Selecting ECS Specifications
Scenarios
Huawei Cloud provides various ECS specifications to meet different service needs. Different types of ECSs provide different computing and storage capabilities. For the same ECS type, you can select different ECS specifications based on the number of vCPUs and memory size.
This section describes how to select ECSs suitable for your service requirements.
Specifications
- To learn details about the available ECS specifications, see A Summary List of x86 ECS Specifications.
- To learn how ECS flavors are named, see ECS Flavor Naming Rules.
- To learn more about common metrics, see vCPUs and Network QoS.
Specification Selection
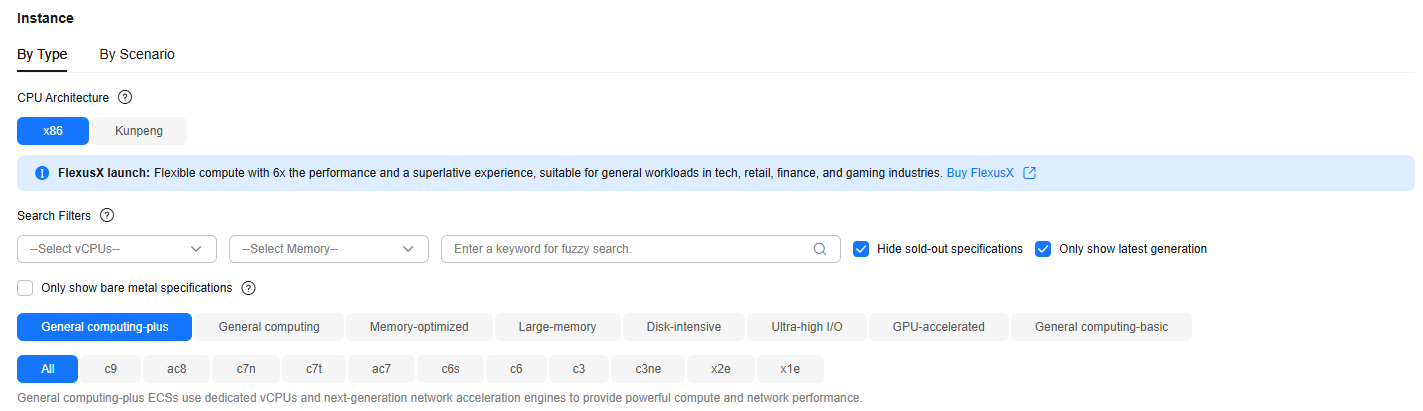
- By type
View the ECS specification details to learn about the major ECS types, computing and network performance, and supported disk types. You can select ECS specifications based on different properties. ECS supports the following CPU architectures: x86 and Kunpeng. For details, see x86 and Kunpeng Architectures.
This section is intended for users who are familiar with the CPU architecture, vCPUs, memory, and instance family and generation of ECSs and want to select specific specifications.
x86 ECSs
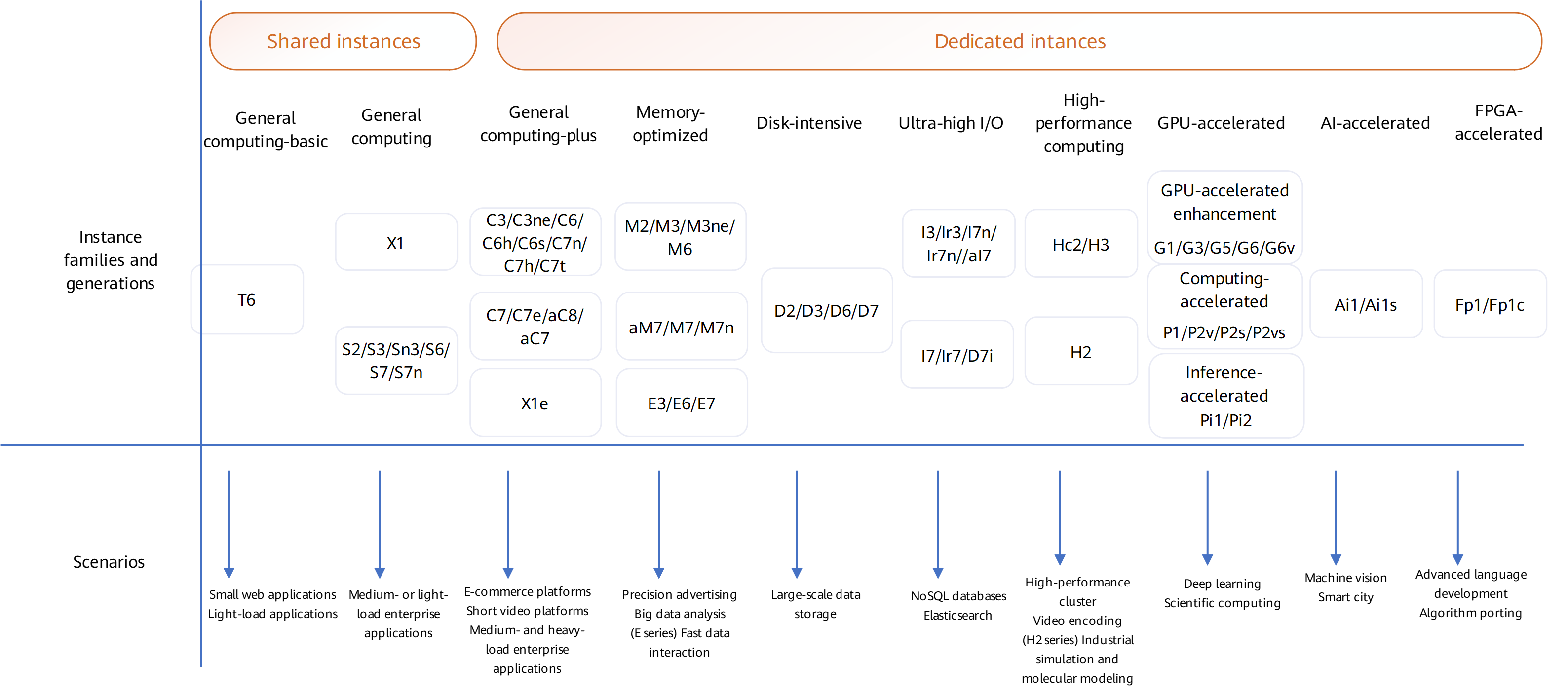
Kunpeng ECSs

On the ECS purchase page, you can select an ECS by specifying its vCPUs, memory, or flavor name.
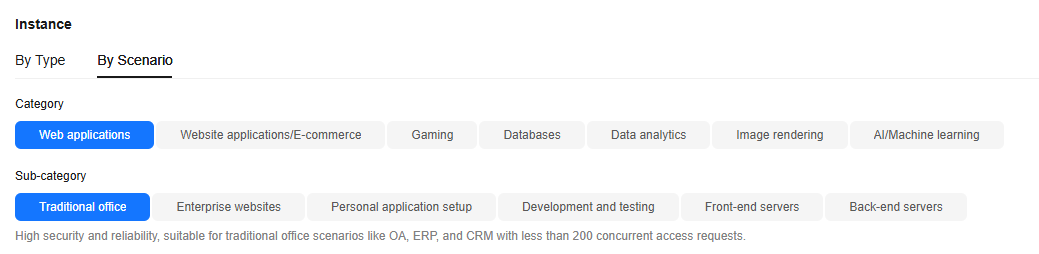
- By scenario
This section is intended for users who have specific service requirements.
