Logging In to the Application Designer
Once your instance is ready, log in to the application designer to start application development.
Logging In to the Application Designer
- Go to the Huawei Cloud Astro Zero console.
- On the homepage, click Access Homepage. The application development page is displayed.
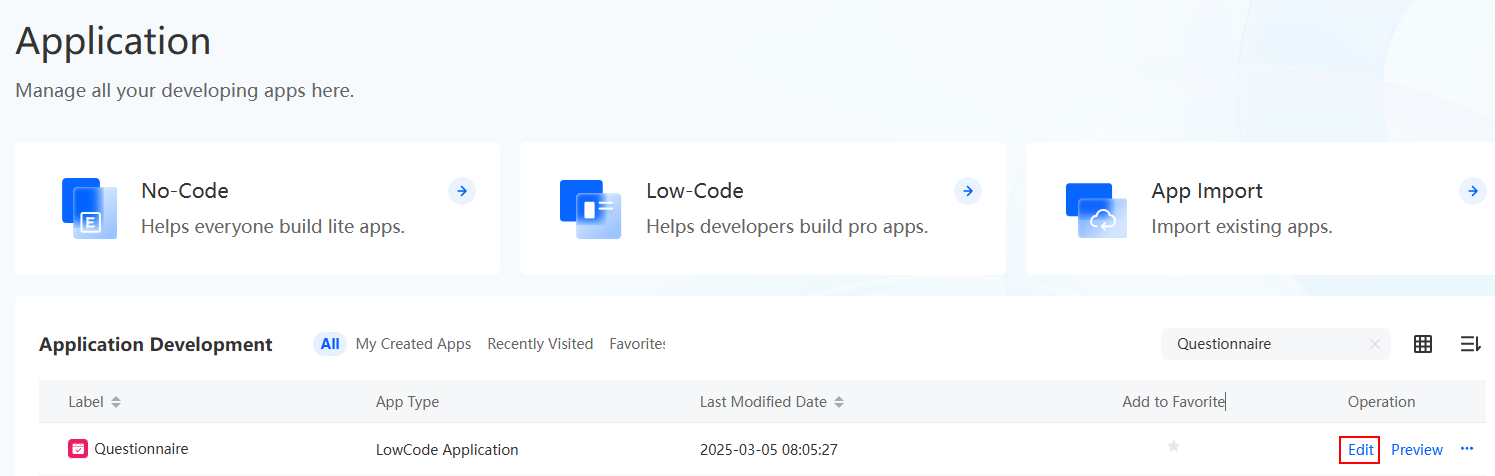
If the system shows a message indicating that you do not have the developer permission, contact the administrator to add it, see How Do I Grant Developer Permissions to a Subuser After Authorization Fails?Figure 1 Application development page
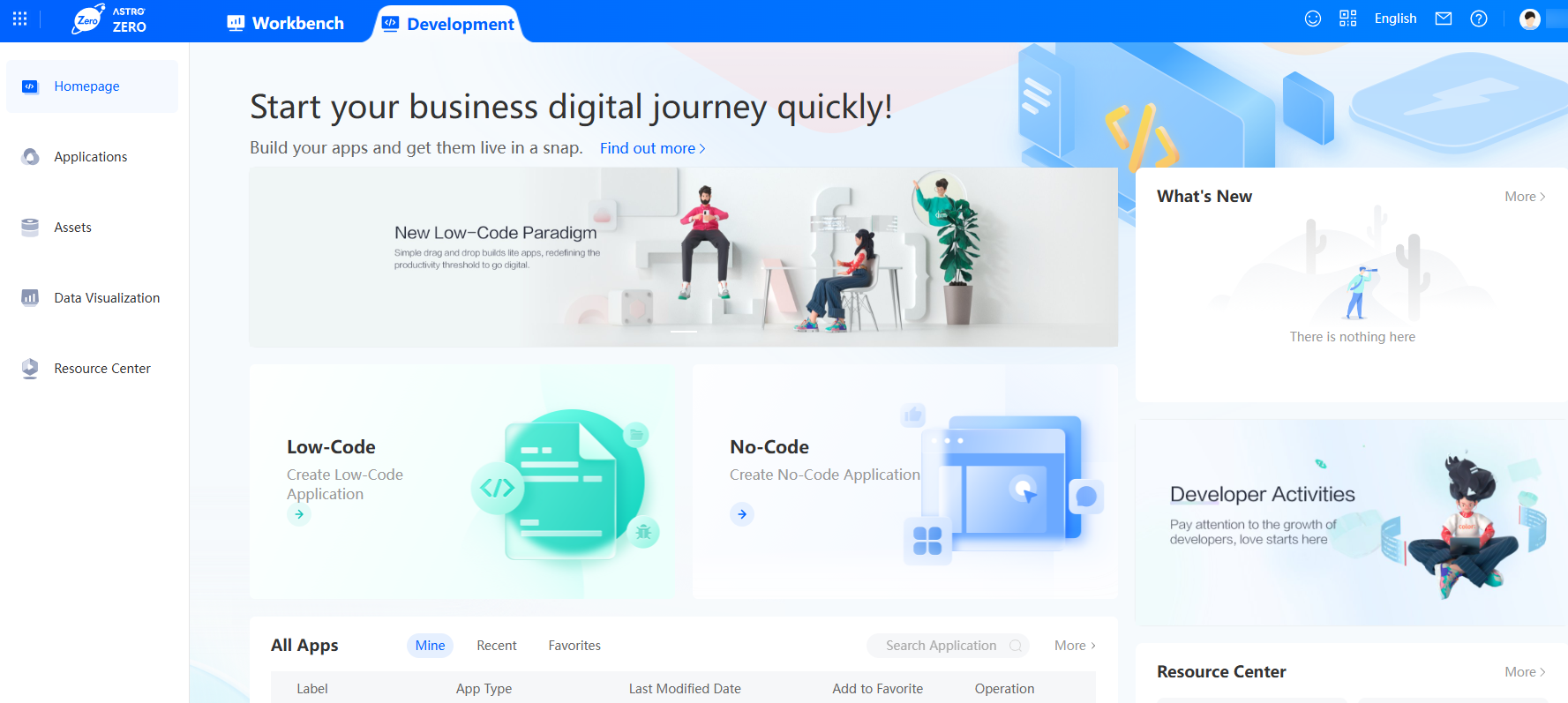
Table 1 Application development page Function
Description
 Homepage
HomepageOn this page, you can quickly build multiple types of applications.
- All Apps displays the applications that are recently created, accessed, and added to favorites by the current user.
- What's New displays notices and upgrade information.
 Applications
ApplicationsAllows you to create no-code and low-code applications and manage all created applications.
 Assets
AssetsAllows you to manage all assets, including reusable BOs and native services developed in traditional languages.
 Visualized Data
Visualized DataAllows you to access the Huawei Cloud Astro Canvas console. Huawei Cloud Astro Canvas is a visual page creation service provided by Huawei Cloud Astro. It offers abundant widgets, flexible data access, multiple construction functions, and multi-screen adaptation. Developers can quickly create and publish professional large screens. For details, see What Is Huawei Cloud Astro Canvas.
 Evaluation
EvaluationClick this icon to rate your satisfaction with the service.
 Chinese
ChineseClick to switch the system language.
 Message Center
Message CenterAccess the Huawei Cloud message center, a platform for efficient customer communication. Users can receive and manage notifications here to prevent information loss.
 Help Center
Help CenterAccess the Huawei Cloud Astro Zero help document for systematic learning.
 Username
UsernameDisplays the current login account name. Click the account name to access menus for viewing system version information, privacy statement, and service statement.
- In the navigation pane, click Applications.
Figure 2 Application management page
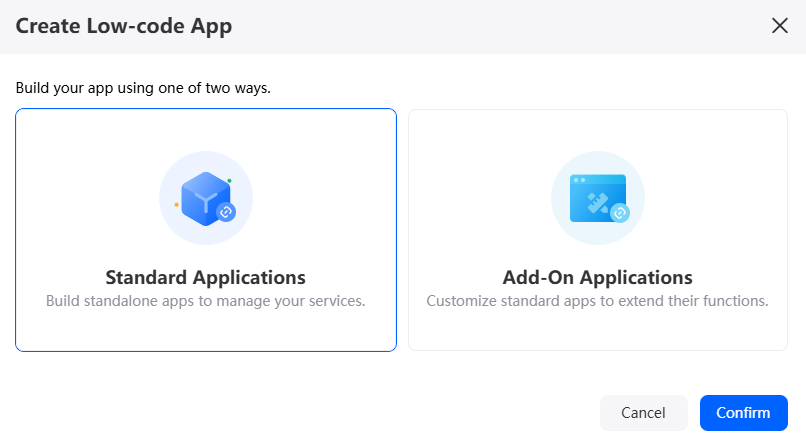
- Click Low-Code or
 .
Figure 4 Creating a low-code application
.
Figure 4 Creating a low-code application
- Select an application type and click the confirm button.
Figure 5 Selecting an application type
- Define a dedicated namespace before creating your first application.
Figure 6 Information
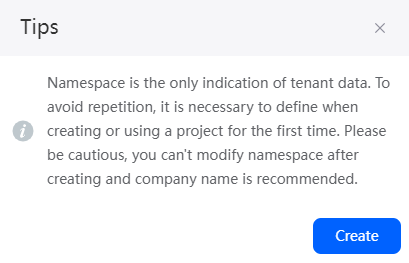
In the displayed dialog box, click the create button, enter a namespace (for example, CNAME), and click Create. The system returns to the application development page. Perform 4 and 5 again.
- Data can be packaged and shared between tenants. To avoid duplicate names of data (such as objects, applications, and flows), define a namespace before creating an application. The namespace of each tenant is unique, and only one namespace can be created by each tenant.
- Once a namespace is created, it cannot be modified or deleted. Before creating a namespace, confirm related information. You are advised to use the abbreviation of the company or team as the namespace.
Figure 7 Creating a namespace
Table 2 Parameters for creating a namespace Parameter
Description
Namespace
Name of the namespace to be created, which cannot be modified or deleted after being set. The naming requirements are as follows:
- Enter up to 15 characters.
- Start with a letter and can contain only letters, digits, and underscores (_). Avoid using two underscores (_) in a row or ending with an underscore (_).
The system automatically adds the namespace before the name of an application or application element (such as an object, script, flow, or page) that you create. For example, if your namespace is CNAME, the names of all applications and application elements (such as objects, scripts, and pages) that you create later will start with CNAME__.
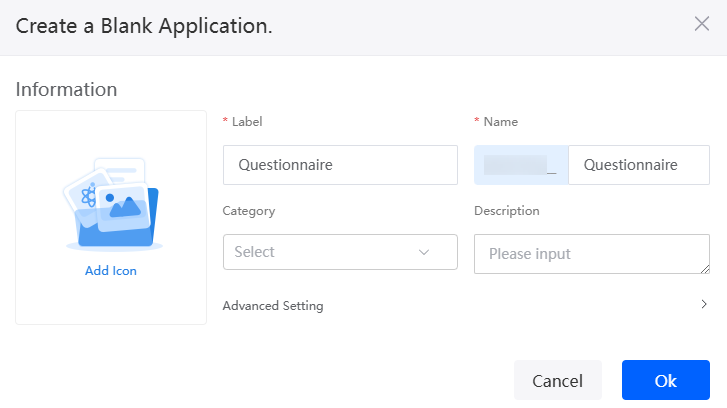
- Enter a label and name of the application, and click the create button. The application designer is displayed.
Figure 8 Creating a blank application
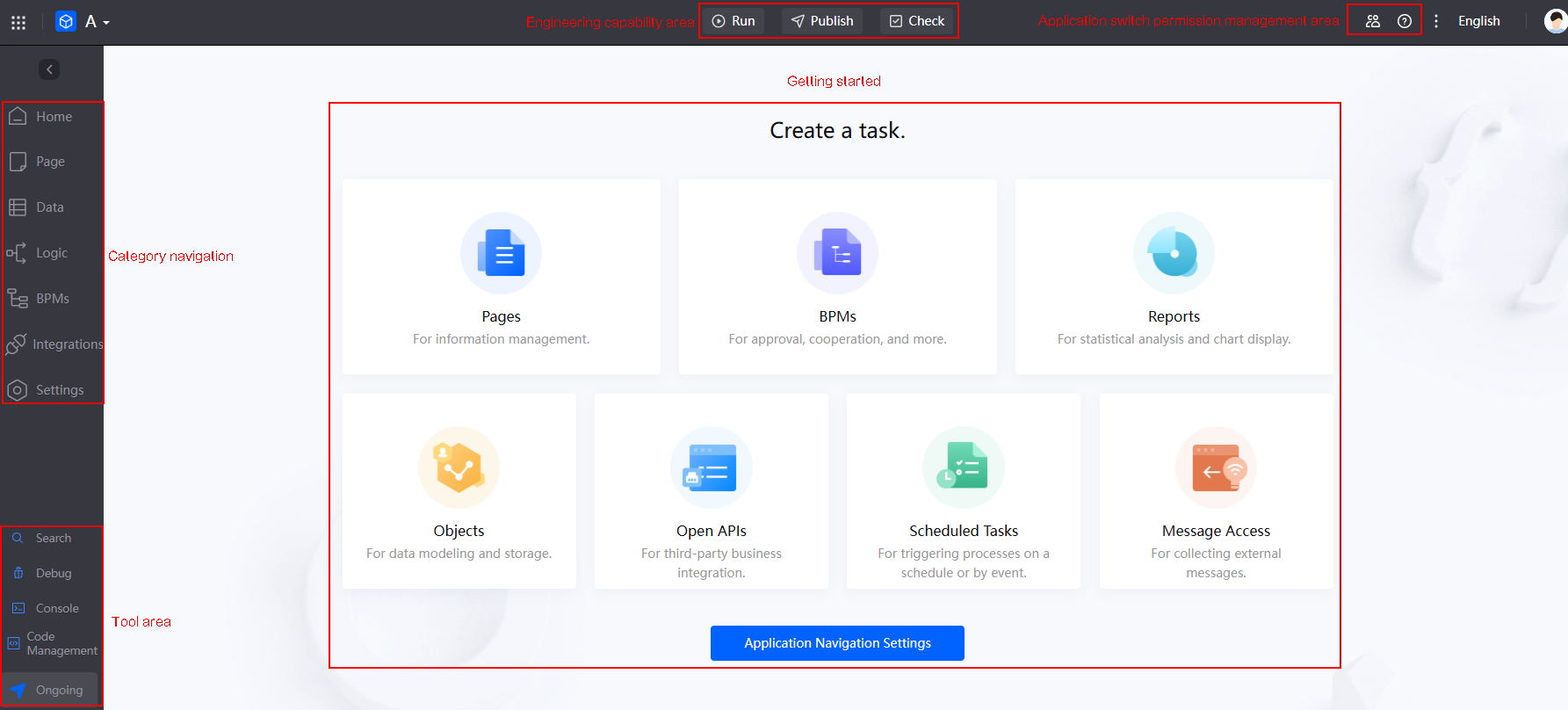
Understanding the Application Designer
|
Area |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Engineering capability area |
In this area, you can run applications, deploy applications in one click, release applications, and check application compatibility.
|
|
Application switch permission management area |
In this area, you can perform collaborative development and switch between light and dark modes.
|
|
Navigation pane |
In this area, you can choose Page, Data, Logic, BPMs, and Integrations.
|
|
Tool area |
The area provides developers with a suite of auxiliary tools, including search, debugging, command line access, and code management features.
|
|
Getting started |
Starts with real-world use cases to guide developers step by step. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot