Queue Resource Management (capacity Plugin)
In a Kubernetes cluster, multiple teams or services (such as AI training, big data analysis, and online services) need to share compute resources, and jobs have different resource requirements and priorities. If all jobs compete for resources, there may be the following problems:
- Resource contention: High-load jobs occupy the CPU or memory of other jobs, causing performance deterioration.
- Unfair scheduling: Key services may be delayed due to insufficient resources, while low-priority jobs occupy too many resources.
- Lack of isolation: Abnormal jobs (for example, jobs that cause memory leak) of a tenant may exhaust node resources. As a result, normal services of other tenants are unavailable.
To address these problems, Volcano Scheduler provides queues for resource management. Queue is a core concept in Volcano. It is designed to support resource allocation and job scheduling in multi-tenant scenarios. With queues, you can implement multi-tenant resource allocation, job priority control, and resource preemption and reclamation. All these significantly improve cluster resource utilization and job scheduling efficiency. Queues have the following main features.
|
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Flexible resource configuration |
|
|
|
|
Intelligent resource scheduling |
|
|
Multi-tenant isolation |
|
Prerequisites
- A CCE standard or Turbo cluster of v1.19 or later is available. For details about how to create a cluster, see Buying a CCE Standard/Turbo Cluster.
- The Volcano Scheduler add-on has been installed. For details, see Volcano Scheduler.
Notes and Constraints
This feature is in the OBT phase. You can experience it. However, the stability has not been fully verified, and the CCE SLA does not apply.
Enabling Queue Resource Management and Scheduling
You can enable the capacity plugin and reclaim action (Volcano Scheduler > Expert mode) to manage and schedule queue resources. The capacity plugin supports only peer queues. You can use hierarchical queues for fine-grained multi-tenant resource allocation.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Settings. Then click the Scheduling tab.
- In Volcano Scheduler configuration, queue resource management is disabled by default. You need to modify the configuration to enable this function.
- In Default Cluster Scheduler > Expert mode, click Try Now.
Figure 1 Expert mode > Try Now
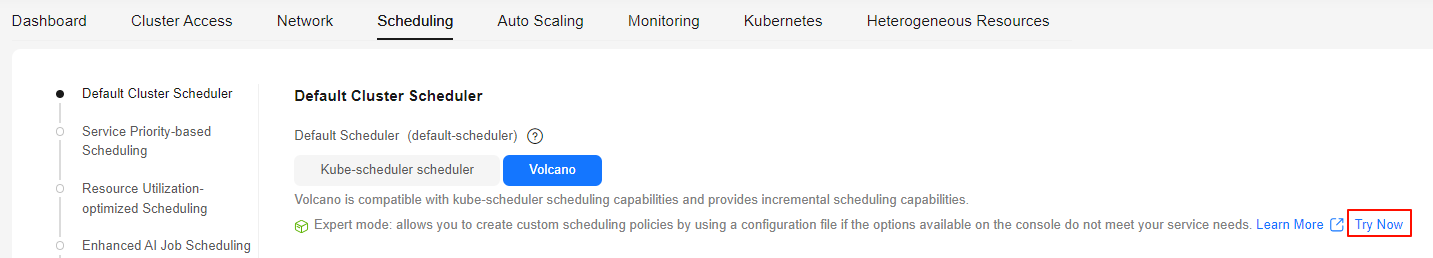
- Add the following parameters to the YAML file to enable the capacity plugin. You also need to enable the reclaim action for resource reclamation between queues. When queue resources are insufficient, resource reclamation is triggered. The system preferentially reclaims resources that exceed the deserved value of the queue and selects an appropriate reclamation object based on the queue/job priority.

The capacity plugin and proportion plugin conflict with each other. Ensure that the proportion plugin configuration has been removed when using the capacity plugin.
... default_scheduler_conf: actions: allocate, backfill, preempt, reclaim # Enable the reclaim action. metrics: interval: 30s type: '' tiers: - plugins: - name: priority - enableJobStarving: false enablePreemptable: false name: gang - name: conformance - plugins: - enablePreemptable: false name: drf - name: predicates - name: capacity # Enable the capacity plugin. - name: nodeorder - arguments: binpack.cpu: 1 binpack.memory: 1 binpack.resources: nvidia.com/gpu binpack.resources.nvidia.com/gpu: 2 binpack.weight: 10 name: binpack - Click Save in the lower right corner.
- In Default Cluster Scheduler > Expert mode, click Try Now.
- Click Confirm Settings in the lower right corner. In the displayed dialog box, confirm the modification and click Save.
- Create a queue.
vim queue.yamlThe file content is as follows (the capacity plugin allows you to explicitly configure the deserved value to specify the queue resource quota):
apiVersion: scheduling.volcano.sh/v1beta1 kind: Queue metadata: name: capacity-queue spec: capability: cpu: "20" memory: "40Gi" deserved: cpu: "10" memory: "20Gi"
For more parameter information, see Queue | Volcano.
Table 2 Queue parameters Parameter
Example Value
Description
capability
cpu: "20"
memory: "40Gi"
(Optional) Specifies the upper limit of resources for the queue. If this parameter is not set, the capability value of the queue is automatically set to realCapability, which is the total resource value of the cluster minus the sum of the guarantee values of other queues.
deserved
cpu: "10"
memory: "20Gi"
Specifies the resources that should be allocated to the queue. The value must be less than or equal to the capability value of the queue. When cluster resources are insufficient, the excess resources are reclaimed first. If the resources allocated to the queue exceed the deserved value, the queue cannot reclaim resources from other queues.
NOTE:When cluster auto scaling components such as Cluster Autoscaler or Karpenter are used, the total cluster resources dynamically change. In this case, if the capacity plugin is used, you need to manually adjust the value of deserved for the queue to adapt to the resource changes.
Use Case
The following uses a typical queue resource management scenario to describe the queue resource reclamation mechanism.
Assume that there are four available CPU cores in the cluster. In the initial state, the cluster has a default queue. This queue can use all resources of the cluster, and all resources used by the queue can be reclaimed. Two jobs are created in the default queue to occupy all CPU cores of the cluster, and then a new queue is created and a new job is submitted. However, no resources are available for the job. Volcano reclaims the resources that exceed the deserved value for the default queue. The process is as follows:
- Create two Volcano jobs (job1 and job2) in the default queue and apply for 1 CPU core and 3 CPU cores for the jobs, respectively.
- Create two YAML files, one for job1 and the other for job2.
vim vcjob-a.yamlThe file content is as follows (1 CPU core for job1 and 3 CPU cores for job2):
# job1 apiVersion: batch.volcano.sh/v1alpha1 kind: Job metadata: name: job1 spec: queue: default #The default queue tasks: - replicas: 1 template: spec: containers: - image: alpine name: alpine resources: requests: cpu: "1" --- # job2 apiVersion: batch.volcano.sh/v1alpha1 kind: Job metadata: name: job2 spec: queue: default tasks: - replicas: 1 template: spec: containers: - image: alpine name: alpine resources: requests: cpu: "3"
- Create two jobs in the default queue.
kubectl apply -f vcjob-a.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
job.batch.volcano.sh/job1 created job.batch.volcano.sh/job2 created
- Create two YAML files, one for job1 and the other for job2.
- Check the pod statuses.
kubectl get pod
If the following information is displayed and the status of each pod is Running, the cluster CPU resources are used up.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE job1-test-0 1/1 Running 0 3h21m job2-test-0 1/1 Running 0 3h31m
- Create the test queue.
- Create a YAML file for the test queue.
vim new_queue.yamlThe file content is as follows:
apiVersion: scheduling.volcano.sh/v1beta1 kind: Queue metadata: name: test spec: reclaimable: true deserved: cpu: 3
- Create the test queue.
kubectl apply -f new_queue.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
queue.scheduling.volcano.sh/test created
- Create a YAML file for the test queue.
- Create a Volcano job (job3) in the test queue and apply for 3 CPU cores (not exceeding the deserved value) to trigger resource reclamation.
- Create a YAML file for job3.
vim vcjob-b.yamlThe file content is as follows (3 CPU cores for job3):
# job3 apiVersion: batch.volcano.sh/v1alpha1 kind: Job metadata: name: job3 spec: queue: test tasks: - replicas: 1 template: spec: containers: - image: alpine name: alpine resources: requests: cpu: "3"
- Create a job in the test queue.
kubectl apply -f vcjob-b.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
job.batch.volcano.sh/job3 created
Resource reclamation is triggered because the cluster CPU resources are used up.
- The system reclaims the resources that are not deserved by the default queue. job2 (3 CPU cores) is evicted because the resource of job1 (1 CPU core) is insufficient for job3 to run. job1 (1 CPU core) is retained.
- job3 (3 CPU cores) starts to run. After job3 is complete, the evicted job is executed again.
- Create a YAML file for job3.
- Check the pod statuses.
kubectl get pod
If the following information is displayed, the system is reclaiming resources:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE job1-test-0 1/1 Running 0 3h25m job2-test-0 1/1 Terminating 0 3h25m job3-test-0 0/1 Pending 0 1m
Wait for several minutes and run the preceding command again to check the pod statuses. If the following information is displayed, the system has successfully reclaimed resources for job3. After job3 is complete and resources are released, the pod whose resources have been reclaimed will run again.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE job1-test-0 1/1 Running 0 3h27m job2-test-0 0/1 Pending 0 3h27m job3-test-0 1/1 Running 0 3m
- Check the pod statuses again to verify whether job2 is running again.
kubectl get pod
If the following information is displayed, the pod whose resources have been reclaimed is running again.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE job1-test-0 0/1 Completed 0 3h37m job2-test-0 1/1 Running 1 3h37m job3-test-0 0/1 Completed 0 13m
Reference
- For more information about hierarchical queues, see Hierarchical Queues.
- For more information about Volcano scheduling, see Volcano Scheduling Overview.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





