.
Block Access to Service Endpoints
No configuration is required.
Configure it as required. If this option is enabled, the VPC loses direct access to service endpoints over the private network.
This parameter can be changed after the VPC is created.
This parameter is available only in certain regions. You can check the regions on the console.
Advanced Settings (Optional) > Tag
No configuration is required.
The tag that is used to classify and identify resources. Add tags to the VPC as required.
After the VPC is created, you can edit tags added to the VPC.
Advanced Settings (Optional) > Description
No configuration is required.
Supplementary information about the VPC. Enter a description as required.
This parameter can be changed after the VPC is created.
Table 2 Subnet parameters Parameter
Example Value
Description
Subnet Name
Subnet-A01
The subnet name.
The name can be modified after the subnet is created.
IPv4 CIDR Block
192.168.0.0/24
The IPv4 CIDR block of the subnet, which is a unique CIDR block with a range of IP addresses in the VPC.
The CIDR block cannot be changed after the subnet is created.
IPv6 CIDR Block (Optional)
Enabled
Whether to automatically assign an IPv6 CIDR block to the subnet.
You can enable or disable this option after the subnet is created.
Associated Route Table
Default
The default route table that the subnet is associated with. Each VPC comes with a default route table. Subnets in the VPC are then automatically associated with the default route table.
The default route table has a preset system route that allows subnets in a VPC to communicate with each other.
After the subnet is created, you can create a custom route table and associate the subnet with it.
Advanced Settings (Optional) > Gateway
192.168.0.1
The gateway address of the subnet. You are advised to retain the default address.
The gateway address cannot be changed after the subnet is created.
Advanced Settings (Optional)- DNS Server Address
- Domain Name
- NTP Server Address
- IPv4 DHCP Lease Time
No configuration is required.
The parameters that are configured for the ECS in the VPC. In this example, retain the default values or leave them blank.
You can change the values after the subnet is created.
Advanced Settings (Optional) > Tag
No configuration is required.
The tag that is used to classify and identify resources. Add tags to the subnet as required.
After the subnet is created, you can edit tags added to the subnet.
Advanced Settings (Optional) > Description
No configuration is required.
Supplementary information about the subnet. Enter a description as required.
The description can be modified after the subnet is created.
- Click Create Now.
You will be redirected to the VPC list, where you can find VPC-A you have created.
- Buy an ECS.
- Go to the page for buying an ECS.
- On the Buy ECS page, configure parameters as required.
In this example, configure the ECS network as follows:
- Network: Select VPC-A and Subnet-A01 you have created.
Select Automatically assign IP address and Automatically-assigned IPv6 address. An IPv4 address and an IPv6 address will be assigned to ECS-A01.
Figure 3 Network settings
- Security Group: Create security group Sg-A and add inbound and outbound rules to it. Each security group comes with system rules. You need to check and modify the rules as required to ensure that all rules in Table 3 are added.
Figure 4 Inbound rules
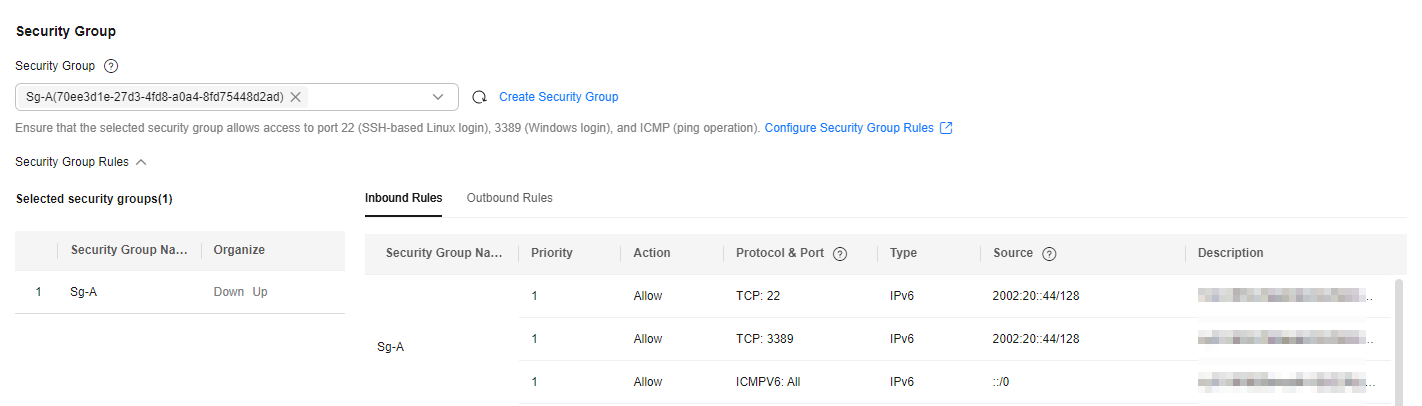 Figure 5 Outbound rules
Figure 5 Outbound rules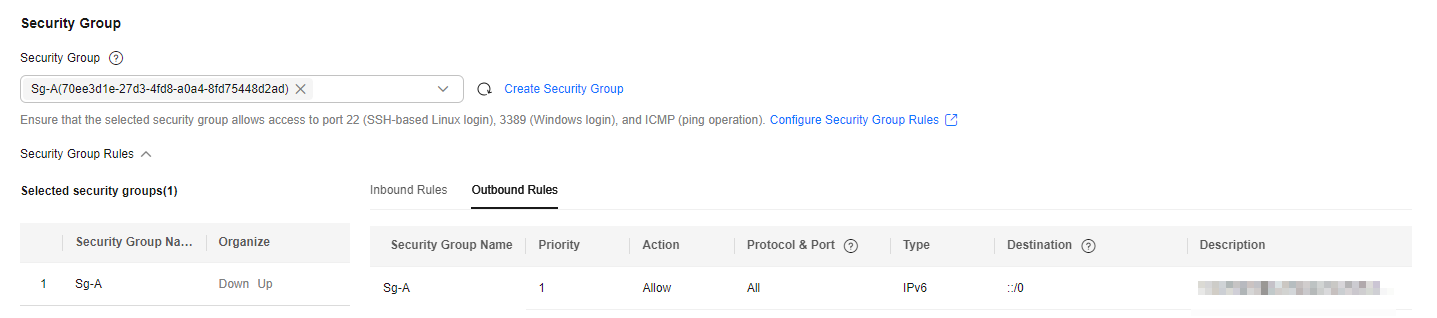
Table 3 Security group Sg-A rules Direction
Action
Type
Protocol & Port
Source/Destination
Description
Inbound
Allow
IPv6
TCP: 22
Source: 2002:20::44/128
Allows the local PC (2002:20::44/128) to remotely log in to the Linux ECS over SSH port 22 using an IPv6 address.
Inbound
Allow
IPv6
TCP: 3389
Source: 2002:20::44/128
Allows the local PC (2002:20::44/128) to remotely log in to the Windows ECS over RDP port 3389 using an IPv6 address.
Inbound
Allow
IPv6
ICMPv6: All
Source: ::/0
Allows IPv6 ping traffic to the ECS in the security group over all ICMP ports to test the ECS network connectivity.
Inbound
Allow
IPv6
All
Source: current security group (Sg-A)
Allows the ECSs in the security group to communicate with each other using IPv6 addresses.
Outbound
Allow
IPv6
All
Destination: ::/0
Allows the ECS in the security group to access the external networks using an IPv6 address.
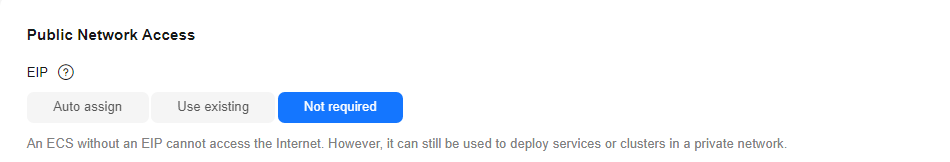
- EIP: Select Not required.
Figure 6 Selecting Not required
Configure other ECS parameters as required. For details, see Purchasing an ECS in Custom Config Mode.
- Network: Select VPC-A and Subnet-A01 you have created.
- Click Submit.
Return to the ECS list to view ECS-A01 you have bought.
- Log in to ECS-A01 and check whether the ECS has obtained an IPv6 address.
- By default, dynamic IPv6 address assignment is enabled for Windows public images.
