Alarm Configuration
- Alarm notification settings are effective only for the current region. To receive notifications from another region, switch to that region and configure alarm notification.
- Alarm notifications may be mistakenly blocked. If you have enabled notifications but not received any, check whether they have been blocked as spam.
- The Simple Message Notification (SMN) service is a paid service. For details about the price, see Product Pricing Details.
Enabling Alarm Notifications
- Log in to the HSS console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner and select a region or project. - In the navigation pane, choose .
- (Optional) If your servers are managed by enterprise projects, you can select an enterprise project to configure alarm notifications.
- If you select a single enterprise project, the alarm notification information takes effect only in the corresponding enterprise project.
- If you select All projects, the alarm notification information takes effect in all enterprise projects.
- Configure the alarm notification parameters as prompted. For more information, see Table 1.
Figure 1 Alarm configurations
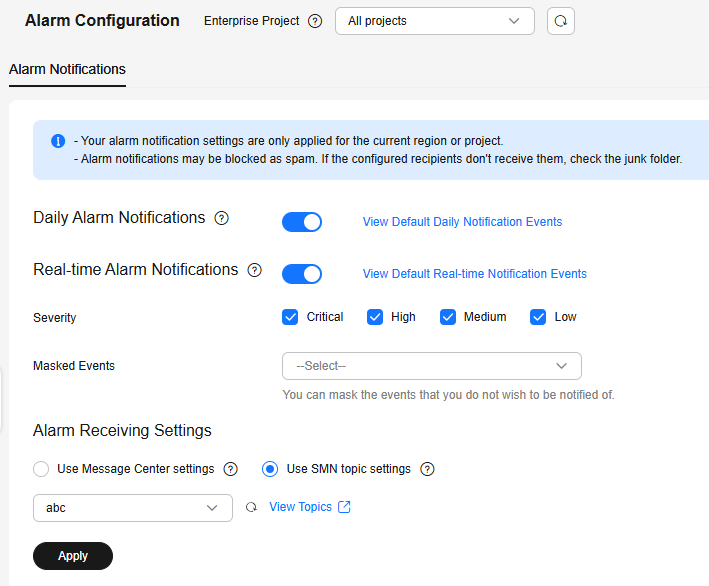
Table 1 Alarm configurations Type
Description
Suggestion
Daily alarm notification
HSS scans the accounts, web directories, vulnerabilities, malicious programs, and key configurations in the server system at 00:00 every day, and sends the summarized detection results to the recipients you set in the Message Center or SMN, depending on which one you chose.
To view notification items, click View Default Daily Notification Events.
- It is recommended that you receive and periodically check all the content in the daily alarm notification to eliminate risks in a timely manner.
- Daily alarm notifications contain a lot of check items. If you want to send the notifications to recipients set in an SMN topic, you are advised to set the topic protocol to Email.
Real-time alarm notification
When an attacker intrudes a server, alarms are sent to the recipients you set in the Message Center or SMN, depending on which one you chose.
To view notification items, click View Default Real-time Notification Events.
- It is recommended that you receive all the content in the real-time alarm notification and view them in time. The HSS system monitors the security of servers in real time, detects the attacker's intrusion, and sends real-time alarm notifications for you to quickly handle the problem.
- Real-time alarm notifications are about urgent issues. If you want to send the notifications to recipients set in an SMN topic, you are advised to set the topic protocol to SMS.
Severity
Select the severities of alarms that you want to be notified of.
All
Masked Events
Select the events that you do not wish to be notified of.
Select events to be masked from the drop-down list box.
Determine the events to be masked based on the description in Alarm Notifications.
- Select the alarm notification mode.
- Use Message Center settings
By default, alarm notifications are sent to the contacts under the account. Notification modes include email, SMS, system notification, and group chatbots (WeCom, DingTalk, Feishu, and WeLink). For more information, see Message Center.
To configure the notification mode and recipients, perform the following steps:
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper right corner to access the Message Center.
in the upper right corner to access the Message Center.
You can view all system notifications on this page.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Message Receiving Management > SMS & Email Settings.
- Choose .
- Select notification modes as required.
You can select Email, SMS, System Notification, and Group Chatbot (WeCom, DingTalk, Feishu, and WeLink).
Figure 2 Configuring notification modes
- In the Operation column, click Modify Recipient or Modify Robot Recipient to configure recipients.
- If you selected email or SMS in 6.e, configure message recipients.
- If you selected group chatbots (WeCom, DingTalk, Feishu, and WeLink) in 6.e, configure robot recipients.
Only the WeCom, DingTalk, Feishu, and WeLink recipients that have been added on the Recipient Management page are available for selection.
- In the Modify Recipient or Modify Robot Recipient dialog box, select recipients and click OK.
Only the robot recipients that have been added on the Recipient Management page are available for selection. For details about how to add a recipient, see Adding Recipients.
- Use SMN topic settings
Select an available topic from the drop-down list or click View Topics and create a topic. Alarm notifications are sent to message topic recipients through SMS, chatbots (DingTalk, WeCom, Feishu, and WeLink), and email. For details about message topics, see Simple Message Notification.
To create a topic and add subscriptions, perform the following steps:- Create a topic.
For details, see Creating a Topic.
- Add one or more subscriptions to the created topic.
For details, see Adding a Subscription.
- After the subscription is added, confirm the subscription as prompted by the received SMS message, email, or other notifications.
The confirmation message about topic subscription may be regarded as spam. If you do not receive the message, check whether it is intercepted as spam.
You can create multiple notification topics based on the O&M plan and alarm notification type to receive different types of alarm notifications.
- Create a topic.
- Use Message Center settings
- Click Apply. A message will be displayed indicating that the alarm notification is set successfully.
Alarm Notifications
Alarm notifications are classified into daily alarm notifications and real-time alarm notifications. The notification items are as follows:
The service checks risks in your servers in the early morning every day, summarizes and collects detection results, and sends the results to your mobile phone or email box at 10:00 every day.
|
Type |
Item |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Assets |
Dangerous ports |
Check for high-risk open ports and unnecessary ports. |
|
Agent not installed |
Check for servers with no HSS agent installed, and remind you to install the agent on these servers in a timely manner. |
|
|
Protection interrupted |
Check for servers whose agent protection is interrupted, and remind you to rectify faults in a timely manner. |
|
|
Vulnerabilities |
Critical vulnerabilities |
Detect critical vulnerabilities and fix them in a timely manner. |
|
Baseline checks |
Unsafe Settings |
Detect unsafe settings of key applications that will probably be exploited by hackers to intrude servers. |
|
Common weak passwords |
Detect weak passwords in MySQL, FTP, and system accounts. |
|
|
Intrusions |
Unclassified malware |
Check and handle detected malicious programs all in one place, including web shells, Trojans, mining software, worms, and viruses. |
|
Rootkits |
Detect server assets and report alarms for suspicious kernel modules, files, and folders. |
|
|
Ransomware |
Check for ransomware in media such as web pages, software, emails, and storage media. Ransomware can encrypt and control your data assets, such as documents, emails, databases, source code, images, and compressed files, to leverage victim extortion. |
|
|
Web shells |
Check whether the files (often PHP and JSP files) detected by HSS in your web directories are web shells.
|
|
|
Reverse shells |
Monitor user process behaviors in real time to detect reverse shells caused by invalid connections. Reverse shells can be detected for protocols including TCP, UDP, and ICMP. |
|
|
Redis vulnerability exploits |
Detect the modifications made by the Redis process on key directories in real time and report alarms. |
|
|
Hadoop vulnerability exploits |
Detect the modifications made by the Hadoop process on key directories in real time and report alarms. |
|
|
MySQL vulnerability exploits |
Detect the modifications made by the MySQL process on key directories in real time and report alarms. |
|
|
File privilege escalations |
Check the file privilege escalations in your system. |
|
|
Process privilege escalations |
The following process privilege escalation operations can be detected:
|
|
|
Abnormal process behaviors |
Check the processes on servers, including their IDs, command lines, process paths, and behavior. Send alarms on unauthorized process operations and intrusions. The following abnormal process behavior can be detected:
|
|
|
High-risk command executions |
Check executed commands in real time and generate alarms if high-risk commands are detected. |
|
|
Abnormal shells |
Detect actions on abnormal shells, including moving, copying, and deleting shell files, and modifying the access permissions and hard links of the files. |
|
|
Suspicious crontab tasks |
Check and list auto-started services, scheduled tasks, pre-loaded dynamic libraries, run registry keys, and startup folders. You can get notified immediately when abnormal auto-started items are detected and quickly locate Trojans. |
|
|
Container image blocking |
If a container contains insecure images specified in suspicious image behaviors, an alarm will be generated and the insecure images will be blocked before a container is started in Docker. |
|
|
Brute-force attacks |
Check for brute-force attack attempts and successful brute-force attacks.
|
|
|
Abnormal logins |
Check and handle remote logins. If a user's login location is not any common login location you set, an alarm will be triggered. |
|
|
Invalid accounts |
Scan accounts on servers and list suspicious accounts in a timely manner. |
|
|
Vulnerability escapes |
The service reports an alarm if it detects container process behavior that matches the behavior of known vulnerabilities (such as Dirty COW, brute-force attack, runC, and shocker). |
|
|
File escapes |
The service reports an alarm if it detects that a container process accesses a key file directory (for example, /etc/shadow or /etc/crontab). Directories that meet the container directory mapping rules can also trigger such alarms. |
|
|
Abnormal container processes |
Container services are usually simple. If you are sure that only specific processes run in a container, you can add the processes to the whitelist of a policy, and associate the policy with the container. The service reports an alarm if it detects that a process not in the whitelist is running in the container. |
|
|
Abnormal container startups |
Check for unsafe parameter settings used during container startup. Certain startup parameters specify container permissions. If their settings are inappropriate, they may be exploited by attackers to intrude containers. |
|
|
High-risk system calls |
Users can run tasks in kernels by Linux system calls. The service reports an alarm if it detects a high-risk call, such as open_by_handle_at, ptrace, setns, and reboot. |
|
|
Sensitive file access |
Detect suspicious access behaviors (such as privilege escalation and persistence) on important files. |
|
|
Web page tampering prevention for Windows servers |
Protect the static web page files on your Windows website servers from malicious modification. |
|
|
Web page tampering prevention for Linux servers |
Protect the static web page files on your Linux website servers from malicious modification. |
|
|
Dynamic WTP |
Protect the dynamic web page files on your Windows and Linux website servers from malicious modification. |
|
|
Application protection |
Protect running applications. You simply need to add probes to applications, without having to modify application files. Currently, only Linux servers are supported, and only Java applications can be connected. |
|
|
Virus scan |
Generates alarms for detected virus-infected files. |
|
|
Suspicious process executions |
Detect and report alarms on unauthenticated or unauthorized application processes. |
|
|
Suspicious process file access |
Detect and report alarms on the unauthenticated or unauthorized application processes accessing specific directories. |
When an event occurs, an alarm notification is immediately sent.
|
Type |
Item |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Assets |
Dangerous ports |
Check for high-risk open ports and unnecessary ports. |
|
Agent not installed |
Check for servers with no HSS agent installed, and remind you to install the agent on these servers in a timely manner. |
|
|
Protection interrupted |
Check for servers whose agent protection is interrupted, and remind you to rectify faults in a timely manner. |
|
|
Intrusions |
Unclassified malware |
Check and handle detected malicious programs all in one place, including web shells, Trojans, mining software, worms, and viruses. |
|
Rootkits |
Detect server assets and report alarms for suspicious kernel modules, files, and folders. |
|
|
Ransomware |
Check for ransomware in media such as web pages, software, emails, and storage media. Ransomware can encrypt and control your data assets, such as documents, emails, databases, source code, images, and compressed files, to leverage victim extortion. |
|
|
Web shells |
Check whether the files (often PHP and JSP files) detected by HSS in your web directories are web shells.
|
|
|
Reverse shells |
Monitor user process behaviors in real time to detect reverse shells caused by invalid connections. Reverse shells can be detected for protocols including TCP, UDP, and ICMP. |
|
|
Redis vulnerability exploits |
Detect the modifications made by the Redis process on key directories in real time and report alarms. |
|
|
Hadoop vulnerability exploits |
Detect the modifications made by the Hadoop process on key directories in real time and report alarms. |
|
|
MySQL vulnerability exploits |
Detect the modifications made by the MySQL process on key directories in real time and report alarms. |
|
|
File privilege escalations |
Check the file privilege escalations in your system. |
|
|
Process privilege escalations |
The following process privilege escalation operations can be detected:
|
|
|
Abnormal process behaviors |
Check the processes on servers, including their IDs, command lines, process paths, and behavior. Send alarms on unauthorized process operations and intrusions. The following abnormal process behavior can be detected:
|
|
|
High-risk command executions |
Check executed commands in real time and generate alarms if high-risk commands are detected. |
|
|
Abnormal shells |
Detect actions on abnormal shells, including moving, copying, and deleting shell files, and modifying the access permissions and hard links of the files. |
|
|
Suspicious crontab tasks |
Check and list auto-started services, scheduled tasks, pre-loaded dynamic libraries, run registry keys, and startup folders. You can get notified immediately when abnormal auto-started items are detected and quickly locate Trojans. |
|
|
Container image blocking |
If a container contains insecure images specified in suspicious image behaviors, an alarm will be generated and the insecure images will be blocked before a container is started in Docker. |
|
|
Abnormal logins |
Check and handle remote logins. If a user's login location is not any common login location you set, an alarm will be triggered. |
|
|
Invalid accounts |
Scan accounts on servers and list suspicious accounts in a timely manner. |
|
|
Vulnerability escapes |
The service reports an alarm if it detects container process behavior that matches the behavior of known vulnerabilities (such as Dirty COW, brute-force attack, runC, and shocker). |
|
|
File escapes |
The service reports an alarm if it detects that a container process accesses a key file directory (for example, /etc/shadow or /etc/crontab). Directories that meet the container directory mapping rules can also trigger such alarms. |
|
|
Abnormal container processes |
Container services are usually simple. If you are sure that only specific processes run in a container, you can add the processes to the whitelist of a policy, and associate the policy with the container. The service reports an alarm if it detects that a process not in the whitelist is running in the container. |
|
|
Abnormal container startups |
Check for unsafe parameter settings used during container startup. Certain startup parameters specify container permissions. If their settings are inappropriate, they may be exploited by attackers to intrude containers. |
|
|
High-risk system calls |
Users can run tasks in kernels by Linux system calls. The service reports an alarm if it detects a high-risk call, such as open_by_handle_at, ptrace, setns, and reboot. |
|
|
Sensitive file access |
Detect suspicious access behaviors (such as privilege escalation and persistence) on important files. |
|
|
Web page tampering prevention for Windows servers |
Protect the static web page files on your Windows website servers from malicious modification. |
|
|
Web page tampering prevention for Linux servers |
Protect the static web page files on your Linux website servers from malicious modification. |
|
|
Dynamic WTP |
Protect the dynamic web page files on your Windows and Linux website servers from malicious modification. |
|
|
Application protection |
Protect running applications. You simply need to add probes to applications, without having to modify application files. Currently, only Linux servers are supported, and only Java applications can be connected. |
|
|
Auto Blocking |
Notify users of successful automatic isolation and killing of malicious programs, automatic blocking of ransomware, and automatic blocking of WTP. |
|
|
Suspicious process executions |
Detect and report alarms on unauthenticated or unauthorized application processes. |
|
|
Suspicious process file access |
Detect and report alarms on the unauthenticated or unauthorized application processes accessing specific directories. |
|
|
Login |
Success login |
Notifications are sent to accounts that have successfully logged in. |
|
Server protection |
Ransomware protection disabled |
An alarm is reported if ransomware prevention is disabled manually or abnormally. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





