Using KMS to Encrypt DWS Clusters
In DWS, you can enable database encryption for a cluster to protect static data. After you enable encryption, data of the cluster and its snapshots is encrypted. DWS encrypts data as it is written to the database, and automatically decrypts it when queried, returning the results to the user.
If you want to encrypt data, you can enable encryption during cluster creation or convert the data for encryption after the cluster is created. Although encryption is an optional setting of DWS, you are advised to enable this setting for clusters to protect data.
Notes and Constraints
- Only storage-compute decoupled clusters of version 9.1.0 and later support database encryption.
- DR clusters cannot be changed to encrypted clusters. If the cluster has a DR relationship, the cluster cannot be encrypted even if the cluster is in the available state. You need to cancel the DR relationship, encrypt the cluster, and then re-establish the DR relationship.
- The database encryption function cannot be disabled once it is enabled. For details, see Encrypting the Database. After a normal cluster is created, you can convert it to an encrypted cluster.
- After Encrypt DataStore is enabled, the key cannot be disabled, deleted, or frozen when being used. Otherwise, the cluster becomes abnormal and the database becomes unavailable.
- Snapshots created after the database encryption function is enabled cannot be restored using open APIs.
How KMS Encrypts DWS Databases
When you choose KMS to manage DWS keys, a three-layer key management structure is adopted, including the cluster master key (CMK), cluster encryption key (CEK), and database encryption key (DEK).
- The CMK is used to encrypt the CEK and is stored in KMS.
- The CEK is used to encrypt the DEK. The CEK plaintext is stored in the DWS cluster's memory, and the ciphertext is stored in DWS.
- The DEK is used to encrypt database data. The DEK plaintext is stored in the DWS cluster's memory, and the ciphertext is stored in DWS.
The procedure of using the keys is as follows:
- You choose a CMK.
- DWS randomly generates the CEK and DEK plaintext.
- Use the master key selected by KMS users to encrypt the CEK plaintext and import the encrypted CEK ciphertext to DWS.
- DWS uses the CEK plaintext to encrypt the DEK plaintext and saves the encrypted DEK ciphertext.
- DWS transfers the DEK plaintext to the cluster and loads it to the cluster's memory.
When the cluster is restarted, it automatically requests the DEK plaintext from DWS through an API. DWS loads the CEK and DEK ciphertext to the cluster's memory, invokes KMS to decrypt the CEK using the CMK, loads the CEK to the memory, decrypts the DEK using the CEK plaintext, loads the DEK to the memory, and returns it to the cluster.
Encryption Key Rotation Process
Encryption key rotation is used to update the ciphertext stored on DWS. On DWS, you can rotate the encrypted CEK of an encrypted cluster.
The procedure of rotating the keys is as follows:
- The DWS cluster starts key rotation.
- DWS decrypts the CEK ciphertext stored on DWS based on the CMK to obtain the CEK plaintext.
- Use the obtained CEK plaintext to decrypt the DEK ciphertext in DWS to obtain the DEK plaintext.
- DWS randomly generates new CEK plaintext.
- DWS uses the new CEK plaintext to encrypt the DEK and saves the encrypted DEK ciphertext.
- Use the CMK to encrypt the new CEK plaintext and import the encrypted CEK ciphertext to DWS.
You can plan the key rotation interval based on service requirements and data types. To improve data security, you are advised to periodically rotate the keys to prevent the keys from being cracked. Once you find that your keys may have been disclosed, rotate the keys in time.

- When DWS rotates the cluster's CEK, snapshots of the cluster do not need CEK rotation, because the CEK is not stored in snapshots. The CEK plaintext is stored in the DWS cluster memory, and the ciphertext is stored in DWS.
- The DEK is not updated during key rotation, so data encryption and decryption are not affected.
Creating a KMS Agency
If you have not created an agency with the KMS Administrator permissions, the Create Delegation dialog box is displayed when you enable database encryption for the first time. Click OK to grant DWS the permissions to access KMS. By default, only Huawei Cloud accounts or users with Security Administrator permissions can query and create agencies. IAM users under an account do not have the permission to query or create agencies by default. Contact a user with that permission and create an agency with the KMS Administrator permission for DWS.
- Click your account in the upper right corner of the page and choose Identity and Access Management.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Agency. In the upper right corner, click Create Agency.
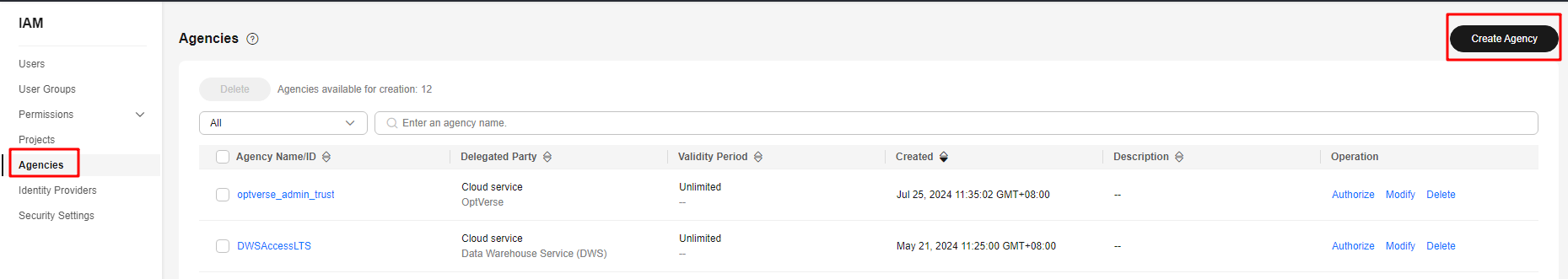
- Select Cloud Service and set Cloud Service to DWS.
- Click Finish. In the displayed dialog box, click OK to grant the KMS Administrator permission to the agency.
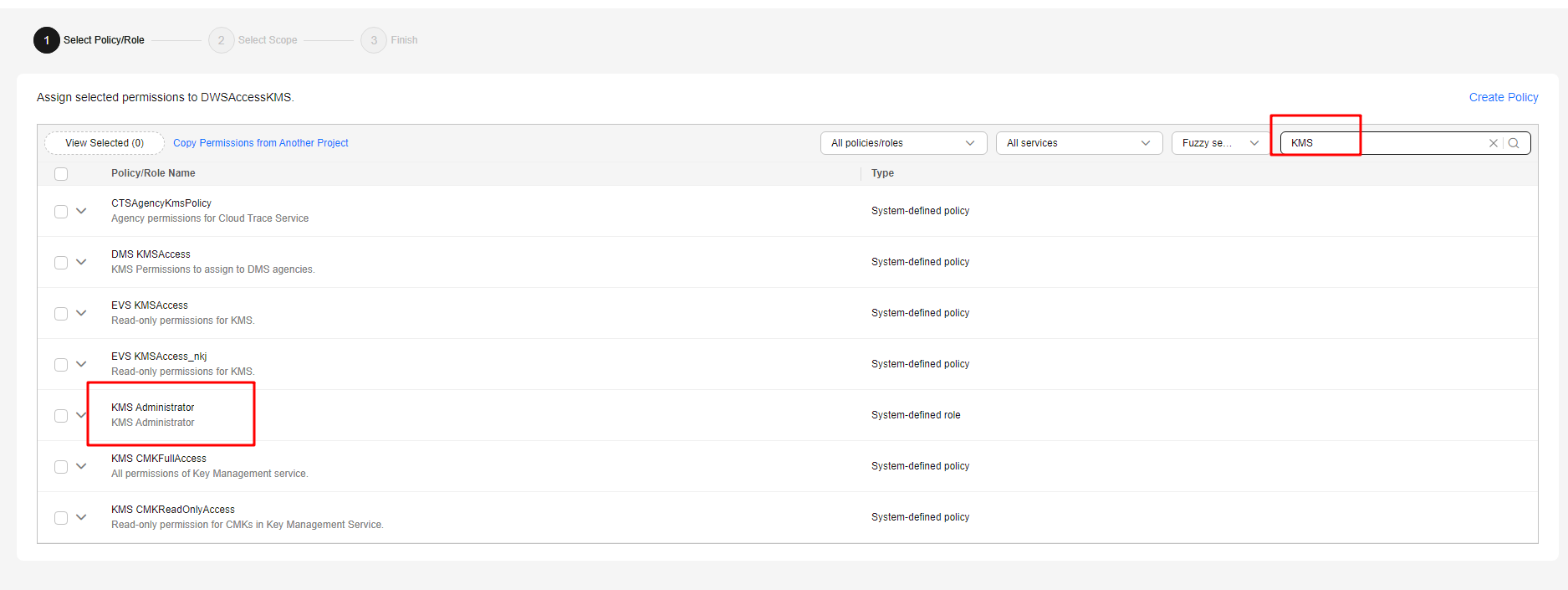
- Click Next. Select All resources or specific resources, confirm the information, and click Submit.
Converting an Unencrypted Cluster to an Encrypted Cluster
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters in the navigation pane.
- In the cluster list, locate the row that contains the target cluster and choose More > Convert to Encrypted Cluster in the Operation column. (Ensure that the cluster is in Available state.)
Converting a cluster to an encrypted cluster is an irreversible high-risk operation and will restart the cluster to ensure data security. As a result, services may be unavailable for a short period of time. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
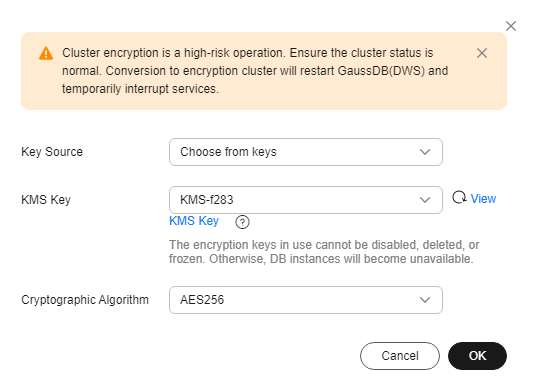
- In the displayed dialog box, select the key source, key name, and cryptographic algorithm.
- Method 1: Select a key name. You can create a resource share to share KMS resources with other members. After accepting the sharing invitation, members can select the shared KMS resource from the key source.
Figure 1 Select from existing keys
- Method 2: Enter the key ID. Enter the key ID used for authorizing the current tenant. For details, see Viewing a CMK.
When you grant permissions on the Creating a Grant page, the authorized object must be an account instead of a user. The authorized operations must at least contain Querying key details, Encrypting data, and Decrypting data.
Figure 2 Entering the key ID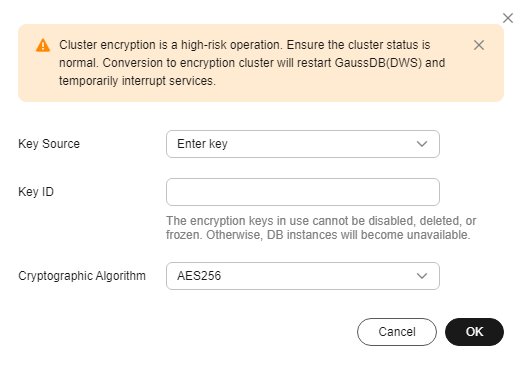
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Key Source
You can select a key name from the key list or directly enter a key name.
Cryptographic Algorithm
Cryptographic algorithms include:
- AES256 (general encryption algorithm, SM algorithms not supported)
- SM4 (compatible with international algorithms)
- Method 1: Select a key name. You can create a resource share to share KMS resources with other members. After accepting the sharing invitation, members can select the shared KMS resource from the key source.
- Click OK. After the conversion, you can click the cluster name to go to the Cluster Details page to view the cluster details. For details, see Viewing Database Encryption Information.
Rotating Encryption Keys for DWS Clusters
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters in the navigation tree on the left.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster and click the cluster name. The Cluster Information page is displayed.
- In the Data Encryption Information area, click Key Rotation.
Each key rotation will update the CEK once. During the key rotation, the cluster is still in Available status.
- In the dialog box that is displayed, click Yes.
Viewing Database Encryption Information
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters in the navigation pane.
- Click the name of a cluster. The Cluster Information page is displayed.
- In the Data Encryption Information area on the cluster information page, view the database encryption information, as shown in Table 2.
If database encryption is disabled by default during cluster creation, the encryption module is not displayed on the cluster details page.
Table 2 Data encryption information Parameter
Description
Key Name
Database encryption key of the cluster when Encrypt DataStore is enabled. You can click Modify to change the KMS master key name. You can select a key name or enter a key ID. For details, see 4.
Last Key Rotation Time
Time when the last encryption key was rotated when Encrypt DataStore is enabled.
Cryptographic Algorithm
Cryptographic algorithm of the cluster when Encrypt DataStore is enabled.
Cryptographic algorithms include:
- AES256 (general encryption algorithm, SM algorithms not supported)
- SM4 (compatible with international algorithms)
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





