Evaluating an Intelligent Analysis Assistant
The system supports detailed analysis and evaluation of the intelligent analysis assistant's Q&A. The evaluation system covers a series of key indicators and is equipped with annotation functions to ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness. Additionally, DataArts Insight introduces a bad case management mechanism for inaccurate Q&A identified during evaluation. It can efficiently track and record Q&A marked as incorrect, facilitating subsequent problem resolution and improvement work.
Evaluating the intelligent analysis assistant can quickly and accurately assess the effectiveness of various modules, and track low-accuracy Q&A questions, supporting rapid optimization and iteration. This section describes how to effectively evaluate Q&A questions.
Notes and Constraints
- To use this function, you must have the administrator permissions.
Prerequisites
- A project has been created by referring to Creating a Project.
- A data source has been connected by referring to Connecting to a Data Source.
- A dataset has been created by referring to Creating a Dataset.
- An intelligent analysis assistant has been created by referring to Creating an Intelligent Analysis Assistant.
Procedure

|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The uploaded evaluation set contains questions for the intelligent analysis assistant. Subsequent evaluations will be based on these questions. |
|
|
Evaluation annotation can quickly and accurately assess the end-to-end effects and module effectiveness of the current intelligent analysis assistant. |
|
|
Choose two intelligent analysis assistants for evaluation annotation under the same evaluation set, to compare Q&A accuracy rates and optimize assistant configuration accordingly. |
|
|
Bad cases can effectively track questions marked as incorrect during evaluation annotation, facilitating subsequent problem handling and improvement. |
Step 1: Upload an Evaluation Set
- Log in to the DataArts Insight console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console to select a region. Then, select an enterprise project in the upper right corner.
in the upper left corner of the management console to select a region. Then, select an enterprise project in the upper right corner. - On the top menu of the console, click Project. On the displayed My Projects page, click the name of the desired project.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > Assessment Management.
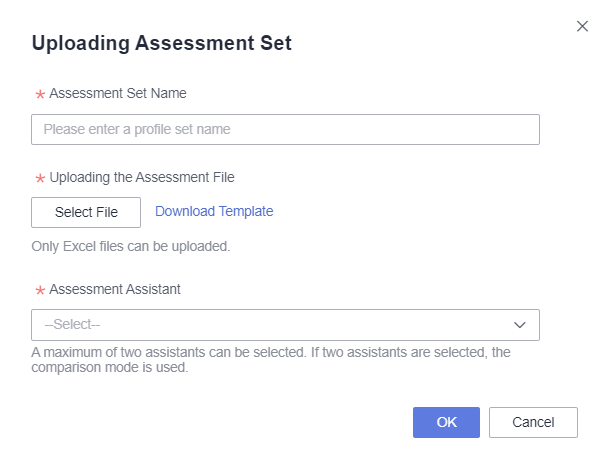
- Click Upload Assessment Set. On the displayed page (Figure 2), enter the evaluation set name.
- Click Download Template, complete the evaluation set template, and click Select File to upload the evaluation file.
- Select an evaluation assistant and click OK.
Table 2 Parameters for uploading an evaluation set Parameter
Description
Assessment Set Name
Name the evaluation set. The name can contain up to 32 characters and must be specified. Only letters, numbers, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed.
Uploading the Assessment File
Subsequent evaluations will be based on the evaluation file. The parameter descriptions for the evaluation template are as follows:
conversationId: Conversation ID, for example, the IDs of the first and second conversations with the intelligent analysis assistant are 1 and 2, respectively.
seqId: IDs of different questions in one conversation, e.g., questions in the first conversation are numbered 1, 2, 3...
question: Different questions in one conversation, e.g., what is the percentage growth in sales of products in different regions?
Assessment Assistant
Select the intelligent analysis assistant to be evaluated, with a maximum of two intelligent analysis assistants.
Step 2: Evaluate and Annotate
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > Assessment Management.
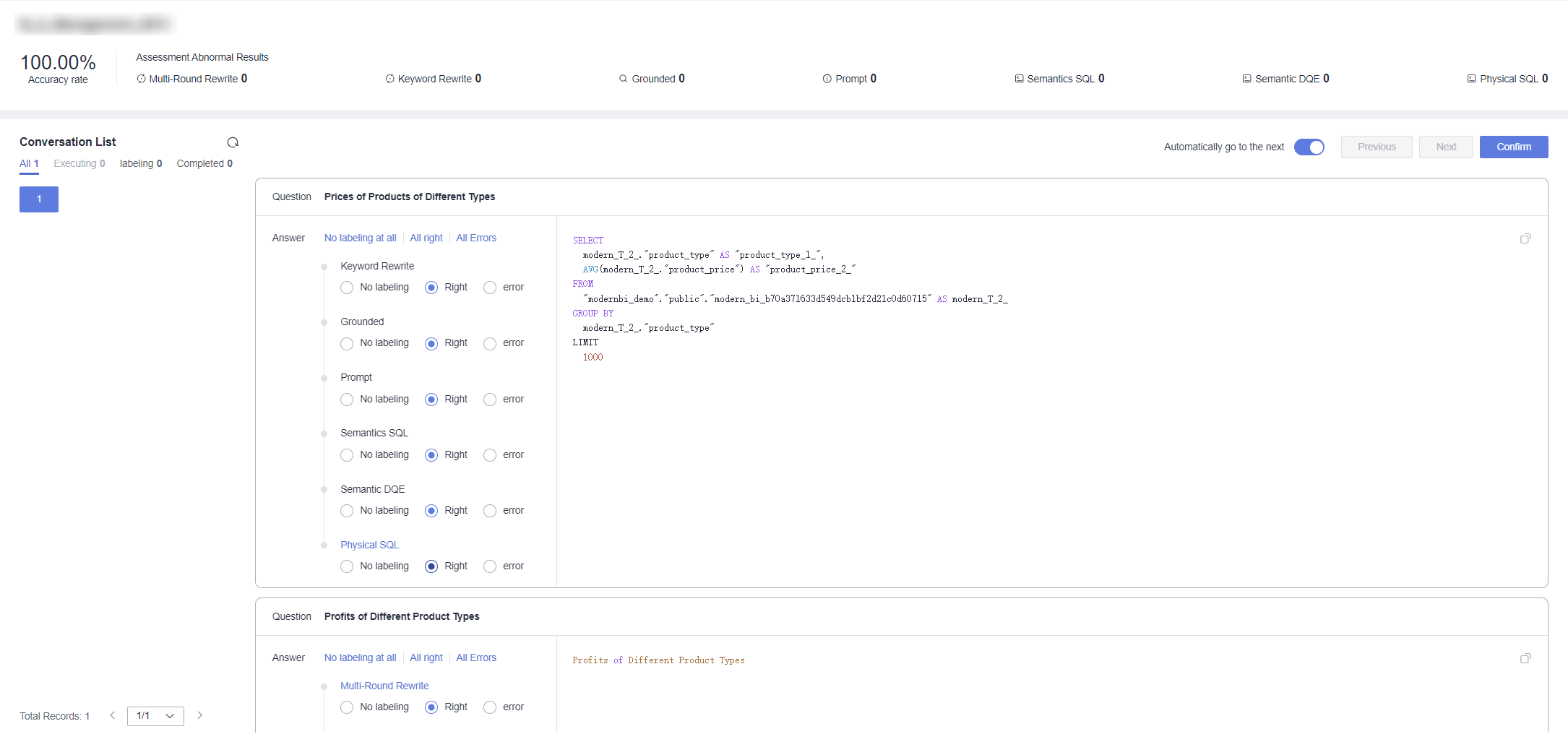
- Click an evaluation set name. The intelligent analysis assistant associated with the evaluation set is displayed on the left of the page, that is, the assessment assistant selected in step 1. The top of the page shows the accuracy of the evaluation results, calculated as: accuracy = 1 – Errors/Total steps.
- In the dialogue list area, annotate each question in the evaluation set. For parameter descriptions, refer to Table 3.
- The left side of the dialogue list area shows different conversations corresponding to the conversationId in the evaluation set template. After completing the annotation of questions in a conversation, click Confirm to complete the evaluation annotation of that conversation (Figure 3).
Questions marked as incorrect during evaluation annotation will be automatically updated to bad case management for subsequent tracking and improvement.
Table 3 Evaluation annotation parameter descriptions Parameter
Description
Keyword Rewrite
You can configure question and answer keywords in the assistant. After multi-turn rewriting, the system will check if the question contains any user-defined keywords. If so, the keywords in the question will be replaced with the configured replacement content.
Grounded
The assistant will search and retrieve relevant data tables, fields, and enumerations based on your query. This search step simplifies the input for the model compared to directly inputting all dataset schemas and enumeration information. It improves the effectiveness of the NL2SQL model and reduces inference latency.
Prompt
Based on prompt word templates and user instructions, as well as search results, the assistant dynamically generates corresponding prompt words for each user query.
Semantics SQL
The foundation model performs inference for the NL2SQL task based on prompt words, generating semantic SQL. Note that semantic SQL is generated based on the dataset schema and is not directly executable physical SQL.
Semantic DQE
Semantic SQL is transformed into data query expressions (DQEs). Compared to SQL, DQE is a more structured data structure and is a universal data query structure in DataArts Insight. During the transformation, semantic SQL is post-processed to validate and correct any illusions or errors, improving the accuracy of the entire data query.
Physical SQL
DQE is further transformed into physical SQL that can be executed by the target data source. This transformation includes mapping the dataset schema to the physical table schema, adapting to the target data source dialect, injecting default filtering conditions and access control conditions.
Step 3: (Optional) Compare Evaluation Results
Choose two intelligent analysis assistants for evaluation annotation under the same evaluation set, to compare Q&A accuracy rates and optimize assistant configuration accordingly.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > Assessment Management.
- Click Upload Assessment Set, select the two intelligent analysis assistants to be compared for evaluation, set parameters, and click Confirm.
- Click an evaluation set name. In the dialogue list area, annotate each question in the evaluation set. For parameter descriptions, refer to Table 3.
Figure 4 Evaluation annotation
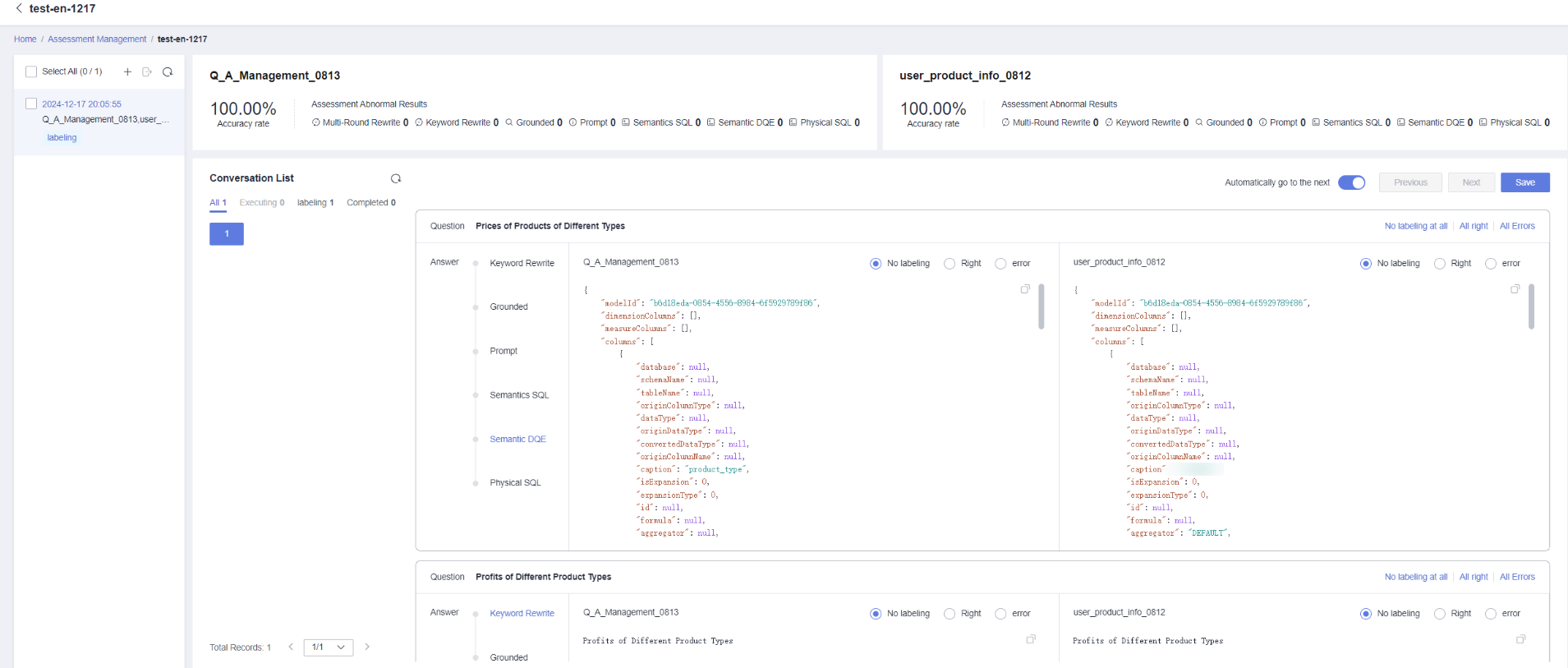
Questions marked as incorrect during evaluation annotation will be automatically updated to bad case management for subsequent tracking and improvement.
Step 4: Manage Bad Cases
Bad cases can effectively track questions marked as incorrect during evaluation annotation, facilitating subsequent problem handling and improvement.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > BadCase Management. This page provides bad case query functions, supports filtering by question, stage, intelligent analysis assistant, owner, and other dimensions, and supports sorting by update time.
Figure 5 Bad case management
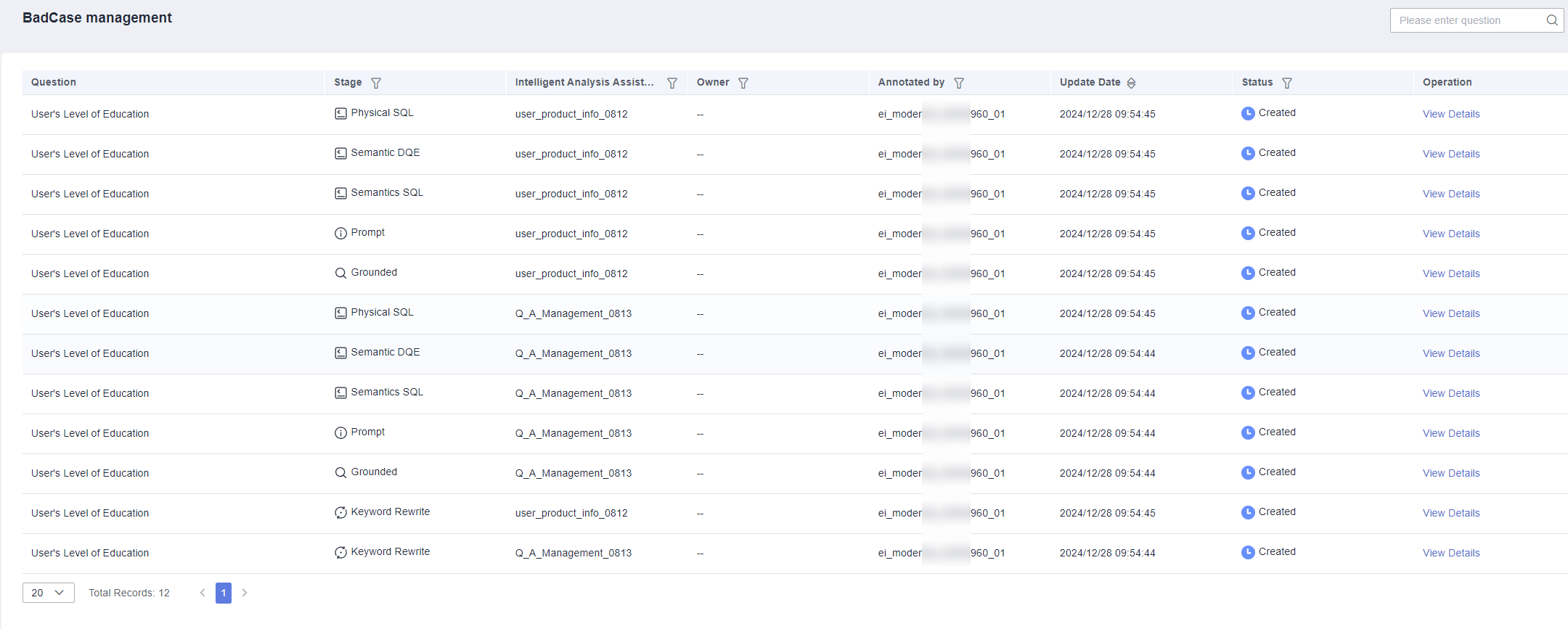
Bad case management displays questions marked as incorrect during evaluation annotation based on different stages of the parsing process (keyword rewriting, retrieval results, prompts, semantic SQL, DQE, SQL).
- Click View Details to enter the bad case details page, where you can modify the bad case status and the current owner. After modification, click OK to save.
Figure 6 Bad case details
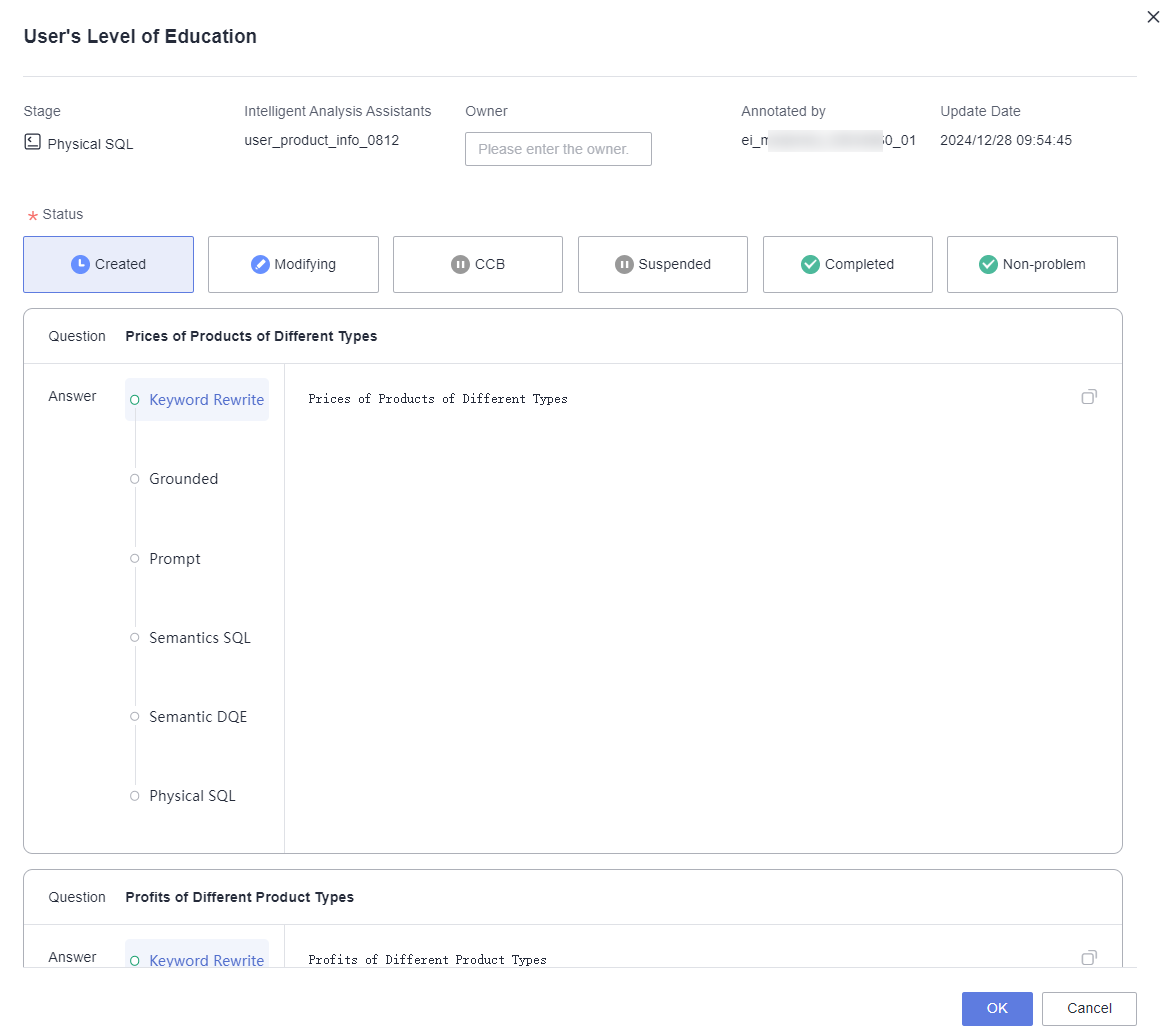
Table 4 Bad case parameter descriptions Parameter
Description
Stage
Stages of the intelligent analysis assistant parsing process, including keyword rewriting, retrieval results, prompts, semantic SQL, DQE, and SQL.
Intelligent Analysis Assistants
The intelligent analysis assistant associated with the bad case, that is, the intelligent analysis assistant associated during evaluation annotation.
Owner
Owner for handling bad cases.
Annotated by
User who annotated the bad case during evaluation.
Update Date
Time when the bad case was last updated.
Status
Created: Default status, indicating that the bad case has been recorded and initially identified.
Modifying: The bad case is currently under review or being modified.
CCB: The bad case has been submitted to the Change Control Board (CCB) for review, currently pending.
Suspended: The bad case is temporarily shelved for some reason, awaiting further processing.
Completed: The bad case has been processed, the issue has been resolved, or necessary measures have been taken.
Non-problem: After further analysis, the originally marked bad case is not actually an issue.
- The bad case status can only be updated sequentially to the next stage and cannot be modified to a previous stage. For example, the status cannot be changed from Completed to Suspended.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot