Overview
Before connecting to a DB instance, you must create one first. For details about how to create a DB instance, see Buying an RDS for MySQL DB Instance. You can connect to an RDS for MySQL instance through a command-line interface (CLI), graphical user interface (GUI), Data Admin Service (DAS), or using Java database connectivity (JDBC).
Connection Methods
|
Connection Method |
Connection Address |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
(Recommended) Connect to an RDS for MySQL instance through DAS |
Not required |
DAS enables you to manage databases on a web-based console. It supports SQL execution, advanced database management, and intelligent O&M, simplifying database management and improving both efficiency and data security. The permissions required for connecting to DB instances through DAS are enabled by default. |
|
Connect to an RDS for MySQL instance through the MySQL CLI client |
For details, see Connecting to a DB Instance over a Private or Public Network Using CLI. |
In Linux, you need to install a MySQL client on the ECS and connect to the instance through the MySQL CLI over a private or public network.
|
|
EIP for read/write |
In Windows, you can use any common database client to connect to an RDS for MySQL instance. |
|
|
Floating IP address for read/write or EIP for read/write |
RDS for MySQL is compatible with the community ecosystem and does not provide the driver service. You can select a community driver version as required. If you are connecting to an instance through JDBC, an SSL certificate is optional, but using an SSL certificate can improve the security of your data. SSL is disabled by default for newly created instances. You can enable SSL by referring to Configuring an SSL Connection. SSL encrypts connections to your instances but it increases the connection response time and CPU usage. For this reason, enabling SSL is not recommended. |
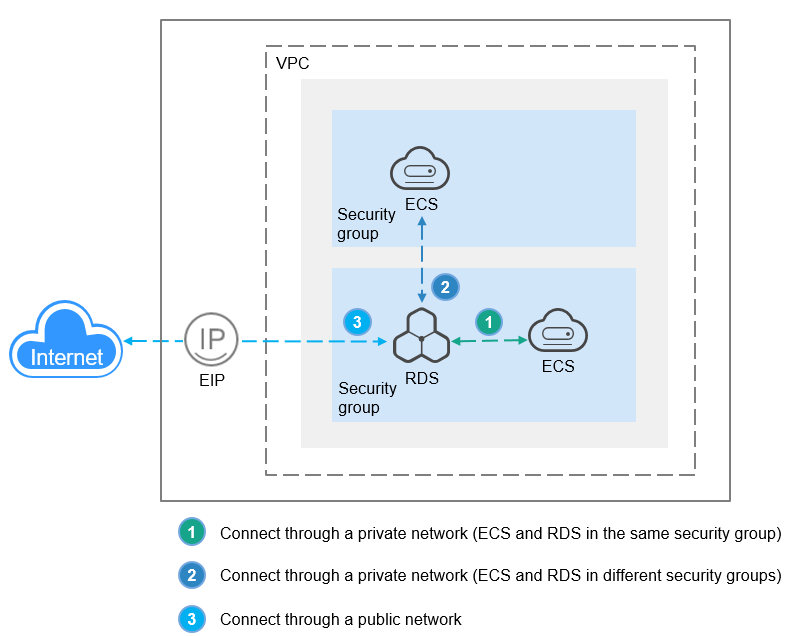
Connecting to a DB Instance over a Private or Public Network Using CLI
Table 2 lists how to use CLI to connect to an RDS for MySQL instance over a private or public network.
|
Connection Method |
IP Address |
Security Group Rules |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Floating IP address |
|
|
|
|
You need to purchase an EIP. For pricing details, see EIP Billing. |
To access a DB instance from resources outside the security group that the DB instance is associated with, you need to configure an inbound rule for the security group. For details, see Configuring a Security Group Rule. |
|
Connection Address Description
- Floating IP address for read/write
This IP address is always bound to the primary node. If your applications are deployed on a server that is in the same VPC as your DB instance, you can connect to the DB instance using this IP address to perform read and write operations. If a failover occurs, this IP address will be reassigned to the new primary node and can still be used for read and write operations.
Figure 2 Floating IP address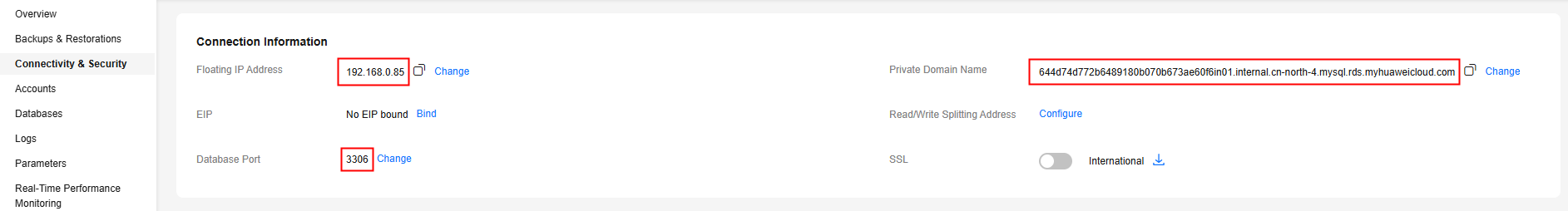
- EIP for read/write (which needs to be bound to an instance)
After you buy and bind an EIP to an instance, you can use this IP address to perform read and write operations on the instance. Just like a floating IP address, an EIP is always bound to the primary node for read and write operations.
Figure 3 EIP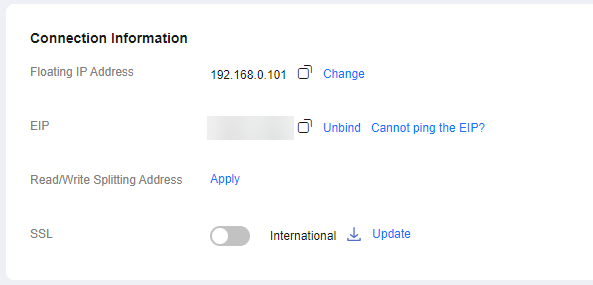
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





