Database Proxy is a network proxy service that sits between RDS for MySQL and applications. It is used to handle all requests from the applications to access RDS for MySQL instances.
Read/write splitting enables read and write requests to be automatically routed through a database proxy address. After creating an RDS for MySQL instance, you can enable database proxy. Through the proxy address, write requests are routed to the primary instance and read requests to read replicas based on the routing policy of the proxy, reducing the read pressure of the primary instance.
Basic Concepts
Proxy Address
After purchasing a database proxy, you can view the proxy address on the Database Proxy page. The database proxy sends write requests to the primary instance and read requests to read replicas through this address.
Proxy Role
There are read-only and read/write proxies. The read/write processing logic varies depending on the proxy role. For details, see Table 1.
- Read-only proxy: The proxy does not connect to the primary instance. It cannot route read requests to the primary instance, and will report an error when receiving a write request.
- Read/write proxy: The proxy connects to the primary instance and read replicas. It distributes read requests to the primary instance and read replicas by read weights and automatically routes write requests to the primary instance.
Table 1 Database proxy processing logic by role
|
Role |
Routing Policy |
Weight of Primary Instance |
Normal Case |
All Read Replicas Are Faulty |
|
Read only |
Weighted
Load balancing |
Not configurable |
Primary instance: does not process read-only requests.
Proxy address: readable but not writable |
Primary instance: does not process read-only requests.
Proxy address: connection error |
|
Read and write |
Load balancing |
Assigned by system |
Primary instance: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
Primary instance: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
|
Weighted |
> 0 |
Primary instance: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
Primary instance: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
|
= 0 |
Primary instance: not readable but writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
Primary instance: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
Transaction Splitting
Database proxies support transaction splitting. With this feature enabled, the read requests prior to write operations in a transaction are routed to read replicas, offloading read pressure from the primary instance.
For more information about transaction splitting, see Configuring Transaction Splitting.
Connection Pool
Database proxies provide session-level connection pooling. It helps reduce the database load caused by frequently setting up short connections.
For more information about connection pools, see Configuring Connection Pools.
Routing Policy
RDS for MySQL database proxies support weighted and load balancing routing policies.
- Weighted: Read requests are routed based on the read weights you specify.
- Load balancing: Read requests are routed to database nodes with fewer active connections. With this policy enabled, you do not need to configure the weights of nodes.
For more information about routing policies, see Configuring the Delay Threshold and Routing Policy.
How Read/Write Splitting Works
Read/write splitting uses database proxies to split read and write requests. You can create one or more database proxies for your DB instance.
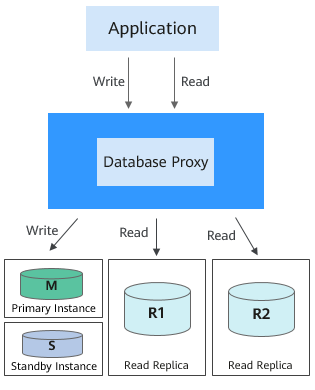
If your RDS for MySQL instance has only one database proxy, applications connect to the database proxy through the proxy address. Write requests are forwarded to the primary instance and read requests to the primary instance or read replicas based on the routing policy you specify.
Figure 1 Read/write splitting with only one database proxy
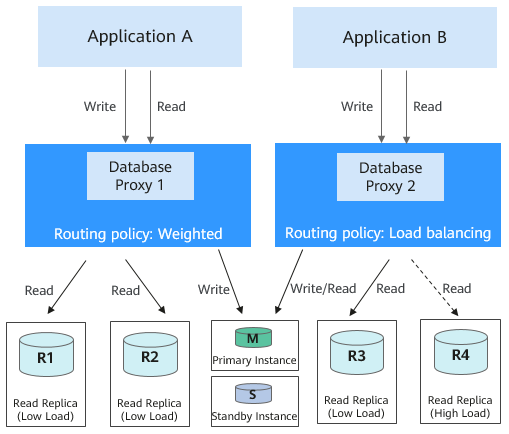
To isolate workloads from one another, you can create up to four database proxies for an RDS for MySQL instance. Different applications can connect to different database proxies as required. The database proxies connect to specified read replicas and forward read requests from different applications to different read replicas for workload isolation.
Figure 2 Read/write splitting with multiple database proxies
Advantages of Read/Write Splitting
- Read/write splitting enables read and write requests to be automatically routed. You can easily scale out a database proxy as required at low maintenance costs.
- Read requests are distributed to your read replicas based on weights to balance your database traffic and improve resource utilization.
- A proxy routes read requests of your application only to the read replicas you specify for the proxy.
- By default, database proxies provide overload protection to prevent operations with large result sets from causing out of memory (OOM) exceptions of the server. If the database kernel pressure is high, database traffic throttling is required.
Request Routing Rules
Requests sent only to the primary node
- INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and SELECT FOR UPDATE
- All DDL operations (such as table/database creation, table/database deletion, table structure change, and permission change)
- All requests in transactions (But if transaction splitting is enabled, some read requests in transactions may be sent to read replicas. For details, see Configuring Transaction Splitting.)
- User-defined functions
- Stored procedures
- Multi-statement requests
- Requests that use temporary tables
- SELECT last_insert_id()
- All queries of and changes to user variables
Requests sent either to the primary node or a read replica
- SELECT not in a transaction
- COM_STMT_EXECUTE
Requests always sent to all nodes
- Changes to all system variables
- The USE command
Billing
Database proxy can be enabled for purchased DB instances. After it is enabled, it is separately billed.
Database proxy supports only pay-per-use billing.
The database proxy service is available for commercial use. It is billed by node. When you purchase a database proxy instance on the console, two nodes are created by default. The total fee is calculated as follows: Total fee = Number of nodes x Unit price. For details about the unit price, see the price of database proxy in RDS Pricing Details.