- Before enabling dynamic IPv6 address assignment for a Linux public image, check whether IPv6 protocol stack is supported first. All Linux public images support the IPv6 protocol stack. You also need to configure the ECS as instructed in Dynamically Assigning IPv6 Addresses. Otherwise, the ECS cannot communicate with others using IPv6 addresses.
Step 2: Create a Global Internet Gateway and Add an IPv6 Route
- Create a global internet gateway.
- Go to the Global Internet Gateways page.
- In the upper right corner of the page, click Create Global Internet Gateway.
The Create Global Internet Gateway dialog box is displayed.
- Configure the parameters based on Table 4.
Table 4 Parameter descriptions Parameter
Example Value
Description
Name
IGW-A
Enter the name of the global internet gateway as required. The name:- Can contain 1 to 64 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
This parameter can be modified after a global internet gateway is created.
Version
IPv6
Select IPv6 for the global internet gateway.
This parameter cannot be modified after a global internet gateway is created.
VPC
VPC-A
Select the VPC of the ECS. Ensure that the VPC is in the same region as the ECS.
This parameter cannot be modified after a global internet gateway is created.
Subnet
Subnet-A01
Select a subnet in the VPC where you want to bind the global internet gateway.
This parameter cannot be modified after a global internet gateway is created.
Default Route
Enable
Select this option, so the default route with the destination 0.0.0.0/0 will be automatically added to the default route table of the selected VPC to direct traffic to the global internet gateway.
This parameter cannot be modified after a global internet gateway is created.
- Click OK.
- Add an IPv6 route pointing to the global internet gateway.
- Go to the VPC list page.
- In the VPC list, locate VPC-A and click the number in the Route Tables column. The route table list page is displayed.
- Click the name of the target route table.
- Click Add Route and configure required parameters.
Table 5 Parameter descriptions Parameter
Example Value
Description
Destination Type
IP address
Select the route destination type.
This parameter can be modified after the route is created.
Destination
0::0/0
Set Destination to 0::0/0, indicating that any IPv6 traffic is matched.
Next Hop Type
Global internet gateway
Select the next hop resource type of the route.
This parameter can be modified after the route is created.
Next Hop
IGW-A
Select the next hop resource of the route.
This parameter can be modified after the route is created.
Description
No configuration is required.
Enter the route description as required.
This parameter can be modified after the route is created.
- Click OK.
You can view the new route in the route list.
Step 3: Buy a Global EIP
- Go to the Assign Global EIP page.
- Configure the parameters based on Table 6.
Table 6 Parameter descriptions Parameter
Example Value
Description
Region
CN-East
Select a region that is close to your services for lower latency.
This parameter cannot be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
City
Shanghai
Select a city that is close to your services for lower latency.
This parameter cannot be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Type
Global EIP
Select Global EIP or Global EIP range.
This parameter cannot be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Version
IPv6
Select IPv4 or IPv6.
This parameter cannot be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Global EIP Type
CU
Select the global EIP type.
After you select a global EIP pool, the system will allocate a global EIP to you from the pool. Select a resource pool close to your services for lower latency.
This parameter cannot be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Global Internet Bandwidth
Assign now
Select Assign now to purchase a new global internet bandwidth.
Billing Mode
Pay-per-use
Select the billing mode for the global internet bandwidth as required.
This parameter cannot be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Bandwidth Type
Standard
Select the type of the global internet bandwidth as required.
This parameter cannot be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Billed By
95th percentile bandwidth (standard)
Select the billing option for the global internet bandwidth as required.
This parameter can be modified after the global internet bandwidth is created.
Guaranteed Bandwidth
No configuration is required.
The value is automatically configured based on the selected billing option.
Bandwidth (Mbit/s)
300
Select the size of the global internet bandwidth as required.
This parameter can be modified after the global internet bandwidth is created.
Global EIP Name
G-EIP1
Enter the name of the global EIP as required. The name:- Can contain 0 to 64 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
This parameter can be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Enterprise Project
default
The enterprise project by which resources are centrally managed. Select an existing enterprise project for the global EIP.
This parameter cannot be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Advanced Settings
Retain the default settings.
Click the drop-down arrow and configure advanced parameters for the global EIP.
Bandwidth Name
IBW-A
Enter the name of the global internet bandwidth as required. The name:- Can contain 0 to 64 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
This parameter can be modified after the global internet bandwidth is created.
Tag
No configuration is required.
Add tags to classify and identify the global EIP as required.
This parameter can be modified after the global EIP is assigned.
Monitoring
No configuration is required.
By default, the following information is monitored for free:
- Network traffic at one-minute intervals
- Bandwidth fluctuations and inbound and outbound bandwidth rates
Quantity
1
Set it to 1.
- Click Next.
- Confirm the configuration and click Submit.
The global EIP list is displayed.
- In the global EIP list, view the global EIP status.
If the status of the global EIP is Unbound, the EIP is assigned successfully.
Step 4: Bind the Global EIP to an ECS and a Global Internet Gateway
- Go to the global EIP list page.
- In the global EIP list, search for G-EIP1 to locate it.
- Locate the row that contains G-EIP1 and click Bind Instance in the Progress column.
The page for binding an instance is displayed.
- Configure the parameters as follows:
- Instance Region: Select the region where ECS-A01 is located.
- Instance Type: Select ECS (IPv6) and select ECS-A01.
- Global Internet Gateway: Select IGW-A created in Step 2: Create a Global Internet Gateway and Add an IPv6 Route.
- Click Next.
- On the Bind Global Connection Bandwidth page, create a global connection bandwidth to be bound to the global EIP.
Table 7 Parameter descriptions Parameter
Example Value
Description
EIP Region
No configuration is required.
The region is determined by that of G-EIP1 and does not need to be configured.
Instance Region
No configuration is required.
The region is determined by that of ECS-A01 and does not need to be configured.
Bandwidth Type
No configuration is required.
The value is determined by the access point of the global EIP and the region where the instance is located. You do not need to set it.
Global Connection Bandwidth
Assign now
Select Assign now to create a global connection bandwidth.
Bandwidth Name
Bandwidth-A
Enter the name of the global connection bandwidth as required. The name:- Can contain 0 to 64 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
This parameter can be modified after the global connection bandwidth is created.
Bandwidth (Mbit/s)
300
Select the size of the global connection bandwidth as required.
This parameter can be modified after the global connection bandwidth is created.
- Click Finish.
In the global EIP list, you can see that the global EIP has an instance bound.
Step 5: Test Network Connectivity
- Check whether you can log in to ECS-A01 using its IPv6 address.
Multiple methods are available for logging in to an ECS. For details, see Logging In to an ECS.
Use PuTTY to remotely log in to ECS-A01 using the IPv6 address.
Enter the IPv6 address of ECS-A01 under Host Name (or IP address), for example, 2407:XXX:e857.
Figure 7 PuTTY Configuration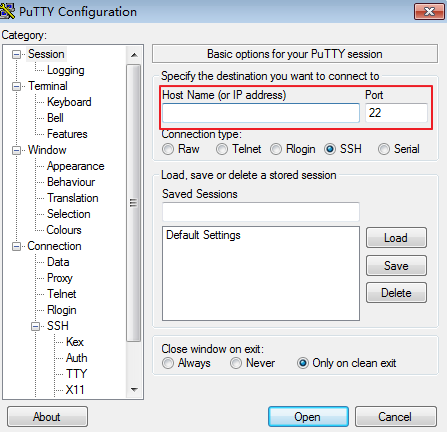
- Test the network connectivity between ECS-A01 and the Internet using an IPv6 address:
In this example, 2002:20::45 is used as a public IP address. An example command is as follows:
ping6 2002:20::45
If information similar to the following is displayed, ECS-A01 can communicate with the Internet using the IPv6 address.[root@ecs-a01 ~]# ping6 2002:20::45 PING 2002:20::45(2002:20::45) from 2002:20::45 : 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 2002:20::45: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.770 ms 64 bytes from 2002:20::45: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.295 ms 64 bytes from 2002:20::45: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.245 ms ^C --- 2002:20::45 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2080ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.245/0.436/0.770/0.237 ms
If your access using an IPv6 address is abnormal, refer to Why Can't I Access Websites Using IPv6 Addresses After IPv4/IPv6 Dual Stack Is Configured?
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot