Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
Basic Settings
- Log in to the ECS console and buy an ECS.
- Select a region.
ECSs in different regions cannot communicate with each other over an intranet. For low network latency and quick resource access, select the nearest region.
- Select a billing mode, Yearly/Monthly, Pay-per-use, or Spot pricing.
- In Yearly/Monthly billing mode, you can select a required duration. Then, the system deducts the fees incurred at one time based on the service price.
Yearly/Monthly ECSs cannot be deleted. If the ECS is no longer required, go to the Elastic Cloud Server page and choose More > Unsubscribe in the Operation column of this ECS.
- In Pay-per-use billing mode, after configuring basic settings, you do not need to select a required duration. The system deducts the expenditures incurred based on the usage duration.
- In Spot pricing billing mode, your purchased ECS is billed based on the service duration at a lower price than that of a pay-per-use ECS with the same specifications. However, a spot ECS may be reclaimed at any time based on the market price or changes in supply and demand. For more information about spot ECSs, see Spot Pricing ECSs.
- In Yearly/Monthly billing mode, you can select a required duration. Then, the system deducts the fees incurred at one time based on the service price.
- (Optional) Set Reserved Instance.
This parameter is displayed only when Billing Mode is set to Pay-per-use and you have applied for the open beta test (OBT) of reserved instances. If you want to associate reserved instances (RIs) with your pay-per-use ECSs, select Associate RI and select an RI.
RIs are in the OBT phase. You can apply for OBT.
For more information, see Reserved Instance Overview.
Figure 1 Reserved instance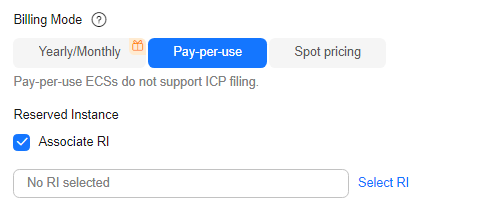
- Select an AZ.
An AZ is a physical location that uses independent power supply and networks. AZs in the same region can communicate with each other over an intranet.
- To enhance application availability, create ECSs in different AZs.
- To shorten network latency, create ECSs in the same AZ.
- During the creation process, you can select a random AZ. The system will use a hash algorithm to select an AZ as the default AZ based on your universally unique identifier (UUID).
If you batch purchase multiple ECSs and want to deploy them in different AZs, select Multi-AZ deployment.
- The available ECS types and flavors vary depending on AZs. To view all supported ECS types and flavors on the cloud service platform, set AZ to Random. Then, the system automatically allocates an AZ according to your selected ECS flavor.
For example, S3 ECSs are available only in AZ1; S2 ECSs are available in AZ2 and AZ3 and have been sold out in AZ1. If you set AZ to Random, you can view both S3 and S2 ECSs. If you create an S3 ECS, the system automatically allocates it to AZ1. If you create an S2 ECS, the system randomly allocates it to AZ2 or AZ3.
- Set Spot Type.
This parameter is optional and is displayed only when Billing Mode is set to Spot pricing. You can select Spot or Spot block. For details, see Spot Pricing ECSs.
- (Optional) Set CPU Architecture.
This configuration is displayed when you select By Type for Instance Selection.
- x86
The x86 CPU architecture uses Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC). CISC is a microprocessor that executes a large number of instructions with different lengths. Single instructions can execute multi-step operations or several low-level operations, which is time-consuming.
- Kunpeng
The Kunpeng CPU architecture uses Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC). RISC is a microprocessor that executes fewer types of computer instructions but at a higher speed than CISC. RISC simplifies the computer architecture and speeds up the instruction execution. Therefore, the Kunpeng architecture provides higher density, lower power consumption, and higher cost-effectiveness than x86.
- x86
- Set Specifications.
The cloud platform provides various ECS types for different application scenarios. You can choose from existing ECS types and flavors in the list. Alternatively, you can enter a flavor or specify vCPUs and memory size to search for the flavor suited to your needs.
- Before selecting an ECS type, learn about various types of ECSs and their precautions. For details, see ECS Types.
- When purchasing an ECS, sold-out vCPU and memory resources cannot be selected. You can select Hide sold-out specifications to hide specifications that have been sold out.
- Select an image.
- Public image
A public image is a standard, widely used image. It contains an OS and preinstalled public applications and is available to all users. You can configure the runtime environment or software in the public image as needed.
- Private image
A private image is an image available only to the user who created it. It contains an OS, preinstalled public applications, and the user's private applications. You can use a private image to create multiple ECSs in a batch, reducing the time for configuring ECSs repeatedly.
For instructions about how to create a private image, see Creating a Private Image.
You can also use an encrypted image to create ECSs. For details, see Encrypting Images.
- If you use a full-ECS image to create an ECS, the EVS disks associated with the full-ECS image do not support the function of creating disks using a data disk image.
- If a full-ECS image is in Normal state and the system displays message "Available in AZx", the full-ECS image can be used to create ECSs in this AZ only, and the encryption attributes of the system and data disks of the created ECSs are the same as those of the system and data disks specified in the full-ECS image. The SCSI, encryption, and sharing attribute settings of the system and data disks cannot be modified during ECS creation.
- If a full-ECS image is in Normal state and the system does not display message "Available in AZx", the full-ECS image can be used to create ECSs in the entire region, and the encryption attributes of the system and data disks of the created ECSs are the same as those of the system and data disks specified in the full-ECS image. The SCSI, encryption, and sharing attribute settings of data disks can be modified during ECS creation.
- An ISO image created from an ISO file cannot be used to create ECSs. You need to install an OS and drivers on the ECS and use the ECS to create a system disk image first.
- You are advised to use ECSs created from ISO images only for OS installation because such ECSs do not support some functions, such as disk attachment.
- To ensure that NIC multi-queue is enabled on an ECS created using a private image, configure NIC multi-queue when creating such a private image. NIC multi-queue routes NIC interrupt requests among multiple vCPUs for higher network packets per second (PPS) and bandwidth.
For details, see How Do I Enable NIC Multi-Queue for an Image?
- Shared image
- KooGallery image
This parameter is available only when Billing Mode is set to Yearly/Monthly or Pay-per-use. A KooGallery image is a high-quality third-party image that has an OS, application environment, and software preinstalled. You can use such an image for website setup, application development, and visualized management with just a few clicks. No additional configurations are required.
If you want to use a KooGallery image, click KooGallery image. The system then displays KooGallery images for you to choose from. For example, if the image product is name1 (test_001), name1 is the image name, and test_001 is the product name. You can search for your desired KooGallery image by image name or product name. Alternatively, you can click the image name to view more information about the image.
- Public image
- (Optional) Set Protection.
When using certain public images, you are advised to enable protection to improve the overall security for ECSs. HSS is designed to improve the overall security for ECSs. It reduces security risks with account cracking prevention, weak password detection, malicious program detection, two-factor authentication, vulnerability management, and web page anti-tampering.
Select one of the following options:- Basic edition (one-month free trial): After this function is enabled, the HSS basic edition can be used free of charge for 30 days. The HSS basic edition supports detection of OS vulnerabilities, weak passwords, and brute force cracking to improve the overall security for your ECSs.
After the free trial period expires, the HSS basic edition quotas will be automatically released, and HSS will not protect your servers.
If you want to retain or upgrade HSS security capabilities, you are advised to enable the advanced HSS edition. For details, see What Should I Do When the Free Trial of HSS Basic Edition Expires?
This option is selected by default.
- Advanced HSS edition (paid): You can choose from HSS basic, professional, enterprise, premium, and Web Temper Protection (WTP) editions and you need to pay for it.
After ECSs are purchased, you can switch between different editions on the HSS console after Advanced HSS edition (paid) is enabled. For details about the differences among different editions, see Specifications of Different Editions.
- None: HSS is disabled and servers are not protected.
After you select an HSS edition, the system automatically installs the HSS agent, enables account cracking prevention, and offers host security functions.
- Basic edition (one-month free trial): After this function is enabled, the HSS basic edition can be used free of charge for 30 days. The HSS basic edition supports detection of OS vulnerabilities, weak passwords, and brute force cracking to improve the overall security for your ECSs.
- (Optional) Set License Type.
Specify a license type for using an OS or software. This parameter is displayed only when the selected image is billed.
- Bring your own license (BYOL)
You can use your existing OS license. In such a case, you do not need to apply for a license again.
For more information about license types, see License Types.
- Bring your own license (BYOL)
- Set System Disk and Data Disk if required.
Disks are classified as EVS disks and DSS disks based on whether the storage resources used by the disks are dedicated. DSS disks allow you to use dedicated storage resources.
- If you have requested a storage pool on the DSS page, click the DSS tab and create disks in the obtained storage pool.
- If you have not requested a dedicated storage pool, click the Disks tab and create EVS disks that use public storage resources.
- When you use DSS resources to create a disk, the disk type must be the same as that of the requested storage pool. For example, both are of high I/O type.
- For more information about DSS, see Dedicated Distributed Storage Service.
- System disk
For details about the disk types supported by ECS, see Disk Types and Performance.
- If the image from which an ECS is created is not encrypted, the system disk of the ECS is not encrypted. If the image from which an ECS is created is encrypted, the system disk of the ECS is automatically encrypted. For details, see (Optional) Encryption-related parameters.
- Data disk
You can create multiple data disks for an ECS and enable required functions for each data disk. During the creation process, you can add a maximum of 23 data disks for each ECS and customize the disk size as needed.
Click Show
 and set the following functions if required:
and set the following functions if required:- SCSI: indicates that the device type of the data disk is SCSI if you select this option. For more information about SCSI disks and ECSs that can have SCSI disks attached, see Device Types.
- Share: indicates that the EVS disk is sharable if you select this option. Such an EVS disk can be attached to multiple ECSs.
- Encryption: indicates that the data disk is encrypted if you select this option. For details, see (Optional) Encryption-related parameters.
- (Optional) Encryption-related parameters
To enable encryption, click Create Xrole to grant KMS access permissions to EVS. If you have the granting permission, grant KMS access permissions to EVS. If you do not have the granting permission, contact the user who has the Security Administrator permissions to grant KMS access permissions.
- Encryption: indicates that the EVS disk has been encrypted.
- Create Xrole: assigns KMS access permissions to EVS to obtain KMS keys. After the permissions are assigned, follow-up operations do not require assigning permissions again.
- Xrole Name: set to EVSAccessKMS, which means that permissions have been assigned to EVS to obtain KMS keys for encrypting or decrypting EVS disks.
- KMS Key Name: specifies the name of the key used by the encrypted EVS disk. You can select an existing key, or click Create KMS Key and create a new one on the KMS console. The default value is evs/default.
- KMS Key ID: specifies the ID of the key used by the encrypted data disk.
If you detach the system disk that is purchased along with a yearly/monthly ECS and want to continue using it as a system disk, you can only attach it to the original ECS. If you want to use it as a data disk, you can attach it to any ECS.
If you detach the non-shared data disk purchased when you buy a yearly/monthly ECS and want to attach it again, you can only attach it to the original ECS as a data disk.
The data disk purchased when you buy a yearly/monthly ECS does not support separate renewal, unsubscription, automatic service renewal, conversion to pay-per-use payment, and release.
- Click Next: Configure Network.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





