OOM Process Control Policy
Background
Both offline and online services can be configured in an OS. When Out Of Memory (OOM) occurs, the system preferentially ends the process that consumes the most memory in the offline service control group to reclaim the memory. However, some core services are often running offline. If the memory consumed by such services is reclaimed, the OS will be greatly affected.
To solve this problem, HCE adjusts the memory reclamation policy during OOM and adds the function of configuring cgroups priority. When the memory is insufficient, the kernel traverses cgroups, ends the processes for cgroups with low priorities, and reclaims the memory so that important offline services can keep running.
Prerequisites
vm.panic_on_oom is disabled (value: 0) by default, which means if the system OOM occurs, kernel panic will not be triggered. Before you use memcg OOM for priority configuration (memcg_qos_enable is set to 1 or 2), if the value of vm.panic_on_oom is not 0, run sysctl -w vm.panic_on_oom=0 first.
Interface Description
|
Interface |
Description |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|
|
memcg_qos_enable |
Specifies whether to enable memcg OOM priority configuration.
|
The value is an integer ranging from 0 to 2. The default value is 0. |
|
memory.qos_level |
Specifies how to configure the priorities of cgroups. A smaller value indicates a lower priority.
NOTE:
|
The value is an integer ranging from -1024 to 1023. The default value is 0. |
Interface Configuration Example
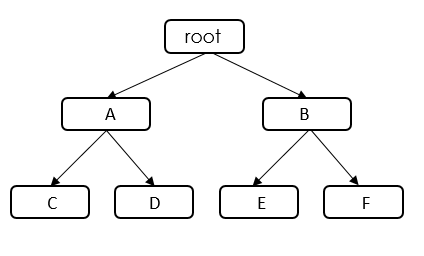
Create six cgroups A, B, C, D, E and F, configure the memcg_qos_enable interface, and set the memcg OOM priorities by specifying memory.qos_level.
|
cgroup |
Value of memory.qos_level |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
A |
-8 |
When the OOM operation is performed in the root cgroup, the kernel traverses all cgroups in the root cgroup and finally selects cgroups A and E, both with the lowest priority. Because A and E have the same priority, the kernel continues to compare the memory used by A and E.
|
|
B |
10 |
|
|
C |
1 |
|
|
D |
2 |
|
|
E |
-8 |
|
|
F |
3 |
- Disable vm.panic_on_oom.
sysctl -w vm.panic_on_oom=0
- Enable memcg OOM priority configuration.
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/memcg_qos_enable
- Create cgroups A and B and set their memcg OOM priorities to -8 and 10.
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/B cd /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A echo -8 > memory.qos_level cd /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/B echo 10 > memory.qos_level
- Create child cgroups C and D under cgroup A and child cgroups E and F under cgroup B, and set the memcg OOM priorities of cgroups C, D, E, and F to 1, 2, -8, and 3.
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/C mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/D mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/B/E mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/B/F cd /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/C echo 1 > memory.qos_level cd /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/D echo 2 > memory.qos_level cd /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/B/E echo -8 > memory.qos_level cd /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/B/F echo 3 > memory.qos_level
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





