Managing Error Codes in Applications
Scenario
If an error occurs in API calling, no result is returned. Identify the cause of error based on the error codes of each API. Huawei Cloud Astro Zero allows users to customize error codes and internationalize error code descriptions in multiple languages so that error code descriptions can be displayed in different languages.
In addition to setting error codes in the environment configuration, you can also set error codes in the application development designer. For details, see Customizing API Error Codes. The difference between the two is that the error codes configured in the application development designer can be packaged and released together with the error codes. For example, if an application is packaged and released to the running environment, error codes are also packaged to the running environment and do not need to be created again in the running environment. Error codes set in the environment configuration cannot be released with applications.
Creating an Error Code
- Log in to the Huawei Cloud Astro Zero console and click Access Homepage. The application development page is displayed.
- In the upper left corner of the page, click
 and choose Environments > Environment Configuration.
and choose Environments > Environment Configuration. - Choose Maintenance from the main menu.
- In the navigation pane, choose Global Elements > Error Codes.
- On the custom error code page, click the create button.
- Custom: displays custom error codes. You can add, delete, and modify custom error codes.
- System: displays the system preset error codes. You can view the preset error codes and their causes, but cannot delete them.
- Set error code parameters and click Save.
Figure 1 Creating an error code
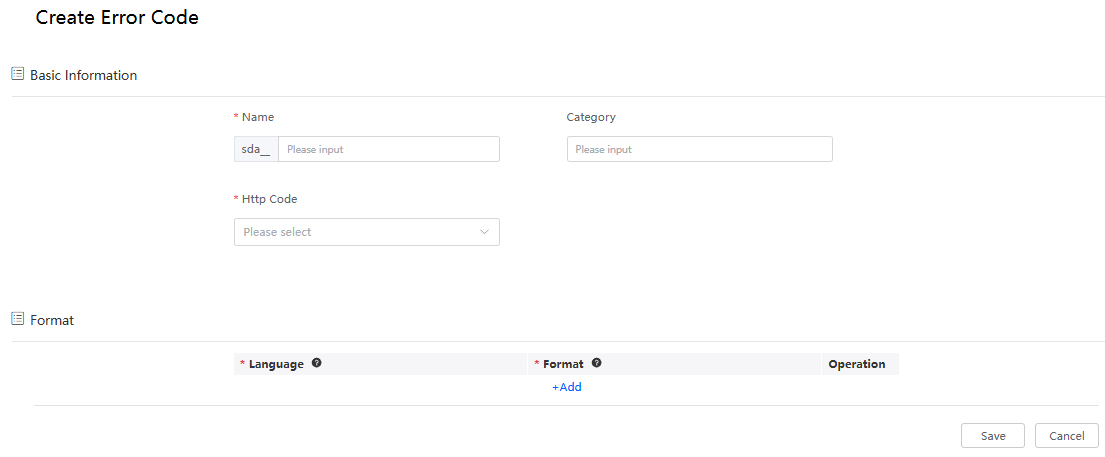
Table 1 Error code parameters Parameter
Description
Name
Name of an error code. The naming rules are as follows: Ensure that the combination of Name and Language is unique. The system will display this error code according to the two parameters.
- The value cannot exceed 64 characters, including the prefix namespace.
To prevent duplicate data names among different tenants in the platform, each tenant must define a unique namespace when first creating an application. A tenant can create only one namespace. After being created, the namespace cannot be modified.
- Start with a letter and can contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
Category
Category of the error code.
HTTP Status Code
HTTP status code.
Language
Select a language from the drop-down list.
- Click the add button to add more language versions for the error code.
- To add more supported languages, click
 next to Language. Click Translation Settings in the displayed message. On the displayed page, you can add languages supported by the system. For details, see Setting the Supported Languages.
next to Language. Click Translation Settings in the displayed message. On the displayed page, you can add languages supported by the system. For details, see Setting the Supported Languages.
Format
Error message, which can contain a maximum of 255 characters. You can add a variable in the format {Number}, For example, {0} indicates the first output variable, {1} indicates the second output variable, and {N} indicates the output variable N+1.
Example: {0} error: {1}
- The value cannot exceed 64 characters, including the prefix namespace.
Using Error Codes
During application development, you can import other error codes of the account to the application development designer. After the import, you can use these error codes in the application development designer. The following uses application A as an example to demonstrate the import process of error codes.
- Access the application designer of application A by referring to Logging In to the Application Designer.
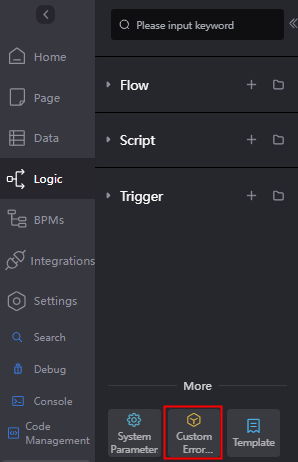
- In the navigation pane, choose Logic and click Custom Error Codes in the lower part of the page.
Figure 2 Clicking Custom Error Codes
- On the Custom tab page, click Import and select an existing error code under the account to import it.
- Use error codes in scripts.
To use a script to throw the error code you just created, add the context function setI18nError('ErrorCodeName','Variable 1','Variable 2') to the script.
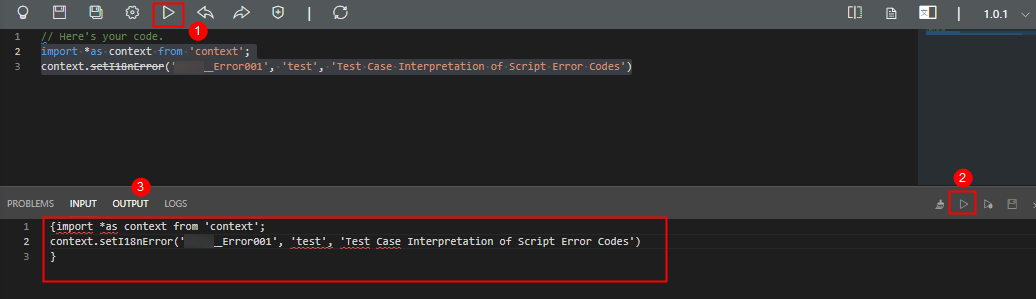
- Create an empty script by referring to Creating a Blank Script.
- Enter the following code in the script editor and click
 .
.
import * as context from'context'; context.setI18nError('Namespace__Error001','Test case','Error code example') - Run the script.
Click
 in the upper part of the editor. Click
in the upper part of the editor. Click  in the upper right corner of the test window at the bottom of the page. Click the output parameters tab. You will see the thrown error code information, as shown in Figure 3.
in the upper right corner of the test window at the bottom of the page. Click the output parameters tab. You will see the thrown error code information, as shown in Figure 3.
- Click
 in the upper part of the script editor to activate the script.
in the upper part of the script editor to activate the script.
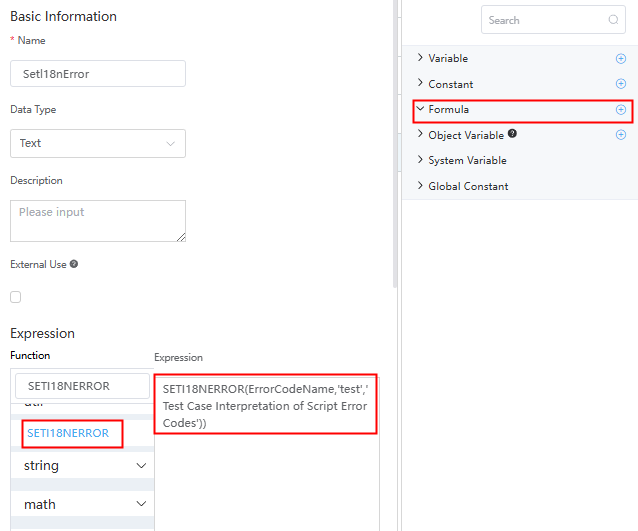
- Use an error codes when creating a flow. See Creating a Blank Flow.
In the context, create a formula variable and use the expression SETI18NERROR(ErrorCodeName','Variable 1','Variable 2') to import the error code.Figure 4 Using an error code in a flow
Currently, error codes in BPMs are thrown by the scripts and flows called by the BPM.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot