Logging In to an RDS for PostgreSQL Instance and Creating a Database Through DAS (Recommended)
Scenarios
Data Admin Service (DAS) enables you to connect to and manage DB instances with ease on a web-based console. The permissions required for connecting to DB instances through DAS are enabled by default. Using DAS to connect to your DB instance is recommended, which is more secure and convenient.
Step 1: Log In to an RDS for PostgreSQL Instance
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
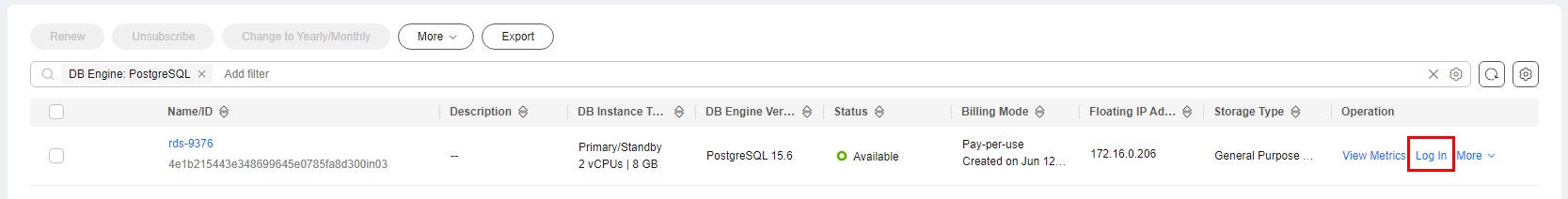
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service. - On the Instances page, locate the DB instance and click Log In in the Operation column.
Figure 1 Logging in to an instance
Alternatively, click the DB instance name on the Instances page. On the displayed Overview page, click Log In in the upper right corner.
Figure 2 Logging in to an instance
- On the displayed login page, enter the username and password and click Log In.
- Login Username: Enter root.
- Database Name: Enter postgres.
- Password: Enter the root password you specified during instance creation. If you forget the password, you can reset it. For details, see Resetting the Administrator Password to Restore root Access.
Figure 3 Logging in to an instance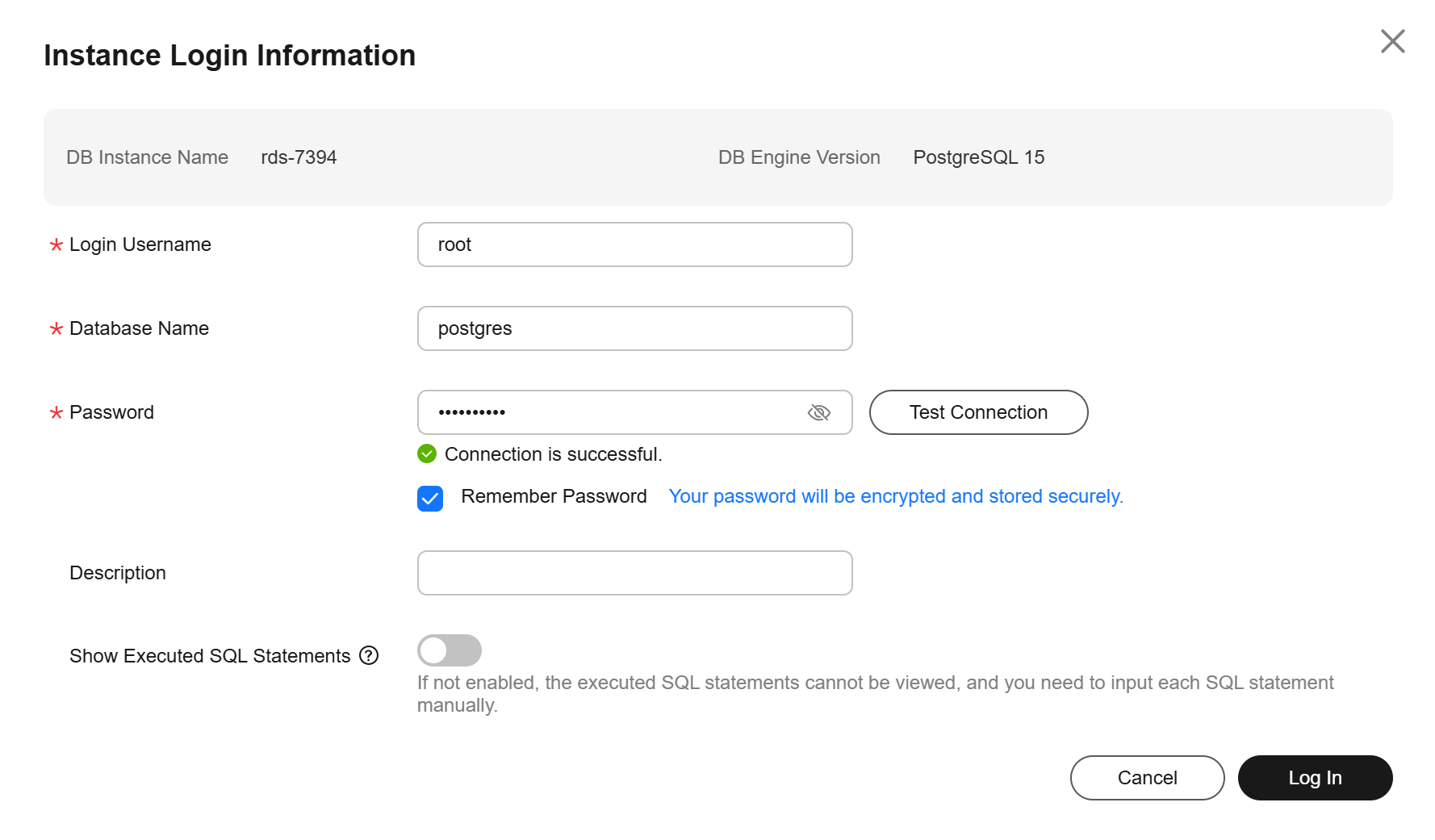
Step 2: Create a Database
- On the DAS console, choose SQL Operations > SQL Query.
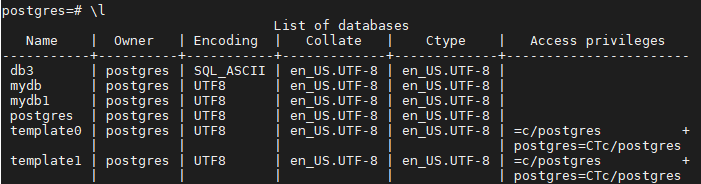
- In the SQL window, run the following command to create a database named db1:
create database db1;
You can also specify a template database and set properties such as character sets, LC_COLLATE (character collation), and LC_CTYPE (character classification) for each database. For details, see Syntax.
CREATE DATABASE name
[ [ WITH ] [ OWNER [=] user_name ]
[ TEMPLATE [=] template ]
[ ENCODING [=] encoding ]
[ LC_COLLATE [=] lc_collate ]
[ LC_CTYPE [=] lc_ctype ]
[ TABLESPACE [=] tablespace_name ]
[ ALLOW_CONNECTIONS [=] allowconn ]
[ CONNECTION LIMIT [=] connlimit ]
[ IS_TEMPLATE [=] istemplate ] ]
- TEMPLATE
RDS for PostgreSQL has two database templates: template0 and template1. The default template is template1. When you use template1 to create a database, do not specify a new character set for the database. Otherwise, an error will be reported. You can also specify a custom template to create a database.
- ENCODING
When creating a database, you can specify a character set using WITH ENCODING. For details about the supported character sets, see the PostgreSQL community documentation.
- LC_COLLATE
String sort order. The default value is en_US.utf8.
Comparison of the same string in different collations may have different results.
For example, after you execute SELECT 'a'>'A';, the result is false if this parameter is set to en_US.utf8 and the result is true if this parameter is set to C. If you need to migrate a database from Oracle to RDS for PostgreSQL, set LC_COLLATE to C. You can query the supported collations from the pg_collation table.
- LC_CTYPE
It is used to classify if a character is a digit, uppercase letter, lowercase letter, and so on. You can query the supported character classifications from the pg_collation table.
- For details about other parameters, see the PostgreSQL community documentation.
- Using TEMPLATE to specify a database template
- When template1 is used, the character set or collation defined in this template cannot be changed. For details about collations, see Configuring the collation of a database in a locale.
CREATE DATABASE my_db WITH TEMPLATE template1 ;
- When template0 is used, you can change the character set and collation. For details, see Configuring the collation of a database in a locale.
CREATE DATABASE my_db WITH ENCODING = 'UTF8' LC_COLLATE ='zh_CN.utf8' LC_CTYPE ='zh_CN.utf8' TEMPLATE = template0 ;
- If no template is specified during database creation, template1 is used by default. You can also specify a custom template to create a database.
CREATE DATABASE my_db WITH TEMPLATE = mytemplate;
- When template1 is used, the character set or collation defined in this template cannot be changed. For details about collations, see Configuring the collation of a database in a locale.
- Using WITH ENCODING to specify a character set
CREATE DATABASE my_db WITH ENCODING 'UTF8';
- LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE
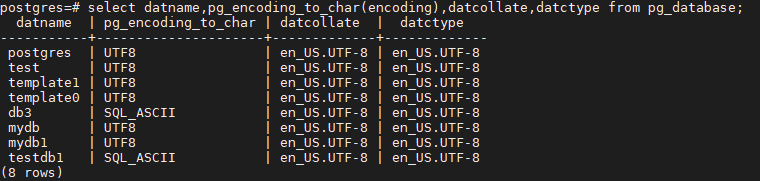
- Querying character sets (encodings) supported by LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE
SELECT pg_encoding_to_char(collencoding) AS encoding,collname,collcollate AS "LC_COLLATE",collctype AS "LC_CTYPE" FROM pg_collation;
If encoding is empty, LC_COLLATE supports all character sets.

- Configuring the collation of a database in a locale
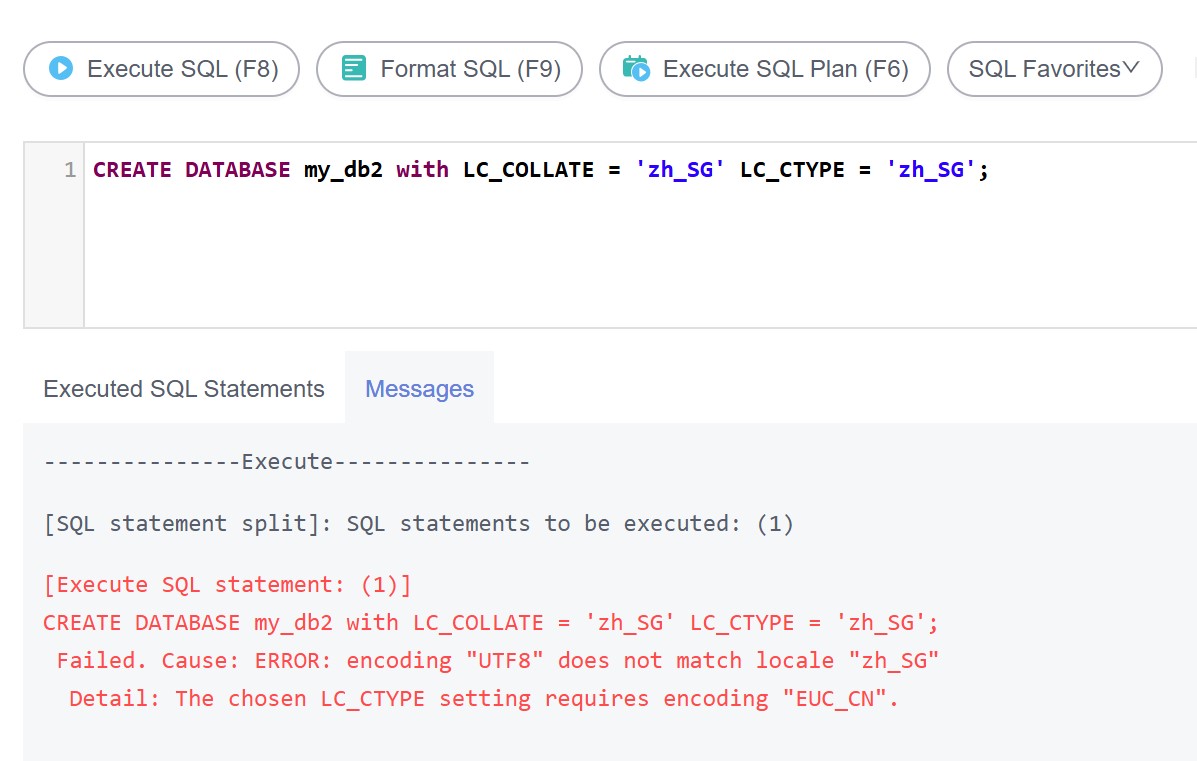
Run the following command to create a database with LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE set to zh_CN.utf8:
CREATE DATABASE my_db WITH ENCODING = 'UTF8' LC_COLLATE ='zh_CN.utf8' LC_CTYPE ='zh_CN.utf8' TEMPLATE = template0 ;
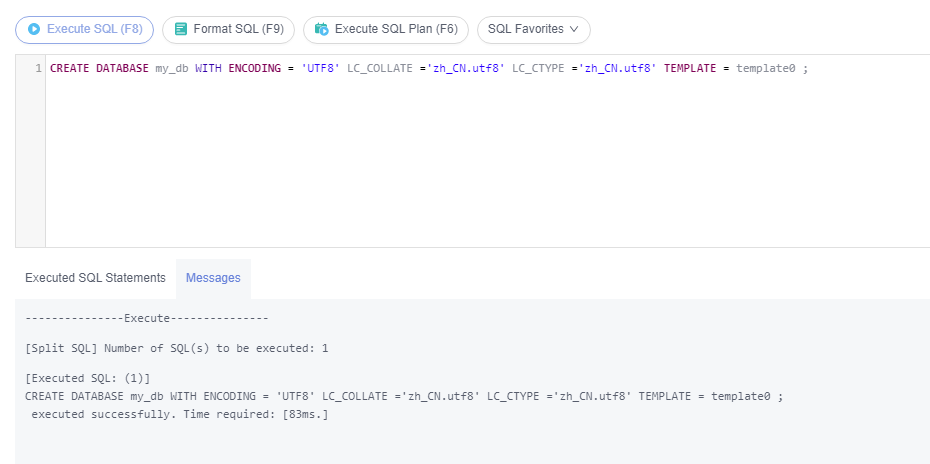
If the specified LC_COLLATE is incompatible with the character set, error information similar to the following is displayed:
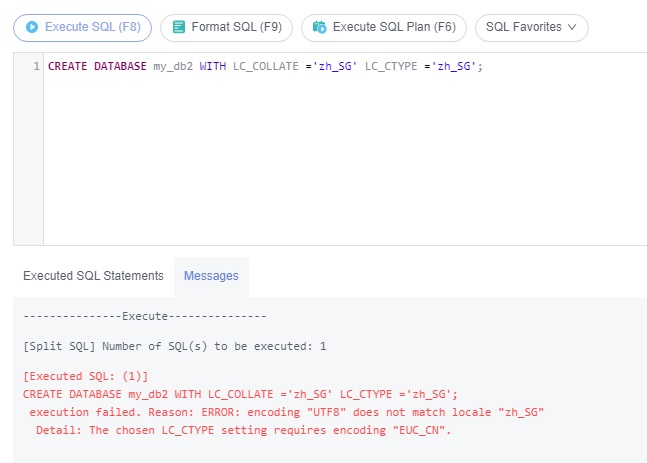

- The specified LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE must be compatible with the target character set. Otherwise, an error is reported. For details, see Querying character sets (encodings) supported by LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE.
- The LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE settings of an existing database cannot be changed by running the ALTER DATABASE statement. You can change them while creating a new database and then import your data to the new database.
- Querying character sets (encodings) supported by LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE
FAQs
Follow-up Operations
After logging in to the DB instance, you can create or migrate your databases.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot