HSS
What Is HSS?
Host Security Service (HSS) is designed to protect server workloads in hybrid clouds and multi-cloud data centers. It integrates server security, container security, and web tamper protection capabilities. HSS protects your system integrity, enhances application security, monitors user operations, and detects intrusions.
HSS is designed to enhance server security through diverse functions, including server management, risk prevention, intrusion detection, security operations, and web tamper protection (WTP). HSS can comprehensively identify and manage information assets on servers, detect server risks in real time, and prevent intrusions. This helps companies build a server security system and reduce threats. For more information about how HSS works, see What Is HSS?
After installing the HSS agent on your ECSs, you will be able to check the ECS security status and risks in a region on the HSS console.
Billing
- HSS provides two billing modes, yearly/monthly and pay-per-use billing, to meet requirements in different scenarios. For details, see HSS Billing Modes.
- When an ECS is stopped, the pay-per-use HSS quota stops being billed.
How Do I Enable HSS?
We provide different methods for you to install the HSS agent depending on whether your ECSs are to be created or already exist.
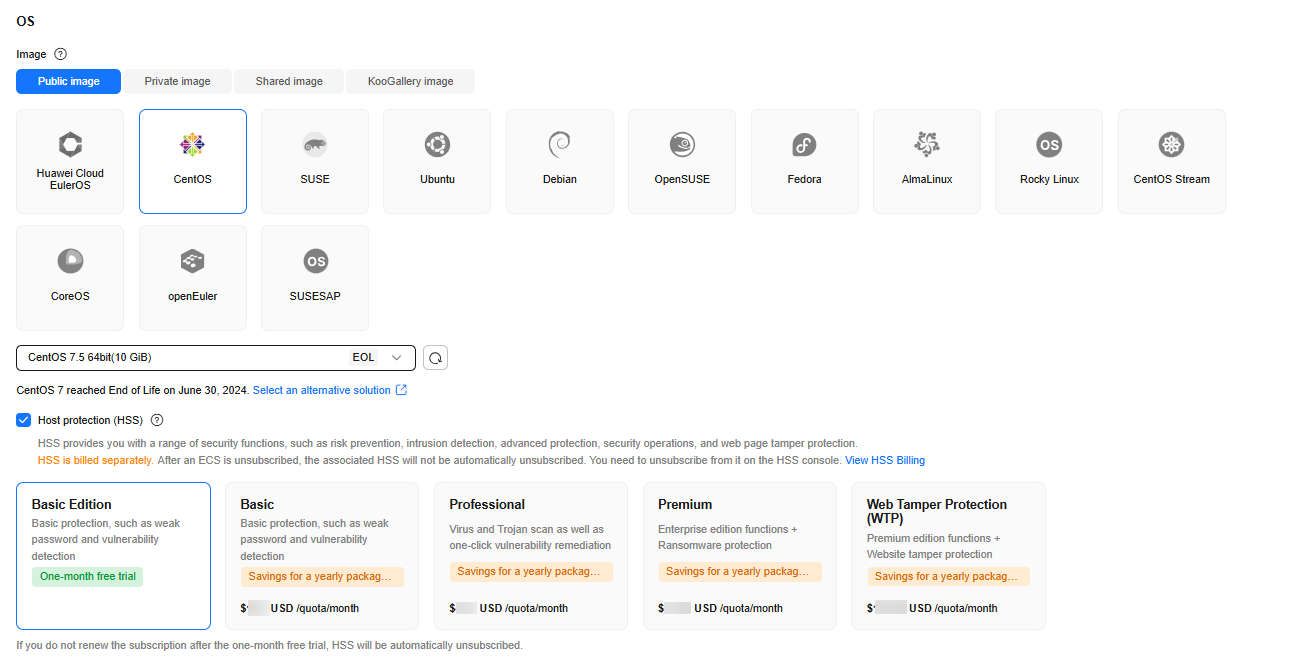
When you use certain public images to create ECSs, you are advised to use HSS to protect your ECSs.
- Basic edition (one-month free trial): After this function is enabled, the HSS basic edition can be used free of charge for 30 days. The HSS basic edition supports detection of OS vulnerabilities, weak passwords, and brute force cracking to improve the overall security for your ECSs.

After the free trial period expires, the HSS basic edition quotas will be automatically released, and HSS will not protect your servers.
If you want to retain or upgrade HSS security capabilities, you are advised to enable the advanced HSS edition. For details, see What Should I Do When the Free Trial of HSS Basic Edition Expires?
This option is selected by default.
- Advanced HSS edition (paid): You can choose from HSS basic, professional, enterprise, premium, and Web Tamper Protection (WTP) editions and you need to pay for it.
After ECSs are purchased, you can switch between different editions on the HSS console after Advanced HSS edition (paid) is enabled. For details about the differences among different editions, see Specifications of Different Editions.
- None: HSS is disabled and servers are not protected.
After you select an HSS edition, the system automatically installs the HSS agent, enables account cracking prevention, and offers host security functions.
If the basic or enterprise edition does not meet your service requirements, you can purchase an HSS quota of your desired edition and change the protection quota edition on the HSS console to obtain advanced protection without reinstalling the agent.
For existing ECSs without host protection enabled, you can enable HSS as needed. The process is as follows.
|
No. |
Step |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
HSS provides the basic, professional, enterprise, premium, web tamper protection, and container editions. Each edition supports different functions and features. You need to purchase the corresponding edition based on your protection requirements for servers. For details about the differences between HSS editions, see Features. |
|
|
2 |
The agent is a piece of software provided by HSS. It is installed on cloud servers to interact with the HSS cloud protection center, performing security checks and protection for servers. You can enable HSS only after the HSS agent is installed on your servers. |
|
|
3 |
You need to enable protection for your ECSs. |
|
|
4 |
(Optional) Enabling Alarm Notifications |
By default, security risks detected by HSS are displayed on the management console. You need to log in to the console and view the risks. If you want to know the security risks of servers or containers in a timely manner, you can enable the alarm notification function. After the function is enabled, HSS will send security risks to you by SMS or email. |
|
5 |
(Optional) Common Security Configuration |
To improve ECS security, you can configure the following ECS security protection items based on your service requirements:
|
How Do I Check Host Security Statuses?
On the Server tab, you can view the ECS security statuses in the current region.
You are advised to periodically check the server protection status and handle security risks in a timely manner to prevent asset loss.
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 and choose Security & Compliance > Host Security Service.
and choose Security & Compliance > Host Security Service. - Choose Asset Management > Servers & Quota and go to the Servers tab to view the protection status of the target servers.
Figure 2 ECS security statuses

Table 2 Statuses Parameter
Description
Agent Status
- Not installed: The agent has not been started or even has not been installed.
- Online: The agent is running properly.
- Offline: The agent fails to communicate with the HSS server. Therefore, HSS cannot protect your ECS.
Click Offline. Then, the ECSs with agent being offline and the offline reasons are displayed.
- Offline: The agent has been installed, but the agent is disconnected from the HSS remote protection center. In this case, HSS cannot provide protection.
Click Offline. Then, the ECSs with agent being offline and the offline reasons are displayed. For details, see How Do I Fix an Abnormal Agent?
- Installation failed: An error or problem occurred, leading to an installation failure.
Click
 next to the installation failure status to view the cause. For details, see What Should I Do If Agent Installation Failed?
next to the installation failure status to view the cause. For details, see What Should I Do If Agent Installation Failed? - Installing: The agent is being installed.
Risk Level
Risk status of a server. (Data is updated every 24 hours.)
- Risky: The ECS is risky.
Hover your cursor over a risk icon to view risk distribution details. Click a risk quantity to go to the risk details page.
- Safe: No risks are detected.
- Pending risk detection: HSS is not enabled for the ECS.
Protection Status
- Protected: The ECS is fully protected by HSS.
- Unprotected: HSS is disabled for the ECS.
After the agent is installed, click Enable in the Operation column to enable protection.
- Protection interrupted: The server is shut down, the agent is offline, or the agent is uninstalled.
You can hover the cursor on
 next to Protection interrupted to view the cause.
next to Protection interrupted to view the cause.
Protection Status
- Enabled: The ECS is properly protected using HSS.
- Disabled: HSS has been disabled on the ECS. If an ECS does not need protection, disable HSS on it to reduce its resource consumption.
Detection Result
- Risky: The ECS is risky.
- Safe: No risks are detected.
- Pending risk detection: HSS is not enabled for the ECS.
For more details, see What Is HSS?
FAQ
For details about how to troubleshoot the agent installation failure, see What Should I Do If Agent Installation Failed?
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





