Multi-level Hybrid Scheduling of Kernel CPU cgroups
Background
In hybrid deployments, the Linux kernel scheduler assigns more scheduling opportunities to high-priority tasks and minimizes the impact of low-priority tasks on kernel scheduling. However, the two-level scheduling of online and offline services cannot meet this requirement.
To solve the problem, HCE 2.0 allows multi-level scheduling of kernel CPU cgroups and provides /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/cpu.qos_level to extend the scheduling levels from two to five, allowing users to set the priority for each cgroup separately.
Constraints
cpu.qos_level is only available for cgroup-v1 and not for cgroup-v2.
Interface Description
Rules for cpu.qos_level to take effect:
- Completely Fair Scheduler (CFS) selects task_group level by level from top to bottom. cpu.qos_level takes effect for child cgroups under the same parent cgroup.
- When a child cgroup is created, it inherits the cpu.qos_level value of the parent cgroup by default, but the cpu.qos_level value can be reconfigured.
- For QoS levels with the same priority, their resource competition complies with the policy of CFS.
- On the same CPU, the tasks with qos_level less than 0 are always unconditionally preempted by tasks with qos_level greater than or equal to 0, regardless of their levels.
When a high-priority task is scheduled:
- Online tasks can unconditionally preempt the CPU resources of offline tasks. During multi-core scheduling, online tasks can preferentially preempt the CPU resources of offline tasks on other cores. In the hyper-thread scenario, online tasks with priority 2 can evict offline tasks on the SMT.
- When a task with a higher priority is woken up, the task is accelerated by time slicing and can immediately preempt the CPU resources of tasks with a lower priority to achieve a response at a lower latency (the minimum running time slice of CFS is ignored).
Interface Configuration Example
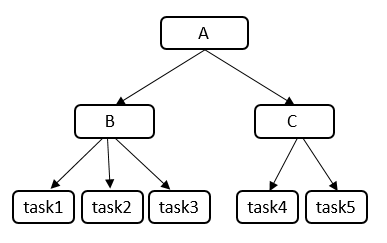
Create cgroups A, B, and C, and configure the cpu.qos_level interface.
|
cgroup |
cpu.qos_level Value |
|---|---|
|
A |
1 |
|
B |
-2 |
|
C |
2 |
- Create cgroup A and child cgroups B and C, and set their CPU scheduling priorities to 1, -2, and 2.
Tasks in cgroups A and C can unconditionally preempt CPU resources of the tasks in cgroup B. cgroup C preferentially preempts CPU resources because the priority of cgroup C is higher than that of cgroup A.
mkdir -p /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A echo 1 > /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/cpu.qos_level mkdir -p /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/B echo -2 > /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/B/cpu.qos_level mkdir -p /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/C echo 2 > /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/C/cpu.qos_level
- Add the task1, task2, and task3 processes to cgroup B.
- Add the task4 and task5 processes to cgroup C.
- View the CPU scheduling priority and processes of cgroup B.
[root@localhost cpu_qos]# cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/B/cpu.qos_level -2 [root@localhost boot]# cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/B/tasks 1879 1880 1881
- View the CPU scheduling priority and processes of cgroup C.
[root@localhost cpu_qos]# cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/C/cpu.qos_level 2 [root@localhost boot]# cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/A/C/tasks 1882 1883
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





