Searching for Logs
After configuring log structuring parsing and indexing, you can enter statements to search for log events that contain specific keywords. You can also search for log data by time range to locate events and issues that occur in a specified period.
Search statements are used to define the filter criteria for log query and obtain the logs that meet the criteria. A search statement may be a keyword, a value, a value range, a space, an asterisk (*), or the like. If it is a space or asterisk (*), no filtering criteria is specified. For more information, see Using Search Syntax.
Searching for Logs
- Log in to the LTS console.
- On the Log Management page, click the target log group or stream to access the log details page.
- On the Log Search tab page, select a time range from the drop-down list and click Search to view log data accordingly.
Figure 1 Time range
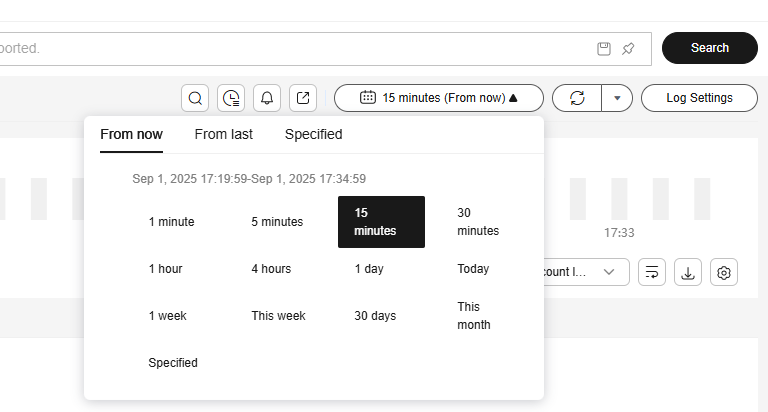
There are three types of time range: relative time from now, relative time from last, and specified time. Select a time range as required.
- From now: queries log data generated in a time range that ends with the current time, such as the previous 1, 5, or 15 minutes. For example, if the current time is 19:20:31 and 1 hour is selected as the relative time from now, the charts on the dashboard display the log data that is generated from 18:20:31 to 19:20:31.
- From last: queries log data generated in a time range that ends with the current time, such as the previous 1 or 15 minutes. For example, if the current time is 19:20:31 and 1 hour is selected as the relative time from last, the charts on the dashboard display the log data that is generated from 18:00:00 to 19:00:00.
- Specified: queries log data that is generated in a specified time range. The time range can be up to three months for common users and six months for whitelisted users. If necessary, submit a service ticket to extend the time range to six months.
- Enter search criteria in the search box by referring to Using Search Syntax to view, search, and filter log data.
Figure 2 Log search
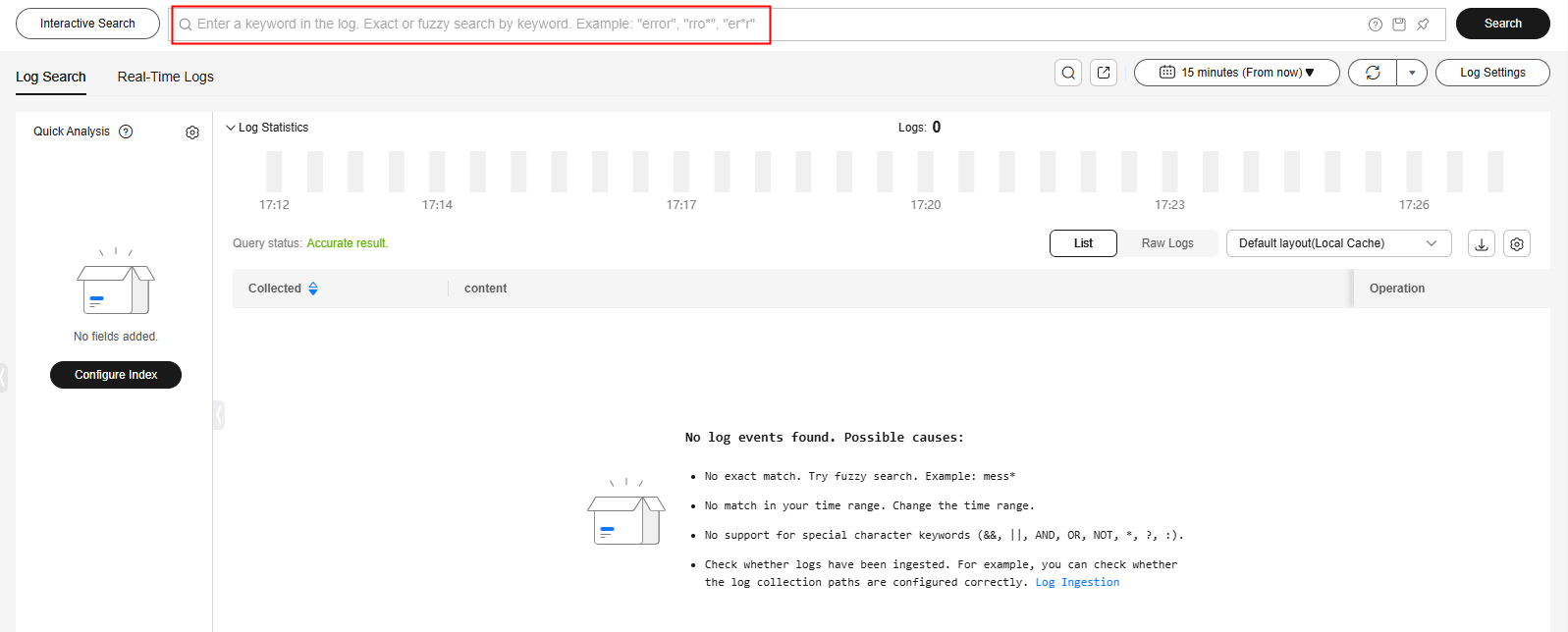
- In the search area, click the search box, enter a keyword or select a field or keyword from the drop-down list, and click Search.
- System reserved fields include appName, category, clusterId, clusterName, and collectTime. By default, the fields are displayed in simplified mode, and hostIP, hostName, and pathFile are displayed at the beginning. For more system reserved fields, see Configuring Log Indexing.
- The structured fields are displayed in key:value format.
- If there is too much content in the log search box, the content can be automatically wrapped and displayed in multiple lines. The height of the search box can be fixed.
- In the search area, press the up and down arrows on the keyboard to select a keyword or search syntax from the drop-down list, press Tab to select a keyword or syntax, and click Search.
- Click a field for which quick analysis has been enabled to add it to the search box. For details about how to enable quick analysis, see Creating a Quick Analysis Task.
If the field you click already exists in the search box, it will be replaced by this newly added one. If the field is added for the first time, fields in the search box are searched using the AND operator.
- In the search area, click the search box, enter a keyword or select a field or keyword from the drop-down list, and click Search.
- On the Log Search tab page, perform the following operations. For more operations, see Common Log Search Operations.
- Under Log Statistics, view the bar chart showing the log quantity in different time segments. The scale of the log quantity is displayed on the left.
Figure 3 Log statistics

If the embedding function is used, you can collapse or expand the log quantity statistics chart. For parameters of embedding LTS, see LTS URL.
- In the log content area, hover the cursor over a field and click the log content in blue. You can search for logs by copying, adding to query, adding to query (interactive mode), creating query, excluding from query (interactive mode), hiding, and excluding from query.
- In the log content area, you can select a list or raw log to display its log content.
The log highlighting mechanism works as follows: Once a log meets the search criteria, the system identifies the log's strings that match these criteria and applies highlight tags to the matching sections, making them visibly highlighted on the page. However, when the query criteria are complex, particularly involving OR relationships, content that does not actually match the criteria may also be highlighted on the page.
If raw logs are not uploaded, Chinese characters may not be highlighted during full-text search. To highlight Chinese characters in a field (for example, field1), use this format: field1:Chinese keyword.
- Under Log Statistics, view the bar chart showing the log quantity in different time segments. The scale of the log quantity is displayed on the left.
- When you search through a large amount of log data on the Log Search tab page, LTS automatically initiates an iterative search.
- During an iterative log search, you cannot enter any information in the search box. To pause the iterative search, click Pause. To resume the search, click Continue. You are advised not to initiate a new search task before the current iterative search is complete.
- For iterative searches that take a long time, you can narrow down the time range or add filters to reduce the number of iterative searches.
- Set the layout of log data, including whether to display fields or display fields in a simple view.
- Select Edit layouts from the layout drop-down list to access the layout setting page. The list also contains options such as the default layout, pure layout, and default container log layout, for you to set whether to display fields.
Figure 4 Editing layouts
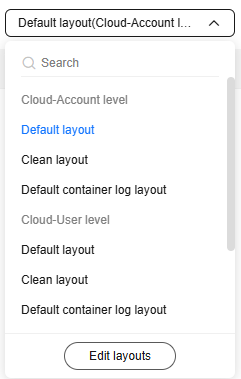
- Cloud: This mode is applicable to users who have the write permission. Layout information is stored on the cloud. You can set the layout configuration at the account or user level.
- Local Cache: This mode is applicable to users who have only the read permission. Layout information is cached in the local browser.
- On the displayed Layout page, click + under Layout List to create a custom layout, name it, and configure how fields are displayed in this layout.
Figure 5 Layout settings
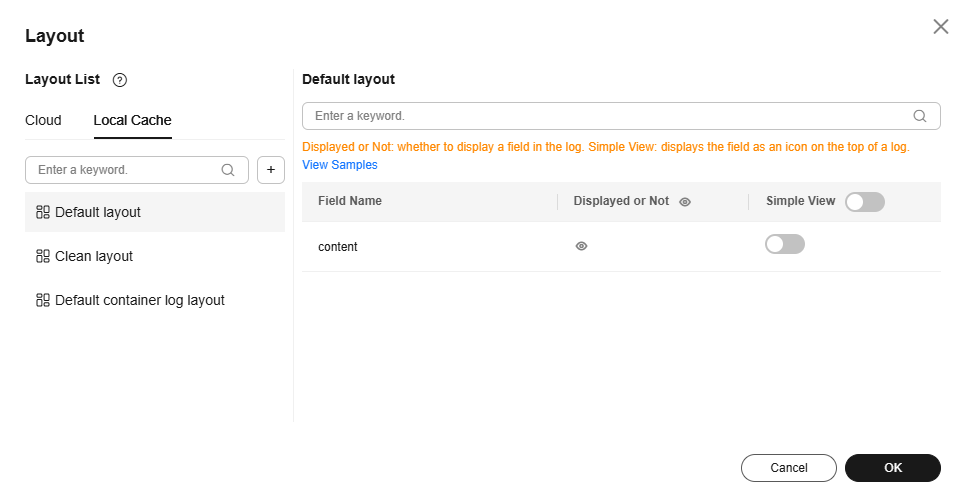
You can perform the following operations on a new layout:
- Edit: Click
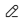 to edit the layout's display name.
to edit the layout's display name. - Copy: Hover the cursor over
 , select Copy To Local Cache, Copy To Cloud-Account level, or Copy To Cloud-User level, and click OK.
, select Copy To Local Cache, Copy To Cloud-Account level, or Copy To Cloud-User level, and click OK. - Delete: Click
 and then Yes to delete the layout.
and then Yes to delete the layout.

Deleted layouts cannot be restored. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- Edit: Click
- After the setting is complete, click OK. The new custom layout is displayed in the drop-down list.
- Select Edit layouts from the layout drop-down list to access the layout setting page. The list also contains options such as the default layout, pure layout, and default container log layout, for you to set whether to display fields.
- On the Log Search tab page, choose List. You can then set the columns to be displayed.
- Hover the cursor over
 and click Set Columns. On the displayed page, set the columns to be displayed.
Figure 6 Setting columns
and click Set Columns. On the displayed page, set the columns to be displayed.
