Cost Management
The following describes how to manage TaurusDB costs to help maximize return on your investment.
Cost Composition
TaurusDB costs consist of two parts:
- Resource costs: costs of compute and storage resources. For details, see Billing Modes.
- O&M costs: labor costs incurred during the use of DB instances.
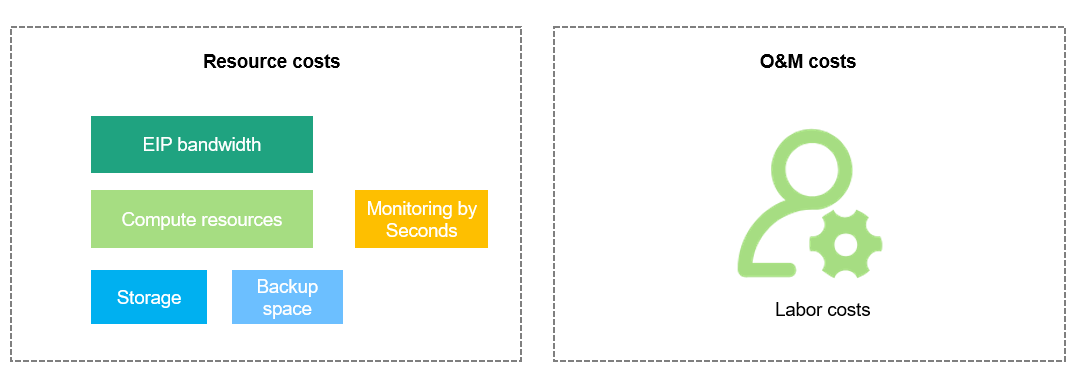
Huawei Cloud Cost Center helps you manage resource costs with ease. However, you need to identify, manage, and optimize O&M costs by yourself.
Cost Allocation
A good cost accountability system is a prerequisite for cost management. It ensures that departments, business teams, and owners are accountable for their respective cloud costs. An enterprise can allocate cloud costs to different teams or projects so as to have a clear picture of their respective costs.
Huawei Cloud Cost Center provides various tools for you to group costs in different ways. You can experiment with these tools and find a way that works best for you.
- By linked account
The enterprise master account can manage costs by grouping the costs of its member accounts by linked account. For details, see Viewing Costs by Linked Account.
- By enterprise project
Before allocating costs, enable Enterprise Project Management Service (EPS) and plan your enterprise projects based on your organizational structure or service needs. When purchasing cloud resources, select an enterprise project so that the costs of the resources will be allocated to the selected enterprise project. For details, see Viewing Costs by Enterprise Project.
Figure 1 Selecting an enterprise project
- By cost tag
You use tags to sort your Huawei Cloud resources in a variety of different ways, for example, by purpose, owner, or environment. The following is the process of managing costs by predefined tags (recommended).
Figure 2 Adding a tag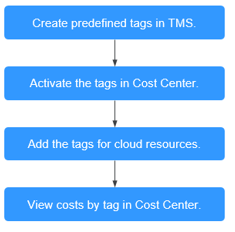
For details, see Viewing Costs by Cost Tag.
- By cost category
You can use cost categories provided by Cost Center to split shared costs. Shared costs are the costs of resources (compute, network, storage, or resource packages) shared across multiple departments or the costs that cannot be directly split by cost tag or enterprise project. These costs are not directly attributable to a singular owner, and they cannot be categorized into a singular cost type. In this case, you can define cost splitting rules to fairly allocate these costs among teams or business units. For details, see Allocating Costs By Cost Category.
Cost Analysis
To precisely control and optimize your costs, you need a clear understanding of what parts of your enterprise incurred different costs. Cost Center visualizes your original costs and amortized costs using various dimensions and display filters for cost analysis so that you can analyze the trends and drivers of your service usage and costs from a variety of perspectives or within different defined scopes.
You can also use cost anomaly detection provided by Cost Center to detect unexpected expenses in a timely manner. In this way, costs can be monitored, analyzed, and traced.
For details, see Making Cost Analysis to Explore Costs and Usage and Enabling Cost Anomaly Detection to Identify Anomalies.
Cost Optimization
You can identify resources with high costs based on the analysis results in the cost center, determine the causes of high costs, and take optimization measures accordingly.
- Resource rightsizing
Cloud Eye helps you monitor resource usage, identify idle resources, and find opportunities to save costs. You can also identify resources with high costs based on the results of Cost Analysis and take optimization measures accordingly.
- View TaurusDB metrics on Cloud Eye, such as the CPU, memory, and disk usage. If the current configuration is too high, you can reduce the configuration by changing specifications.
- Monitor idle TaurusDB resources and delete idle instances in a timely manner.
- If your services have low requirements on performance and stability, purchase a general-purpose DB instance to reduce your costs. For example, in the same specifications (32 vCPUs and 128 GB of memory), the cost of a general-purpose DB instance is 30% lower than that of a dedicated DB instance.
- Billing mode selection
Different types of services have different requirements on resource usage periods, so the most economical billing mode for one resource may not be the best option for another resource.
- For mature services that tend to be stable for the long term, select yearly/monthly billing.
- For short-term, unpredictable services that experience traffic bursts and cannot afford to be interrupted, select pay-per-use billing.
- Monitor the lifecycle of instances and renew yearly/monthly resources that are about to expire in a timely manner.
- O&M automation
Configure auto scaling policies for DB instances on the Basic Information page. When configuring auto scaling policies, you can enable or disable Auto Scale-up or Auto Scale-down. The scaling type includes changing instance specifications or the number of read replicas. For details, see Configuring an Auto Scaling Policy for a DB Instance.
Buy serverless DB instances. Configure minimum billing unit and scaling scope for serverless DB instances. Serverless DB instance resources automatically grow based on workloads. For details, see Buying a Serverless DB Instance.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





