HTTP(S) Access
Introduction
IoTDA supports HTTPS, a secure communication protocol derived from HTTP and secured with SSL encryption. HTTPS is commonly employed for data collection and analysis due to HTTP's efficiency in transmitting and processing structured data. Additionally, it is utilized in scenarios where devices require non-persistent connections and unidirectional data upload.
In HTTPS-based authentication, a device utilizes the HTTPS-based device authentication API to securely transmit the device ID and secret. The secret is encrypted using an algorithm. After the authentication is successful, the connection between the device and the platform is established, and the platform returns an access token.
Constraints
- An access token is required when HTTPS APIs for property reporting and message reporting are called.
- If an access token expires, you need to authenticate the device again to obtain an access token.
- If you obtain a new access token before the old one expires, the old access token will be valid for 30 seconds before expiration.
|
Description |
Constraint |
|---|---|
|
Supported HTTP version |
HTTP 1.0 HTTP 1.1 |
|
Supported HTTPS |
The platform supports only the HTTPS protocol. For details about how to download a certificate, see Certificates. |
|
Supported TLS version |
TLS 1.2 |
|
Body length |
1 MB |
|
API specifications |
|
|
Number of child devices of which properties can be reported by a gateway at a time |
50 |
|
Data delivery |
Not supported |
Endpoints
For details about the platform endpoint, see Platform Connection Information.
Use the endpoint of IoTDA and the HTTPS port number 443.
Process

- An application calls the API for registering a device. Alternatively, a user uses the IoTDA console to register a device.
- The platform allocates a globally unique device ID and secret to the device.
The secret can be defined during device registration. If no secret is defined, the platform allocates one.
- When a device attempts to connect to the platform, the device calls the HTTPS device authentication API to send an access authentication request to the platform. The request carries the device ID and the secret generated using the HMACSHA256 algorithm. The secret is the value obtained after the password allocated by the platform is signed using the timestamp as the key. For details, see Huawei Cloud IoTDA MQTT ClientId Generator.
- If the authentication is successful, the platform returns a success message, and the device is connected to the platform.
Procedure
When a device connects to the platform through HTTPS, HTTPS APIs are used for their communication. These APIs can be used for device authentication as well as message and property reporting.
|
Message Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Devices obtain access tokens. |
|
|
Devices report property data in the format defined in the product model. |
|
|
Devices report custom data to IoTDA, which then forwards reported messages to an application or other Huawei Cloud services for storage and processing. |
|
|
A gateway reports property data of multiple child devices to the platform. |
- Create a product on the IoTDA console or by calling the API for creating a product.
- Register a device on the IoTDA console or by calling the API for creating a device.
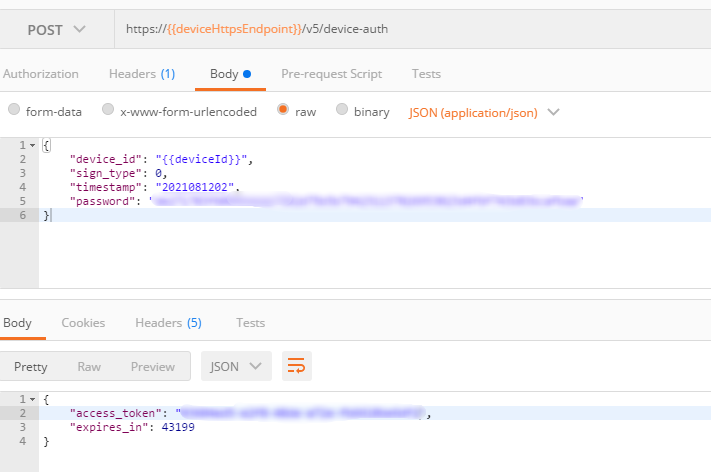
- After the device is registered, obtain the access token of the device through the API for device authentication.
Figure 2 Obtaining the access token
- Use the access token in the message header to report device messages or properties. The following figures use property reporting as an example.
Figure 3 Reporting properties
 Figure 4 Reporting properties
Figure 4 Reporting properties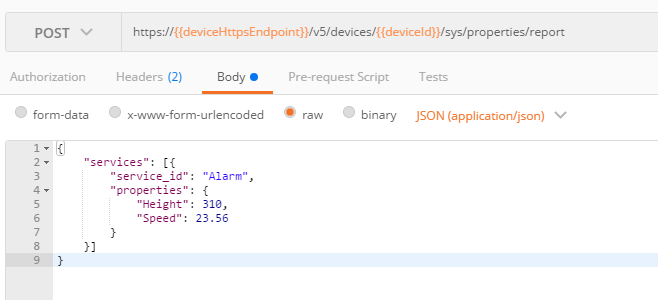
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





