Multi-level Memory Reclamation Policy
Background
In high-density hybrid container deployments, offline services with a large number of I/O reads and writes consume a large amount of page cache. As a result, the idle memory of the system decreases, and memory reclamation is triggered when the idle memory watermark is reached. Online tasks enter the slow path for memory reclamation when applying for memory, causing latency and jitter.
To solve this problem, multi-level memory reclamation is provided by HCE 2.0. You can set a memory warning value to trigger a memory reclamation task, which ensures available memory space. For memory reclamation, you can set multiple levels of memory protection watermarks to protect task availability.
Constraints
memory.min and memory.low take effect only on leaf cgroups. When a memory cgroup is created, memory.min and memory.low of the parent cgroup are cleared.
Interface Description
The memory.min, memory.low, and memory.high interfaces exist in the non-root memory cgroup by default. You can write values to the files or read the current configuration. The proper value sequence is memory.min ≤ memory.low < memory.high. The three values can be used independently or together.
The following figure shows the memory reclamation mechanism.
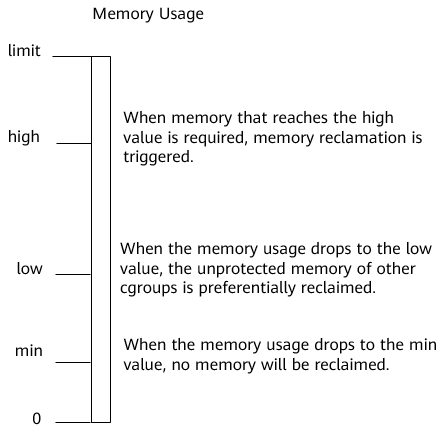
|
Interface |
Description |
|---|---|
|
memory.min |
Specifies the minimum amount of memory the cgroup must always retain. The default value is 0. Even if there is no memory that can be reclaimed, the system will not reclaim the memory that is less than or equal to the value of this parameter. The read and write operations are described as follows:
|
|
memory.low |
Specifies the best-effort memory protection. The default value is 0. The system preferentially reclaims the memory of unprotected cgroups. If the memory is still insufficient, the system reclaims the memory between memory.min and memory.low. The read and write operations are described as follows:
|
|
memory.high |
Specifies the memory reclamation warning. The default value is max. When the memory usage of a cgroup reaches the high value, a synchronous memory reclamation task is triggered for the cgroup and its child cgroups. The memory is limited to a value lower than the high value to prevent OOM caused by the memory limit. The read and write operations are described as follows:
|
Interface Configuration Example
Create cgroups A, B, C, D, E and F and configure the memory.min interface.
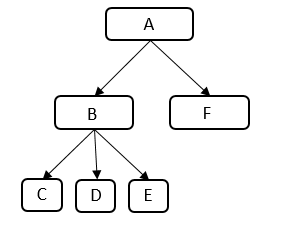
|
cgroup |
memory.limit_in_bytes |
memory.min |
memory.usage_in_bytes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A |
200M |
0 |
- |
|
B |
- |
0 |
- |
|
C |
- |
75M |
50M |
|
D |
- |
25M |
50M |
|
E |
- |
0 |
50M |
|
F |
- |
125M |
- |
- Create cgroup A and set memory.limit_in_bytes to 200M.
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A echo 200M > /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/memory.limit_in_bytes
- Create cgroup B.
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/B
- Create cgroup C, set memory.min to 75M, and create a process that will use 50-MB cache in the cgroup.
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/B/C echo 75M > /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/B/C/memory.min
- Create cgroup D, set memory.min to 25M, and create a process that will use 50-MB cache in the cgroup.
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/B/D echo 25M > /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/B/D/memory.min
- Create cgroup E, set memory.min to 0, and create a process that will use 50-MB cache in the cgroup.
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/B/E
- Create cgroup F, set memory.min to 125M, and request 125-MB cache for memory protection.
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/F echo 125M > /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/F/memory.min
Information similar to the following is displayed:
cgroup C: memory.min=75M, memory.usage_in_bytes=50M
cgroup D: memory.min=25M, memory.usage_in_bytes=25M
cgroup E: memory.min=0, memory.usage_in_bytes=0
cgroup B: memory.usage_in_bytes=75M
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





