Scenarios
Data Admin Service (DAS) enables you to connect to and manage DB instances with ease on a web-based console. By default, you have the remote login permission. Using DAS to connect to your DB instance is recommended, which is more secure and convenient.
Procedure
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
- On the Instances page, locate the DB instance and click Log In in the Operation column.
Figure 1 Logging in to an instance
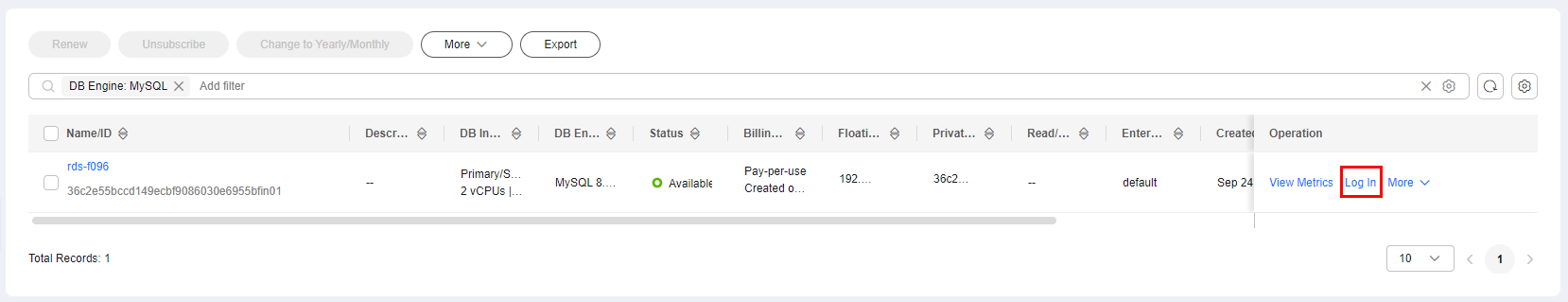
Alternatively, click the DB instance on the Instances page. On the displayed Overview page, click Log In in the upper right corner.
Figure 2 Logging in to an instance
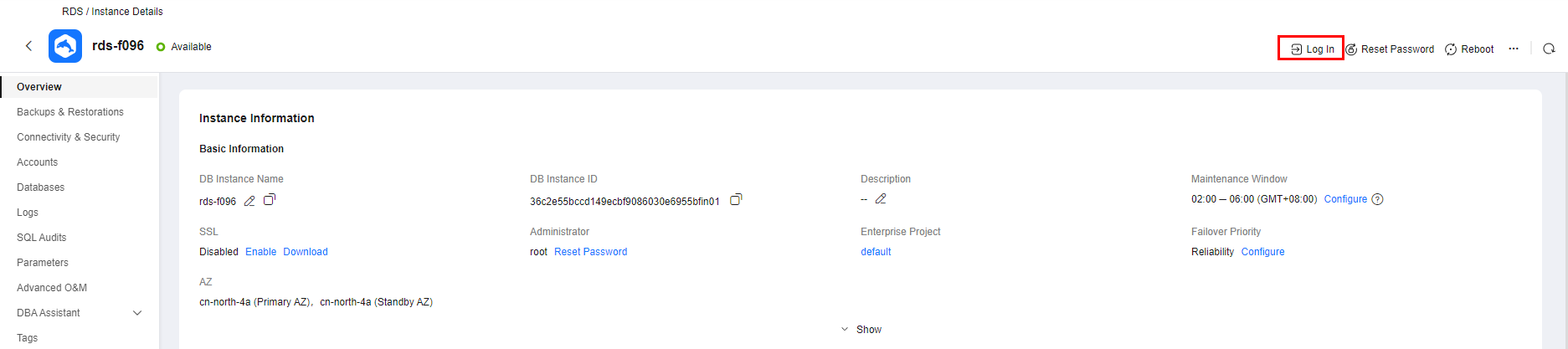
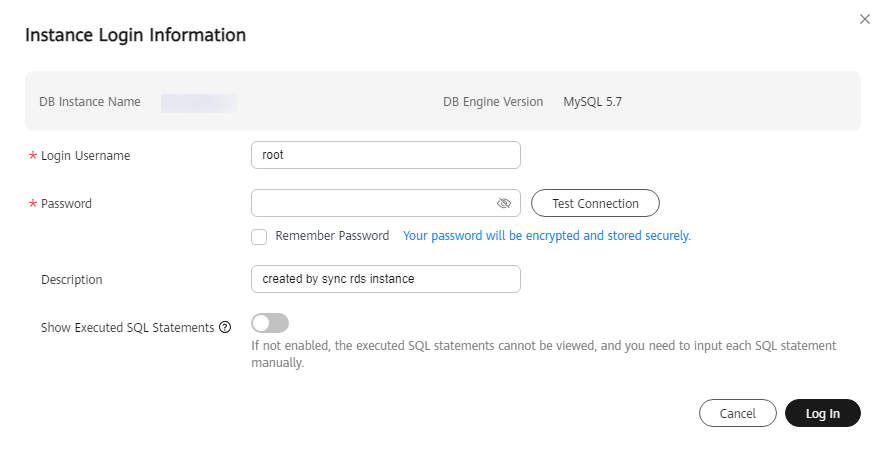
- On the displayed login page, enter the username and password and click Log In.
Figure 3 Login page
FAQ
What Can I Do If the DAS Console Is Not Displayed After I Click Log In in the Operation Column of an Instance on the Instances Page?
Set your browser to allow pop-ups and try again.
What Should I Do If I Can't Connect to My DB Instance Due to Insufficient Permissions?
- Error message: You do not have the required permission. The policy does not allow action das:connections:xxx.
Error cause: Your account does not have the DAS FullAccess permission.
Solution: Add the DAS FullAccess permission by referring to Creating a User and Granting Permissions.
- Error message: You do not have the permission to perform this operation. Contact your administrator to request the required permission.
Error cause: Your account does not have the DAS FullAccess permission.
Solution: Add the DAS FullAccess permission by referring to Creating a User and Granting Permissions.
- Error message: Your current account only has the read-only permission and cannot perform this operation. To ensure that you can use DAS smoothly, add the DAS Administrator permission.
Error cause: Your account does not have the DAS FullAccess permission.
Solution: Add the DAS FullAccess permission by referring to Creating a User and Granting Permissions.
What Should I Do If I Fail to Connect to My DB Instance Using DAS?
- Error message: Access denied for user 'user_name'@'100.xxx.xx.xx' (using password: YES).
- Error cause: The username or password of the RDS instance is incorrect.
Solution: Check whether the username and password are correct. If you are not sure, reset the password on the RDS console.

Changing the password may affect services.
If the username and password are correct, log in to the database using a client or CLI and run select * from mysql.user where user = 'user_name' to check user details. If 100.% (an IP address starting with 100) is assigned to a user, only the user can connect to the database through DAS. user_name @% and user_name @100.% are different users with independent passwords and permissions. Enter the password of user_name @100.%.
- Error cause: The IP address of the DAS server is not in the whitelist of the login user.
Solution: Log in to the database using a client or CLI, and create a user account that can be used to access the database through DAS.
create user 'user_name'@'100.%' identified by 'password';
grant select on *.* to 'user_name'@'100.%';

- Ensure that the IP address of the DAS server is in a CIDR block starting with 100. Add the IP address to the whitelist of the login user.
- Grant permissions to user user_name@100.% based on service requirements.
- Error cause: The SSL function is not enabled on the server.
Solution: Run the following statement to check whether the user is an SSL user. If yes, enable SSL on the RDS instance details page. The user is an SSL user if the ssl_type field has a value.
select user, host, ssl_type from mysql.user where user = 'user_name';
- Error message: Trying to connect with ssl, but ssl not enabled in the server.
Error cause: The SSL function is not enabled on the server.
Solution: Run the following statement to check whether the user is an SSL user. If yes, enable SSL on the RDS instance details page. The user is an SSL user if the
ssl_type field has a value.
select user, host, ssl_type from mysql.user where user = 'user_name';
- Error message: Client does not support authentication protocol requested by server. plugin type was = 'sha256_password'.
- Error cause: DAS does not allow you to connect to the database as a user whose password is encrypted using sha256_password.
Solution: Execute the following SQL statements to change the password encryption method to mysql_native_password.
alter user 'user_name'@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by 'password';
- Error cause: For MySQL 8.0, the IP address of the DAS server is not in the whitelist of the user.
Solution: Log in to the database using a client or CLI, and create a user that can be used to access the database through DAS.
- Error message: Communications link failure The last packet sent successfully to the server was 0 milliseconds ago. The driver has not received any packets from the server.
Error cause: The network between the DAS server and the instance is disconnected.
Solution: Submit a service ticket to contact customer service.
- Error message: Instance connect timeout, please login again.
Error cause: The connection to the DAS server timed out.
Solution: Submit a service ticket to contact customer service.
- Error information: RSA public key is not available client side (option serverRsaPublicKeyFile not set).
Error cause: The identity authentication mode of the database user has high requirements on password security. The password transmitted over the network during user authentication must be encrypted.
- For an SSL connection, the SSL certificate and key pair are used during the TSL handshake to securely establish a symmetric key. This symmetric key is then used to encrypt the password and data.
- For a non-SSL connection, the client uses the RSA public key of the MySQL server to encrypt the user password, and the server uses the RSA private key to decrypt and verify the password. This protects the password against snooping during network transmission.
Solution: Enable SSL for the instance or change the identity authentication mode of the database user.
Follow-up Operations
After logging in to the DB instance, you can create or migrate your databases.
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.










