Overview
EIP
The Elastic IP (EIP) service enables your cloud resources to communicate with the Internet using static public IP addresses and scalable bandwidths. EIPs can be bound to or unbound from ECSs, BMSs, virtual IP addresses, NAT gateways, or load balancers. Various billing modes are provided to meet different service requirements.
Each EIP can be used by only one cloud resource at a time. EIPs must be in the same region as the bound resources. EIPs cannot be used across regions.

EIP Bandwidth
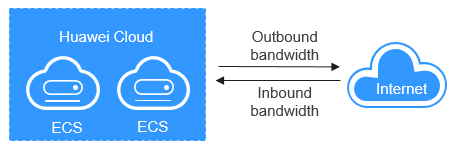
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted in a given amount of time (generally one second). A larger bandwidth value indicates a stronger transmission capability. Bandwidth is classified into public bandwidth and private bandwidth.
Private bandwidth is the bandwidth consumed when data is transferred between ECSs in the same region and on the same private network. ECSs can also be connected to cloud databases, load balancers, and OBS through private bandwidth. The private bandwidth size depends on the instance specifications.
For details, see ECS Types.
Public bandwidth is the bandwidth consumed when data is transferred between Huawei Cloud and the Internet. You can configure the public bandwidth when creating an ECS or bind an EIP to an ECS after the EIP is created.
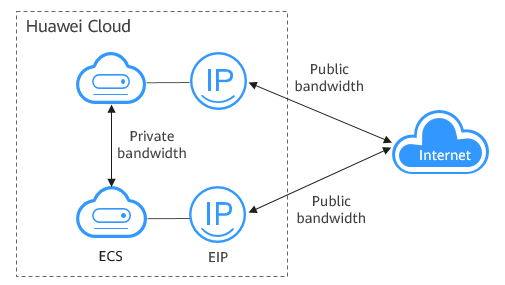
- The metrics about outbound bandwidth on the Cloud Eye console are Outbound Bandwidth and Outbound Traffic.
- The metrics about inbound bandwidth on the Cloud Eye console are Inbound Bandwidth and Inbound Traffic.
|
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Outbound bandwidth |
Bandwidth consumed when data is transferred from Huawei Cloud to the Internet. For example, the outbound bandwidth is consumed when ECSs provide services accessible from the Internet or when FTP clients download resources from the ECSs. The metrics about outbound bandwidth on the Cloud Eye console are Outbound Bandwidth and Outbound Traffic. You are only billed for the outbound bandwidth you have used.
NOTE:
|
|
Inbound bandwidth |
Bandwidth consumed when data is transferred from the Internet to Huawei Cloud. For example, the inbound bandwidth is consumed when downloading resources from the Internet to ECSs and when FTP clients upload resources to the ECSs. The metrics about inbound bandwidth on the Cloud Eye console are Inbound Bandwidth and Inbound Traffic.
The maximum inbound bandwidth depends on the size of the outbound bandwidth.
The preceding bandwidth limit is not applicable in CN North-Beijing1 and CN East-Shanghai2. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot