- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
- On the Instances page, locate the target instance and click Log In in the Operation column.
Alternatively, on the Instances page, click the instance name. On the displayed Basic Information page, click Log In in the upper right corner.
- Enter the database username and password and click Test Connection.
- After the connection test is successful, click Log In.
- Choose SQL Operations > SQL Window and run the following command to create a stored procedure.
Ensure that the database specified in the stored procedure exists. If not, create a database and import data.
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE archive_table_non_first_partition(
IN dbName VARCHAR(64) -- Input parameter: database name
)
BEGIN
-- ===================== All DECLARE statements must be placed at the beginning. =====================
-- 1. Declare variables.
DECLARE tableName VARCHAR(64); -- Table name
DECLARE partitionName VARCHAR(64); -- Partition name
DECLARE done INT DEFAULT 0; -- End flag of the cursor loop.
DECLARE partitionCount INT DEFAULT 0;-- Total number of partitions in a single table
DECLARE partitionIndex INT DEFAULT 0;-- Partition traversal index (used to skip the first partition)
-- 2. Declare all cursors (declare them upfront to prevent syntax errors).
-- Cursor 1: Obtain all partitioned tables in a specified database.
DECLARE cur_partition_tables CURSOR FOR
SELECT DISTINCT t.TABLE_NAME
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES t
INNER JOIN INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PARTITIONS p
ON t.TABLE_SCHEMA = p.TABLE_SCHEMA
AND t.TABLE_NAME = p.TABLE_NAME
WHERE t.TABLE_SCHEMA = dbName
AND t.TABLE_TYPE = 'BASE TABLE'
AND p.PARTITION_NAME IS NOT NULL -- Filter partitioned tables.
ORDER BY t.TABLE_NAME;
-- Cursor 2: Obtain all partitions of a single partitioned table (sorted by creation time).
DECLARE cur_partitions CURSOR FOR
SELECT PARTITION_NAME
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PARTITIONS
WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = dbName
AND TABLE_NAME = tableName
AND PARTITION_NAME IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY PARTITION_ORDINAL_POSITION;
-- Cursor 3: Obtain all non-partitioned tables in a specified database.
DECLARE cur_non_partition_tables CURSOR FOR
SELECT t.TABLE_NAME
FROM information_schema.TABLES t
WHERE t.TABLE_SCHEMA = dbName
AND t.TABLE_TYPE = 'BASE TABLE'
AND NOT EXISTS ( -- Exclude partitioned tables.
SELECT 1
FROM information_schema.PARTITIONS p
WHERE p.TABLE_SCHEMA = t.TABLE_SCHEMA
AND p.TABLE_NAME = t.TABLE_NAME
AND p.PARTITION_NAME IS NOT NULL
);
-- 3. Declare the cursor end handler (only once).
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET done = 1;
-- ===================== Part 1: processing partitioned tables (non-first partition) =====================
-- Step 1: Traverse all partitioned tables.
OPEN cur_partition_tables;
partition_table_loop: LOOP
FETCH cur_partition_tables INTO tableName;
IF done = 1 THEN
LEAVE partition_table_loop;
END IF;
-- Reset the variable and count the total number of partitions in the current table.
SET done = 0;
SET partitionIndex = 0;
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT PARTITION_NAME) INTO partitionCount
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PARTITIONS
WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = dbName
AND TABLE_NAME = tableName
AND PARTITION_NAME IS NOT NULL;
-- Skip the table that has only one partition (the first partition, which does not require processing).
IF partitionCount <= 1 THEN
ITERATE partition_table_loop;
END IF;
-- Step 2: Traverse all partitions of the current partitioned table.
OPEN cur_partitions;
partition_loop: LOOP
FETCH cur_partitions INTO partitionName;
IF done = 1 THEN
LEAVE partition_loop;
END IF;
-- Skip the first partition.
SET partitionIndex = partitionIndex + 1;
IF partitionIndex = 1 THEN
ITERATE partition_loop;
END IF;
-- Concatenate and execute SQL statements for archiving partitions.
SET @sql = CONCAT(
'call dbms_schs.make_io_transfer(\'start\', \'',
dbName, '\', \'', tableName, '\', \'', partitionName, '\', \'\', \'obs\')'
);
PREPARE stmt FROM @sql;
EXECUTE stmt;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt;
END LOOP partition_loop;
CLOSE cur_partitions;
END LOOP partition_table_loop;
CLOSE cur_partition_tables;
-- ===================== Part 2: processing non-partitioned tables =====================
-- Reset the end flag (to avoid inheriting the cursor status of the previous round).
SET done = 0;
-- Step 1: Traverse all non-partitioned tables.
OPEN cur_non_partition_tables;
non_partition_table_loop: LOOP
FETCH cur_non_partition_tables INTO tableName;
IF done = 1 THEN
LEAVE non_partition_table_loop;
END IF;
-- Concatenate and execute SQL statements for archiving non-partitioned tables (the parameter sequence is the same as that of partitioned tables).
SET @sql = CONCAT(
'call dbms_schs.make_io_transfer(\'start\', \'',
dbName, '\', \'', tableName, '\', \'\', \'\', \'obs\')'
);
PREPARE stmt FROM @sql;
EXECUTE stmt;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt;
END LOOP non_partition_table_loop;
CLOSE cur_non_partition_tables;
END //
DELIMITER ;
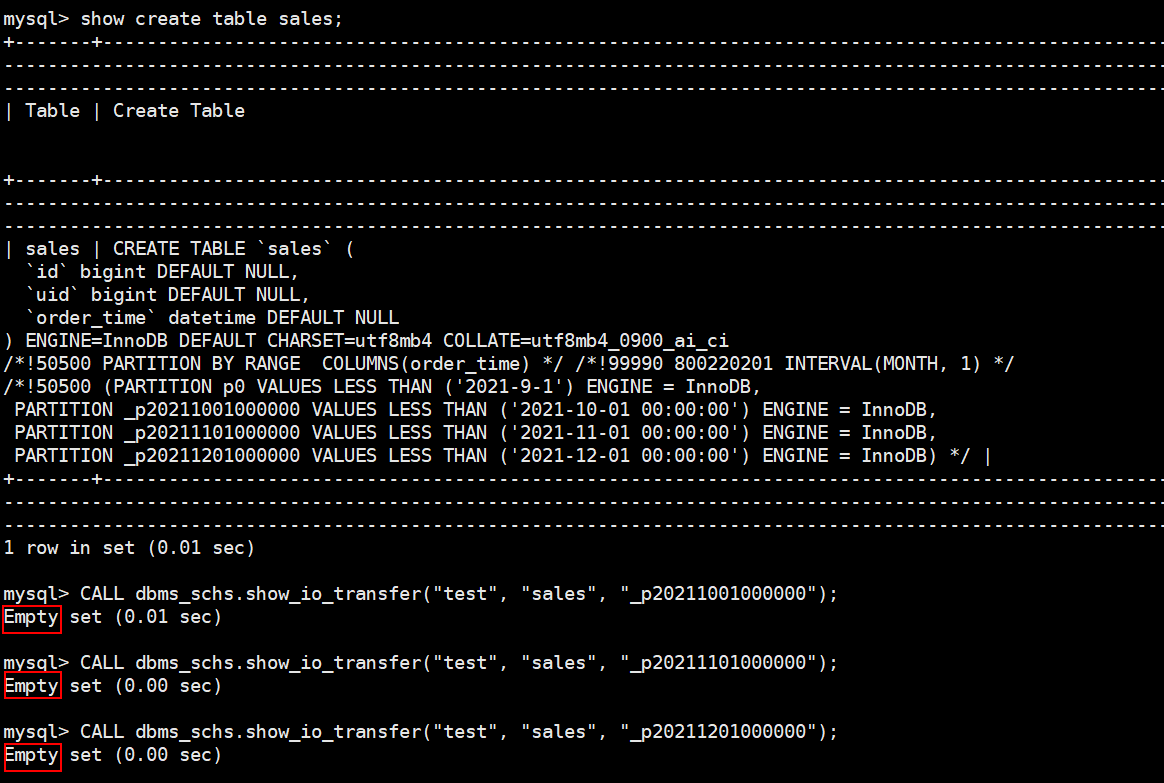
- (Optional) Run the following SQL statement to check the types of tables in the current database.
The test database is used as an example. It has partitioned tables t1_p, t2_p, and order_info, and three non-partitioned tables t1, t2, and t3.
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,PARTITION_NAME from information_schema.PARTITIONS where TABLE_SCHEMA = 'test';

- Run the stored procedure to archive all tables in the specified database. The results are only returned after all tables are archived. The entire process may take a long time.
call archive_table_non_first_partition('test');

- Run the stored procedure to view archived cold data.
sys.schs_show_all(database, table, partition) is a built-in stored procedure of TaurusDB. The three parameters indicate the database name, table name, and partition name, respectively.
- If you do not specify the table name and partition name, all archived tables in the database will be queried.
- If you do not specify the partition name, all archived partitions of the specified table will be queried.
Examples:
- Querying all cold tables on an instance
CALL sys.schs_show_all( "", "", "");
- Querying all cold partitions or cold tables whose database name is test
CALL sys.schs_show_all( "test", "", "");
- Querying cold partitions or cold tables whose database name is test and table name is table1
CALL sys.schs_show_all( "test", "table1", "");
TaurusDB's cold and hot data separation does not support archiving the first partition of partitioned tables, so the first partition p0 of table t1_p, the first (and only) partition p0 of table t2_p, and the first partition p_Beijing of table order_info are not archived.
The following uses the test database as an example:
call sys.schs_show_all('test', '', '');
If FINISH is displayed in the status column, the partitioned tables have been archived.

- Check that the used storage space has dropped, indicating the cold tables' space has been released (monitoring data may be delayed).