Deploying Hubble for DataPlane V2 Network Observability
In a cluster with DataPlane V2 enabled, you can deploy Hubble, an open-source observability project, for the visual display of container network traffic and container network observability.
Prerequisites
- CCE DataPlane V2 is released with restrictions. To use this feature, submit a service ticket to CCE.
- Currently, Hubble can only be deployed in CCE standard clusters of v1.27.16-r50, v1.28.15-r40, v1.29.15-r0, v1.30.14-r0, v1.31.10-r0, v1.32.6-r0, and later versions with DataPlane V2 enabled.
Step 1: Configure a ConfigMap and Rebuild yangtse-cilium
- Connect to your cluster using kubectl. For details, see Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl.
- Specify the following native ConfigMap configuration of the Cilium community:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: cilium-config namespace: kube-system data: enable-hubble: "true" hubble-disable-tls: "true" hubble-listen-address: :4244 hubble-metrics: dns drop tcp flow port-distribution icmp http hubble-metrics-server: :9965
Table 1 Parameters Parameter
Description
Remarks
enable-hubble
Whether to enable Hubble. true indicates Hubble is enabled, and false indicates Hubble is disabled.
This parameter is set to true here.
hubble-disable-tls
Whether to disable TLS on the Hubble server. true indicates TLS is disabled, and false indicates TLS is enabled.
This parameter is set to true here.
hubble-listen-address
Listening address of the Hubble server.
This parameter is set to :4244 here. The colon cannot be omitted.
hubble-metrics
Metrics to be collected by Hubble. Separate multiple metrics with spaces.
The metrics that can be collected by Hubble include dns, drop, tcp, flow, flows-to-world, httpV2, icmp, kafka, and port-distribution. For details, see Metrics supported by the Cilium community.
If you specify a large number of metrics, the Hubble performance will be affected.
hubble-metrics-server
Address for accessing Hubble metrics.
This parameter is set to :9965 here. The colon cannot be omitted.
- Roll back and rebuild yangtse-cilium to apply the configuration.
uuid=$(uuidgen) kubectl patch daemonset -nkube-system yangtse-cilium --type='json' -p="[{\"op\": \"add\", \"path\": \"/spec/template/metadata/annotations/change-id\", \"value\": \"$uuid\"}]"
Step 2: Deploy Hubble Components
- Create the hubble.yaml file.
The following is the file content:

Change the value of valid-cluster in the following configuration file to the name of your cluster.
--- apiVersion: v1 automountServiceAccountToken: false kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: hubble-relay namespace: kube-system --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: hubble-ui namespace: kube-system --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: hubble-ui roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: hubble-ui subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: hubble-ui namespace: kube-system --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: hubble-ui rules: - apiGroups: - networking.k8s.io resources: - networkpolicies verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - "" resources: - componentstatuses - endpoints - namespaces - nodes - pods - services verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - apiextensions.k8s.io resources: - customresourcedefinitions verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - cilium.io resources: - '*' verbs: - get - list - watch --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app: hubble-relay name: hubble-relay namespace: kube-system spec: internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster ipFamilies: - IPv4 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack ports: - port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: grpc selector: app: hubble-relay sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: annotations: prometheus.io/port: "9965" prometheus.io/scrape: "true" labels: app: hubble name: hubble-metrics namespace: kube-system spec: clusterIP: None clusterIPs: - None internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster ipFamilies: - IPv4 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack ports: - name: hubble-metrics port: 9965 protocol: TCP targetPort: hubble-metrics selector: app: yangtse-cilium sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app: cilium name: hubble-peer namespace: kube-system spec: internalTrafficPolicy: Local ipFamilies: - IPv4 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack ports: - name: peer-service port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 4244 selector: app: yangtse-cilium sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: v1 data: nginx.conf: "server {\n listen 8081;\n listen [::]:8081;\n server_name \ localhost;\n root /app;\n index index.html;\n client_max_body_size 1G;\n\n location / {\n proxy_set_header Host $host;\n proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;\n\n location /api {\n proxy_http_version 1.1;\n proxy_pass_request_headers on;\n proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8090;\n \ }\n location / {\n # double `/index.html` is required here \n try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html /index.html;\n }\n\n \ # Liveness probe\n location /healthz {\n access_log off;\n add_header Content-Type text/plain;\n return 200 'ok';\n }\n }\n}" kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: hubble-ui-nginx namespace: kube-system --- apiVersion: v1 data: # Change the value of valid-cluster to the name of your cluster. config.yaml: "cluster-name: valid-cluster\npeer-service: \"hubble-peer.kube-system.svc.cluster.local.:80\"\nlisten-address: :4245\ngops: true\ngops-port: \"9893\"\nretry-timeout: \nsort-buffer-len-max: \nsort-buffer-drain-timeout: \ndisable-client-tls: true\n\ndisable-server-tls: true\n" kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: hubble-relay-config namespace: kube-system --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: hubble-relay name: hubble-relay namespace: kube-system spec: progressDeadlineSeconds: 600 replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 selector: matchLabels: app: hubble-relay strategy: rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 25% maxUnavailable: 1 type: RollingUpdate template: metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: app: hubble-relay spec: affinity: podAffinity: requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: - labelSelector: matchLabels: app: yangtse-cilium topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname automountServiceAccountToken: false containers: - args: - serve command: - hubble-relay image: quay.io/cilium/hubble-relay:v1.17.6 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent livenessProbe: failureThreshold: 12 grpc: port: 4222 service: "" initialDelaySeconds: 10 periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 10 name: hubble-relay ports: - containerPort: 4245 name: grpc protocol: TCP readinessProbe: failureThreshold: 3 grpc: port: 4222 service: "" periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 3 resources: {} securityContext: capabilities: drop: - ALL runAsGroup: 65532 runAsNonRoot: true runAsUser: 65532 startupProbe: failureThreshold: 20 grpc: port: 4222 service: "" initialDelaySeconds: 10 periodSeconds: 3 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 1 terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log terminationMessagePolicy: FallbackToLogsOnError volumeMounts: - mountPath: /etc/hubble-relay name: config readOnly: true dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always schedulerName: default-scheduler securityContext: fsGroup: 65532 serviceAccount: hubble-relay serviceAccountName: hubble-relay terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 1 volumes: - configMap: defaultMode: 420 items: - key: config.yaml path: config.yaml name: hubble-relay-config name: config --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: hubble-ui name: hubble-ui namespace: kube-system spec: progressDeadlineSeconds: 600 replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 selector: matchLabels: app: hubble-ui strategy: rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 25% maxUnavailable: 1 type: RollingUpdate template: metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: app: hubble-ui spec: automountServiceAccountToken: true containers: - image: quay.io/cilium/hubble-ui:v0.13.2 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent livenessProbe: failureThreshold: 3 httpGet: path: /healthz port: 8081 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 1 name: frontend ports: - containerPort: 8081 name: http protocol: TCP readinessProbe: failureThreshold: 3 httpGet: path: / port: 8081 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 1 resources: {} terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log terminationMessagePolicy: FallbackToLogsOnError volumeMounts: - mountPath: /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf name: hubble-ui-nginx-conf subPath: nginx.conf - mountPath: /tmp name: tmp-dir - env: - name: EVENTS_SERVER_PORT value: "8090" - name: FLOWS_API_ADDR value: hubble-relay:80 image: quay.io/cilium/hubble-ui-backend:v0.13.2 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: backend ports: - containerPort: 8090 name: grpc protocol: TCP resources: {} terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log terminationMessagePolicy: FallbackToLogsOnError dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always schedulerName: default-scheduler securityContext: fsGroup: 1001 runAsGroup: 1001 runAsUser: 1001 serviceAccount: hubble-ui serviceAccountName: hubble-ui terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30 volumes: - configMap: defaultMode: 420 name: hubble-ui-nginx name: hubble-ui-nginx-conf - emptyDir: {} name: tmp-dir - Deploy components.
kubectl apply -f hubble.yaml
Step 3: Deploy the hubble-ui Service
You can deploy a Service of the NodePort or LoadBalancer type to provide the hubble-ui service externally.
A NodePort Service is used as an example here.
- Create the hubble-ui.yaml file.
The following is the file content:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app: hubble-ui name: hubble-ui namespace: kube-system spec: externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster ipFamilies: - IPv4 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack ports: - name: http nodePort: 32222 port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8081 selector: app: hubble-ui sessionAffinity: None type: NodePort - Create a NodePort Service.
kubectl apply -f hubble-ui.yaml
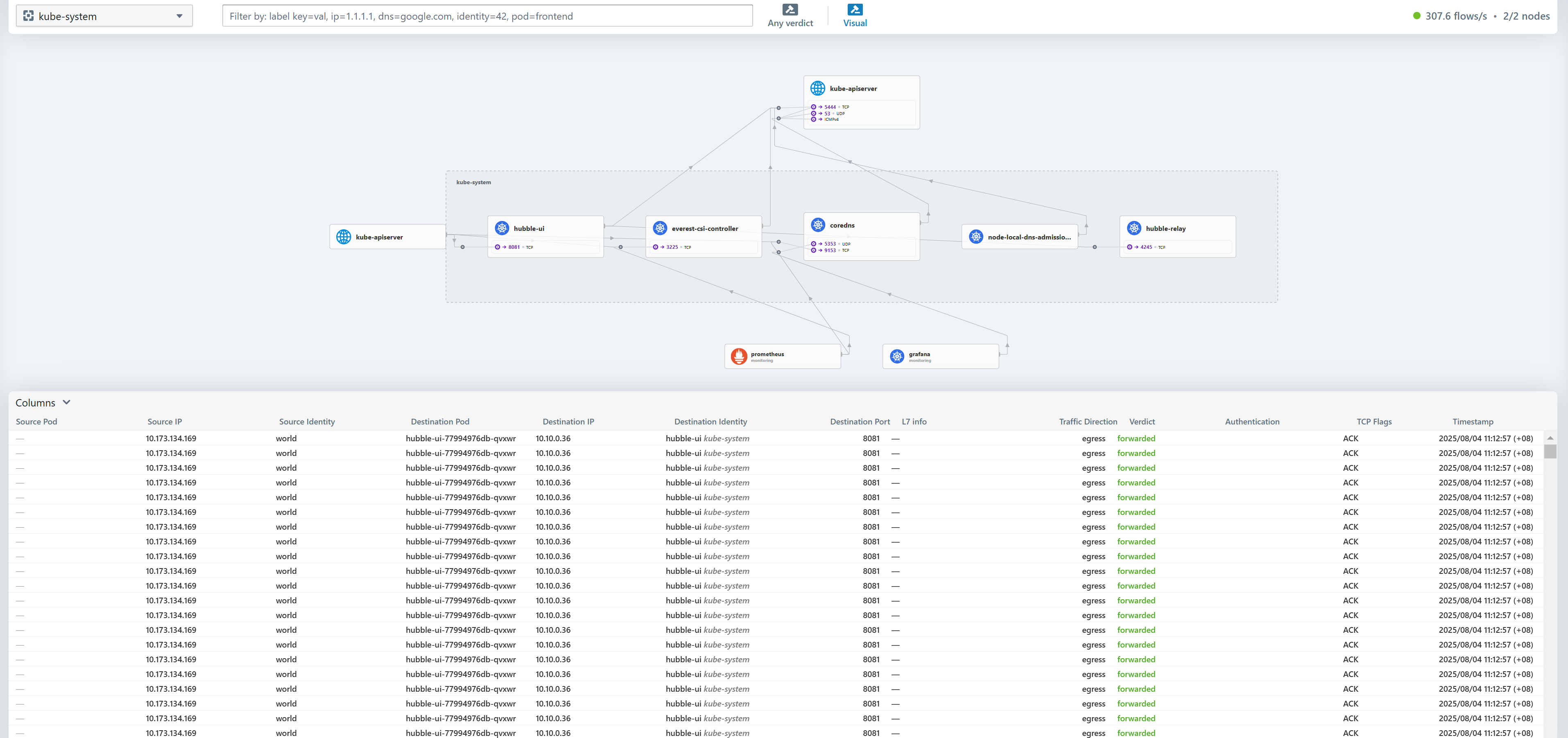
Step 4: Access hubble-ui
Enter the external access address of hubble-ui in the browser, for example, http://{EIP-of-the-node}:32222.
Step 5: Install Add-ons
- Install the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring and Grafana add-ons in the cluster.
- Install the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on. For details, see Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring.
- Install the Grafana add-on. For details, see Grafana.
- Create the hubble-monitor.yaml file.
The following is the file content:
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1 kind: ServiceMonitor metadata: name: hubble namespace: monitoring spec: endpoints: - honorLabels: true path: /metrics port: hubble-metrics relabelings: - action: replace replacement: ${1} sourceLabels: - __meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name targetLabel: node scheme: http jobLabel: hubble namespaceSelector: matchNames: - kube-system selector: matchLabels: app: hubble - Create a monitoring task.
kubectl create -f hubble-monitor.yaml
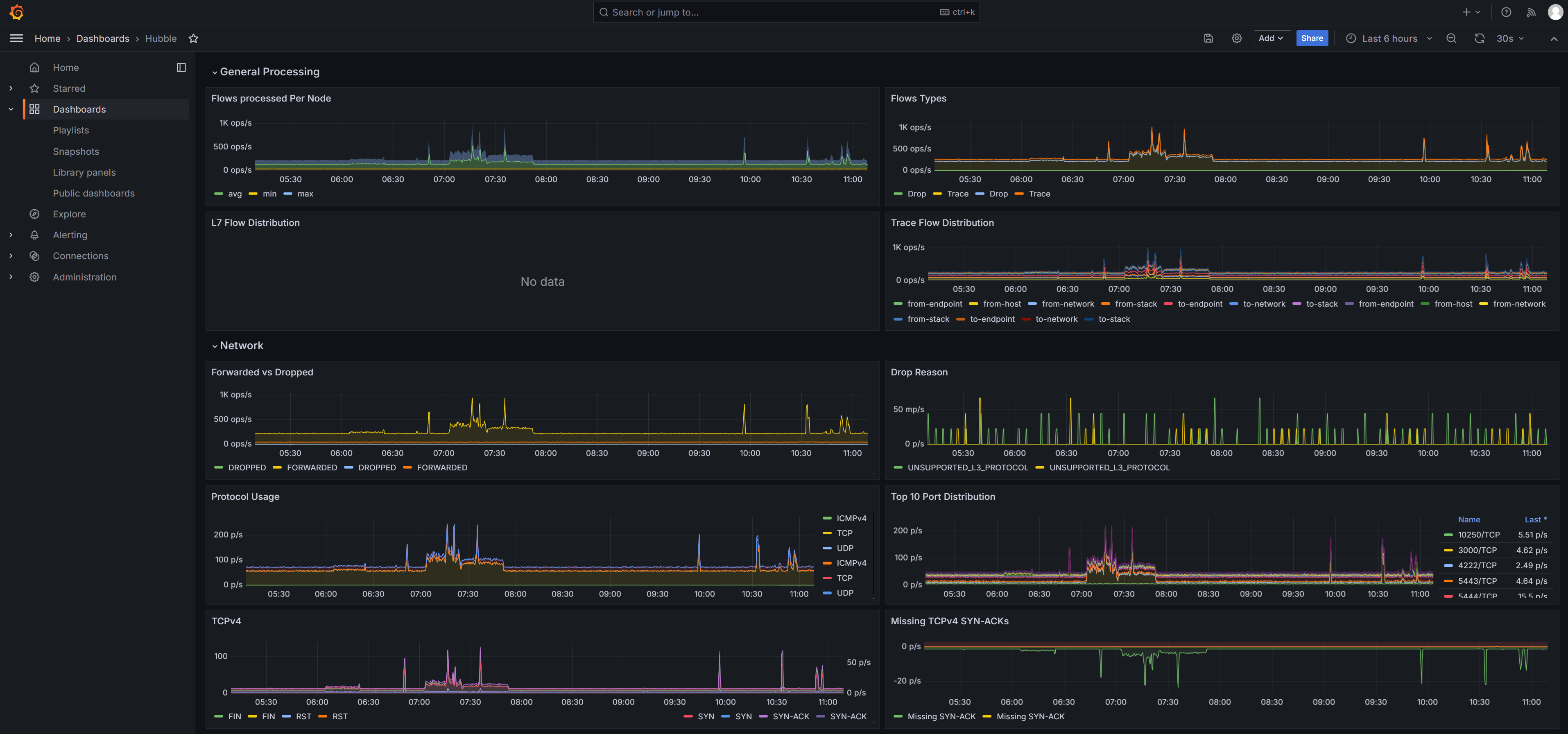
Step 6: Configure the Hubble Metric Dashboard
The Cilium official website provides a Grafana dashboard for Hubble metrics. Compared with the monotonous metrics of Prometheus, the Grafana dashboard is more attractive. You can access the dashboard to view Hubble metrics.
- Prepare the configuration file of the Hubble metric dashboard. Open the Prometheus sample file in the Cilium community, locate hubble-dashboard.json in the file, and copy it.
- Log in to Grafana, choose Dashboards, and import the hubble-dashboard.json file.

If you have enabled Interconnect with AOM when installing the Grafana add-on in Step 5: Install Add-ons, change the value of datasource in the hubble-dashboard.json file to prometheus-aom, and then import the file.
- Access the dashboard to view Hubble metrics. For details about Hubble metrics, see hubble-metrics.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





