Function Overview
- ALL
- Data Warehouse Service
- Purchasing DWS
- Tools
- Connecting to Clusters
- Database parameter management
- Snapshots
- Capacity Expansion and Upgrade
- Scaling In a Cluster
- Data Import
- Data Export
- Canceling Read-only Status
- Development and Design Proposal
- SQL Syntax
- Java UDF
- TopSQL
- SQL Performance optimization
- Resource Management
- Fine-Grained Policies
- Database Permission
- Data Redaction
- Row-Level Access Control
- PostGIS
- Differences with PostgreSQL
- Logical Clusters
- CNs
- Databases Monitoring
- Alarm Management
- Associating and Disassociating ELB
- Nodes
- Cluster Redistribution
- Performing a Primary/Standby Switchback
- Cluster Log Management
- Intelligent O&M
- SQL supports Roaring Bitmaps
- List partitioning
- JSON foreign tables are supported
- Fine-grained permission management
- Changing All Specifications
- O&M Account
- Database User Management
- Data Migration
-
Data Warehouse Service
-
DWS is an online data processing database that uses the public cloud infrastructure to provide scalable, fully-managed, and out-of-the-box analytic database service that frees you from database management and monitoring. It is a native cloud service based on the Huawei converged data warehouse GaussDB, and is fully compatible with the standard ANSI SQL 99 and SQL 2003, as well as the PostgreSQL and Oracle ecosystems. DWS provides competitive solutions for PB-level big data analysis in various industries.
Typical Scenarios: The data warehouse is an important data analysis system for enterprises. As the service volume grows, performance of self-built data warehouses cannot meet the actual service requirements due to their poor scalability and high costs. As an enterprise-class data warehouse on the cloud, DWS features high performance, low cost, and easy scalability, satisfying requirements in the big data era.

Release area: All
-
-
Purchasing DWS
-
DWS can be purchased in pay-per-use or yearly/monthly mode.
• Pay per use (hourly): This mode is applicable to customers who need to perform preliminary operation tests and Proofs-of-Concept verifications, and short-term users.
• Yearly/Monthly: Recommended for long-term users. You can purchase cloud services in yearly/monthly mode and enjoy a larger discount than in the pay-per-use mode. A purchased cloud service is bound to a cloud service instance that is enabled or used. When the validity period expires, the cloud service enters the retention period (grace period). After the retention period expires, the cloud service is automatically released. You can renew the service to continue using it.
• Discount package: You can make a one-off payment according to the purchased service duration. The service duration ranges from one month to three years.

Release area: All
-
-
Tools
-
DWS supports a series of ecosystem tools throughout the lifecycle of data warehouses, including SQL tools, import and export, and syntax migration tools.
-
-
Connecting to Clusters
-
After purchasing a cluster, you can use SQL tools or third-party drivers such as JDBC/ODBC to connect to the cluster and access the cluster database.
To connect to the cluster, perform the following steps:
1. Obtain the cluster address.
2. (Optional) Use SSL encryption.
3. Select either of the following methods to connect to the cluster:
• SQL client tool: gsql, and Data Studio are supported.
• Use JDBC/ODBC connection.
• Use DAS Connection.
• Use the Python Library psycopg2/PyGreSQL Connection.

Release area: All
-
-
Database parameter management
-
After a cluster is created, you can modify the cluster's database parameters as required. On the DWS management console.

Release area: All
-
-
Snapshots
-
A snapshot is a complete backup that records point-in-time configuration data and service data of a data warehouse cluster. You can use it to restore the cluster data backed up during snapshot creation. Snapshots are stored on OBS.
-
-
Capacity Expansion and Upgrade
• Capacity expansion: If your data warehouse cluster has been used for a period of time, the CPU, memory, and disk I/O cannot meet the database performance requirements as services and data volume increase. In this case, you can add cluster nodes to implement elastic resource scaling. DWS does not support disk capacity expansion.
• Upgrade: You do not need to worry about patching or upgrading the data warehouse cluster because DWS will automatically process the version upgrade.
-

Release area: All
-
-
Scaling In a Cluster
supported by 8.1.1.300 and later versions
-
You can scale in your clusters on the console to release unnecessary computing and storage resources provided by DWS.

Release area: All
-
-
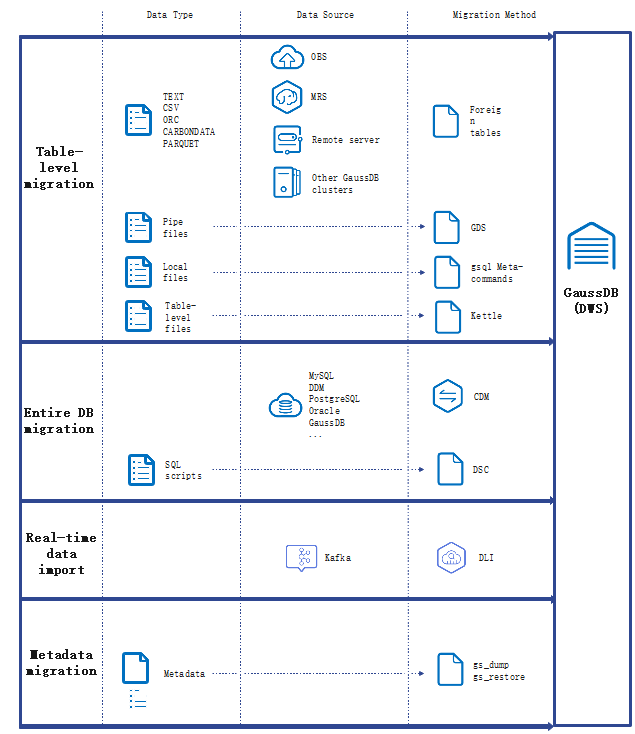
Data Import
-
DWS provides flexible data import modes. You can import data from multiple data sources to DWS.
· OBS import: You can concurrently import data in TXT, CSV, ORC, and CARBONDATA formats stored on OBS to DWS. You can query data after the import and remotely read data from OBS. Recommended import mode for DWS.
· GDS import: Use the GDS tool provided by DWS to import data from a remote server to DWS in parallel mode. This method is highly efficient and applicable to importing a large number of data into the database.
· MRS import: Connect a DWS cluster to an MRS cluster and read data from the HDFS of MRS to DWS.
· CDM import: CDM allows you to migrate data in batches between homogeneous and heterogeneous data sources, helping you migrate data from multiple types of data sources to DWS. When migrating data to DWS, CDM uses the copy mode and GDS parallel import mode.
· Importing gs_restore: In database migration scenarios, you can use gs_restore to import the file format exported using gs_dump to the DWS cluster to import metadata, such as table definitions and database object definitions. Imported data includes the following:
- All database object definitions.
- Definition of a single database object.
- Defines a single schema.
- Defines a single table.
· Other methods: Import data using the INSERT statement, COPY FROM STDIN, gsql meta-command, and third-party ETL tools.
-
-
Data Export
-
DWS supports the following data export modes:
• Export using an OBS foreign table: Specify the data file to be exported based on the export mode and data format set in the OBS foreign table. This method is recommended for DWS.
• GDS export: Use GDS to export data from the database to a common file system. This mode applies to scenarios where a large amount of data is exported concurrently.
• Run the gs_dump and gs_dumpall commands to export data: You can export a single database and its objects, or all databases and public global objects in a cluster.
-
-
Canceling Read-only Status
Only 1.7.2 and later versions support this function.
-
If a cluster enters the read-only status, you cannot perform any database operations on it. You can cancel the read-only status for the cluster on the management console.

Release area: All
-
-
Development and Design Proposal
Only 1.7.2 and later versions support this function.
-
This chapter describes the design specifications for database modeling and application development. Modeling compliant with these specifications fits the distributed processing architecture of DWS and provides efficient SQL code.

Release area: All
-
-
SQL Syntax
-
DWS supports standard SQL syntax and DDL, DML, and DCL syntax.
• Data definition language (DDL) is used to define or modify an object in a database, such as a table, index, or view.
• Data Manipulation Language (DML) is used to perform operations on data in database tables, such as inserting, updating, querying, or deleting data.
• Data control language (DCL) is used to set or modify database users or role rights.
-
-
Java UDF
-
UDF is short for User Defined Function. DWS provides various built-in functions to meet your computing requirements. You can also use Java to create custom functions to meet different computing requirements.
With the DWS PL/Java functions, you can choose your favorite Java IDE to write Java methods and install the JAR files containing these methods into the DWS database before invoking them. DWS PL/Java is developed based on open-source Greenplum PL/Java 1.4.0. PL/Java uses JDK 1.8.0_201.

Release area: All
-
-
TopSQL
-
DWS supports top SQL query, including real-time top SQL query and historical top SQL query. The views record the resource usage (including memory, disk, CPU time, and I/O) and performance alarms during job execution. Based on the recorded information, you can evaluate whether the query has performance bottlenecks and whether it affects the cluster performance.
• Real-Time TopSQL: When a database user performs a query job, the system provides real-time resource monitoring views at the query- and operator-levels to query SQL queries in the Active state for the real-time TopSQLs whose execution cost is greater than resource_track_cost.
• Historical TopSQL: After the execution of a job is complete, you can retrieve its historical information, including the resource usage (such as the usage of memory, disk, CPU time, and I/O), running status (such as error, terminated, and exception), and performance alarms. You can use historical resource monitoring views at the query- and operator-levels to query for historical TopSQLs whose execution cost is greater than resource_track_cost.

Release area: All
-
-
SQL Performance optimization
-
The aim of SQL tuning is to maximize the utilization of resources, including CPU, memory, disk I/O, and network I/O. To maximize resource utilization is to run SQL statements as efficiently as possible to achieve the highest performance at a lower cost. For example, when performing a typical point query, you can use the seqscan and filter (that is, read every tuple and query conditions for match). You can also use an index scan, which can be implemented at a lower cost but achieve the same effect.

Release area: All
-
-
Resource Management
-
When multiple database users query jobs at the same time, some complex queries may occupy cluster resources for a long time, affecting the performance of other queries. For example, a group of database users continuously submit complex and time-consuming queries, while another group of users frequently submit short queries. In this case, short queries may have to wait in the queue for the time-consuming queries to complete.
To improve efficiency, you can use the DWS workload management function to handle such problems. For example, classify database users who frequently submit complex query jobs into one type, create a workload queue for these users, allocate more resources to the queue, and then add these users to the queue. In this case, the complex jobs submitted by these users can use only the resources of the created queue. Also, create a queue that occupies fewer resources and allocate it to users who submit short queries. In this way, the two types of jobs can be executed at the same time without affecting each other.
-
-
Fine-Grained Policies
-
In actual services, you may need to grant different operation permissions on resources to users of different roles. The IAM service provides fine-grained access control. On IAM, the administrator (that is, a user in the admin user group) can create a custom policy containing various required permissions. After a policy is granted to a user group, users in the group can obtain all permissions defined by the policy. In this way, IAM implements fine-grained permission management.

Release area: All
-
-
Database Permission
-
Database permission division prevents objects in the database from being added, deleted, or modified. DWS supports Separation of Duty to prevent multiple users from operating a group of database objects, ensuring database security and data validity.
You can further classify permissions by managing roles, schemas, and private users.

Release area: All
-
-
Data Redaction
-
The huge value of data in the big data era also brings difficulties in protecting privacy information. Data Redaction is used to achieve efficient sharing of big data and protect sensitive information.
Customers can identify sensitive data based on their service scenarios and create an anonymization policy based on the table column unit. After an anonymization policy is configured, only administrators and table object owners can access raw data.
Application scenario: Industries involving sensitive information, such as finance, government, and healthcare, have natural requirements for data anonymization. Data is required in application development, testing, and training activities. Therefore, the anonymization function can be used to prevent sensitive information leakage.

Release area: All
-
-
Row-Level Access Control
-
The row-level access control feature enables database access control to be accurate to each row of data tables. In this way, the same SQL query may return different results for different users. That is, in the same table, you can view only the data related to your own table, but cannot view the data of other users.

Release area: All
-
-
PostGIS
-
DWS provides PostGIS Extension (PostGIS-2.4.2). PostGIS Extension is a spatial database extender for PostgreSQL. It provides the following spatial information services: spatial objects, spatial indexes, spatial functions, and spatial operators. PostGIS Extension complies with the OpenGIS specifications.
In DWS, PostGIS Extension depends on the listed third-party open-source software.
• Geos 3.6.2
• Proj 4.9.2
• Json 0.12.1
• Libxml2 2.7.1
• Gdal 1.11.0

Release area: All
-
-
Differences with PostgreSQL
-
DWS is compatible with the PostgreSQL ecosystem, but its syntax is different from that of PostgreSQL.

Release area: All
-
-
Logical Clusters
supported by 8.1.0.100 and later versions
-
A physical cluster can be divided into logical clusters that use the node-group mechanism. Tables in a database can be allocated to different physical nodes by logical cluster. A logical cluster can contain tables from multiple databases.

Release area: All
-
-
CNs
supported by 8.1.1.100 and later versions
-
After a cluster is created, the number of required CNs varies with service requirements. The CN management function enables you to adjust the number of CNs in the cluster.

Release area: All
-
-
Databases Monitoring
supported by 8.1.1.200 and later versions
-
DMS is provided by DWS to ensure the fast and stable running of databases. It collects, monitors, and analyzes the disk, network, and OS metric data used by the service database, as well as key performance metric data of cluster running. It also diagnoses database hosts, instances, and service SQL statements based on the collected metrics to expose key faults and performance problems in a database in a timely manner, and guides customers to optimize and resolve the problems.
-
-
Alarm Management
supported by 8.1.1.200 and later versions
-
Alarm management includes viewing and configuring alarm rules and subscribing to alarm information. Alarm rules display alarm statistics and details of the past week for users to view tenant alarms. In addition to providing a set of default DWS alarm rules, this feature allows you to modify alarm thresholds based on your own services. DWS alarm notifications are sent using the SMN service.

Release area: All
-
-
Associating and Disassociating ELB
supported by 8.1.1.200 and later versions
-
If the internal IP address or EIP of a CN is used to connect to a cluster, the failure of this CN will lead to cluster connection failure. If a private domain name is used for connection, connection failures can be avoided by polling. However, private domain names cannot be used for public network access, and requests cannot be forwarded in the case of a CN failure. Therefore, ELB is used to avoid single CN failures.

Release area: All
-
-
Nodes
supported by 8.1.1.200 and later versions
-
On the Nodes tab page, you can view the node list of the current cluster, add new nodes to or remove nodes from it, and view the node usage, status, and flavors.

Release area: All
-
-
Cluster Redistribution
supported by 8.1.1.200 and later versions
-
Data redistribution, where data in existing nodes is evenly allocated to the new nodes after you scale out a cluster, is a time-consuming yet crucial task that accelerates service response.
By default, redistribution is automatically started after cluster scale-out. For enhanced reliability, disable the automatic redistribution function and manually start a redistribution task after the scale-out is successful. In this way, both scale-out and redistribution can be retried upon failures.

Release area: All
-
-
Performing a Primary/Standby Switchback
supported by 8.1.1.202 and later versions
-
In the Unbalanced state, the number of primary instances on some nodes increases. As a result, the load pressure is high. In this case, the cluster is normal, but the overall performance is not as good as that in a balanced state. Restore the primary-standby relationship to recover the cluster to the available state.

Release area: All
-
-
Cluster Log Management
supported by 8.1.1.300 and later versions
-
Cluster logs are collected and sent to Log Tank Service (LTS). You can check or dump the collected cluster logs on LTS.

Release area: All
-
-
Intelligent O&M
supported by 8.1.3 and later versions
-
Intelligent O&M helps DWS users with O&M tasks. With this feature, you can specify the proper time window and number of tasks to execute based on the cluster workload. Besides, Intelligent O&M can adjust task execution policies according to service changes in a timely manner to reduce the impact on services. Periodic tasks and one-off tasks are supported, and you can configure the time window as required.

Release area: All
-
-
SQL supports Roaring Bitmaps
supported by 8.1.3 and later versions
-
Supports bitmap roaring bitmap data types and corresponding common functions. It is widely used in the Internet, retail, education, and gaming industries to extract user features and user profiles. For example:
1. In the e-commerce industry, before launching a marketing campaign, a merchant needs to select a group of target users with specific characteristics to push advertisements based on the purpose of the campaign.
2. In the education industry, it is necessary to push specific exercises according to students' different characteristics to help students find out and fill in gaps.
3. In search, video, and portal websites, different content can be pushed based on the hotspots that users are concerned about.

Release area: All
-
-
List partitioning
supported by 8.1.3 and later versions
-
On the basis of the existing range partitioning, the list partitioning mode is supported: PARTITION BY LIST (partition_key, [...]), which meets user habits.
List partition policy partition key supported data types: TINYINT,SMALLINT, INTEGER, BIGINT, NUMERIC/DECIMAL, TEXT, NVARCHAR2, VARCHAR(n), CHAR, BPCHAR, TIME, TIME WITH TIMEZONE, TIMES TAMP, TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, DATE, INTERVAL,SmallDATETIME.

Release area: All
-
-
JSON foreign tables are supported
supported by 8.1.3 and later versions
-
The HDFS/OBS foreign table READ ONLY foreign table supports JSON format.

Release area: All
-
-
Fine-grained permission management
supported by 8.1.3 and later versions
-
The system table can be assigned to common users, the vacuum can be assigned independently, and the function of pre-defined roles can be extended:
-
1. Added the ALTER, DROP and VACUUM permissions at table level.
-
2. Added the ALTER and DROP permissions at schema level.
-
3. Add the preset roles role_signal_backend and role_read_all_stats.

Release area: All
-
-
-
Changing All Specifications
supported by 8.1.3.200 and later versions
-
If you want to change your cluster topology or capacity but the Change node flavor option is grayed out, you can select Change all specifications to increase or decrease the nodes and their capacities on the DWS console. First, you need to configure the new specifications you want, and a cluster with these specifications will be created. Then, data will be migrated from the old cluster to the new one. In case you need to restore data, a full snapshot will be taken for the old cluster, and the old cluster will be retained for a period of time.

Release area: All
-
-
O&M Account
supported by 8.1.3.110 and later versions
-
If you need technical support when using a cluster, you can authorize them to use an O&M account on the DWS console to access the cluster for fault locating.

Release area: All
-
-
Database User Management
supported by 8.1.3.322 and later versions
-
DWS allows you to manage database users on the console. You can create, delete, and update database users and manage their permissions on the console.

Release area: All
-
-
Data Migration
supported by 8.2.0 and later versions
-
DWS helps you migrate data from multiple sources and integrate diverse data sources, quick and easy. Currently, data can be migrated from Kafka and MRS to DWS.

Release area: All
-
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.