Category
Sub-category
Characteristics
Recommended ECS (Example)
Web applications
Traditional office
High security and reliability, suitable for traditional office scenarios like OA, ERP, and CRM with fewer than 200 concurrent access requests
C7 and C6
Enterprise websites
A balance of compute, memory, and network resources with a baseline level of vCPU performance and high cost-effectiveness
- C7 and C6
- S7 and S6
Personal application setup
A balance of compute, memory, and network resources with a baseline level of vCPU performance and high cost-effectiveness
- S7 and S6
- T6
Development and testing
A balance of compute, memory, and network resources with a baseline level of vCPU performance and the ability to provide burst CPU power at any time for as long as required
S7 and S6
Front-end servers
A balance of compute, memory, and network resources with a baseline level of vCPU performance. These ECSs can be used as front-end servers like Apache, Nginx, and IIS
S7 and S6
Back-end servers
High vCPUs-to-memory ratios, high performance, and low latency These ECSs are cost-effective options for back-end servers like Tomcat and JBoss
C7, C6, and C6s
Website applications/E-commerce
≤ 100,000 pageviews/1,000 active users
Cost-effective, flexible, elastic resources available anytime
- S7 and S6
- T6
100,000 to 500,000 pageviews/1,000 to 5,000 active users
Suitable for e-commerce websites, which require high-performance cloud servers with fast elasticity and high stability to handle traffic bursts typical of special promotions, flash sales, and live commerce
- C7, C6, and C6s
- S7 and S6
≥ 500,000 pageviews/5,000 active users
Suitable for e-commerce websites, which require high-performance cloud servers with fast elasticity and high stability to handle traffic bursts typical of special promotions, flash sales, and live commerce
C7, C6, and C6s
Gaming
Gaming
Suitable for gaming services, which require high performance, high stability, high cost-effectiveness, and low latency
C7, C6, and C6s
Databases
Compute
Stable, high-performance compute
C7, C6, and C6s
Storage
Servers that use local disks with high storage bandwidth and IOPS to provide cost-effective mass data storage
- M7 and M6
- D7 and D6
Network
High PPS performance, high TPS throughput, and low network latency for rapid data exchange and processing
- E7 and E6
- M7 and M6
- C7, C6, and C6s
Data analytics
Management nodes
A large volume of compute resources scheduled to accelerate data processing
C7, C6, and C6s
Compute nodes
Balanced compute with high performance and stability
- M7 and M6
- C7, C6, and C6s
- I7, Ir7, I3, and Ir3
- S7 and S6
Storage nodes
Cost-effective, high-bandwidth storage for processing large amounts of reads and writes
- I3 and Ir3
- D7, D6, and D3
Image rendering
Animation rendering
CPU-accelerated rendering with high precision and stability
- aC7, C6, and C3
- G5 and G6
Video rendering
GPU-accelerated rendering with high processing speed
G5 and G6
AI/Machine learning
AI training
Compatible with NVIDIA smart NICs for deep learning training, scientific computing, computational fluid dynamics, computational finance, seismic analysis, molecular modeling, and genomics
P2vs, P2v, and P2s
AI inference
Compatible with NVIDIA smart NICs for image classification and recognition, speech recognition, natural language processing, video encoding and decoding, machine learning, and lightweight training
Pi2
On the ECS purchase page, you can select specifications based on service scenarios.
- By application
If you have a specific application to run on an ECS, you can select the recommended ECS based on the application type.
Scenario
Application
Requirement
Recommended ECS (Example)
Cache
Redis
Memcached
Low CPU computing capability
Very high memory
M7 and M6
Big data
Spark
Hive
High CPU computing capability
High memory bandwidth
I/O: high storage bandwidth
D7i, I7, and D7
Load balancing
Nginx
Very high CPU computing capability
C7, C6, and X1
Database
MySQL
NoSQL
Lightweight database
aC8 and C7
Real-time computing
Flink
You can select general-purpose ECSs or cloud disks based on the storage capacity.
You can also select disk-intensive ECSs.
I7 and D7
Offline computing
Hadoop
HDFS
vCPU to memory ratio: 1:4 (preferred)
D7i and D7
Message queue
Kafka
RabbitMQ
vCPU to memory ratio: 1:1
aC8, C7, and X1
Text search
Elasticsearch
Large vCPU-to-memory ratio
I7
Verification and Adjustment
After selecting an ECS and using it, you can check whether the selected ECS specifications are proper based on performance monitoring of the ECS within a period of time.
If the CPU usage of the ECS is too low, check whether the memory usage is very high. For details, see Cloud Eye Monitoring.
If the memory usage of the ECS is very high, you can adjust the vCPU-to-memory ratio to an appropriate ratio. For details, see Modifying Specifications of Individual ECSs.
Helpful Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