Figure 6 Setting columns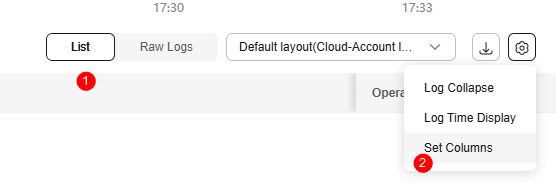
- By default, the display of the time column and content column is enabled. All visible field names are listed under Displayed Columns. You can set aliases for fields. Properly configured aliases can make your logs easier to read and maintain, improving query efficiency. Click OK.
Figure 7 Set Columns page
- You can display or hide fields as described in Creating a Quick Analysis Task or 7.
- Hover the cursor over
Interactive Mode
Before using the interactive mode function, ensure that logs are properly reported and structured, and indexing have been configured. For details, see Using ICAgent to Collect Host Logs and Configuring Log Indexing.
If you have not configured ICAgent structuring parsing when configuring log ingestion to LTS, you can configure ICAgent or cloud configuring parsing for the target log stream separately. ICAgent structuring parsing is recommended. For details, see Configuring ICAgent Structuring Parsing.
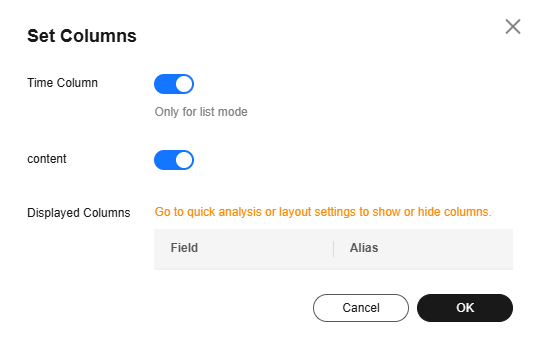
The interactive search function generates simple search statements, allowing you to set search criteria and specify query filter rules on the LTS console to filter log records. For more functions or nested queries, enter SQL statements manually. For details, see Using SQL Analysis Syntax.
- Click Interactive Search in front of the search box to access the interactive search page.
Figure 8 Interactive Mode
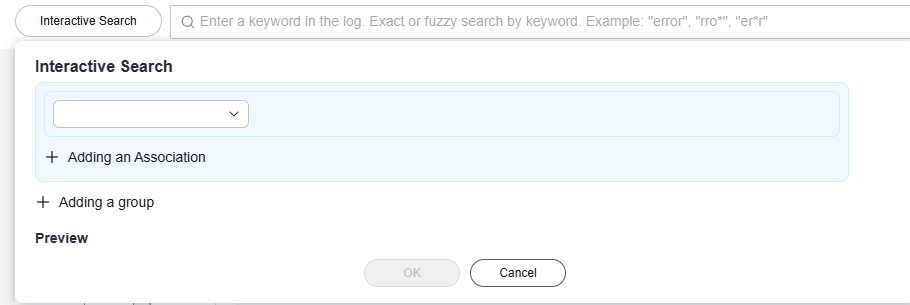
- Select the log search field and criteria from the drop-down list. The corresponding values of the field will be displayed in the search box. Add associations or groups to customize your search mode.
- The drop-down list displays index fields, structured fields, and system reserved fields.
- And indicates that all conditions must be met.
- Or indicates that only one of the conditions needs to be met.
For example, you can select fields such as content, collectTime, and category and set different conditions. Then you can preview the search statement at any time and modify the search criteria with ease.
(The following figure is for reference only.)
(content:"{\"write_traffic\":11,\"index_traffic\":133,\"storage\":17107}" AND collectTime=1728631667089) OR category:LTS
- After setting the parameters, click OK. LTS searches logs based on your search statement and displays the search results on the Log Search tab page.
Common Log Search Operations
In the log content display area, you can share and download logs, and view context. For details, see Table 1.
If your service network is unstable, the system is overloaded, or other unpredictable factors occur, a few logs may be duplicated or lost when they are reported to LTS.
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Creating a quick search |
Click |
|
Viewing dashboards |
Click |
|
Adding alarm rules |
Click |
|
Sharing logs |
Click |
|
Refreshing logs |
You can click
|
|
Copying logs |
Click |
|
Viewing context of a log |
Click You can select Simple View to view the log context. You can also download the context. |
|
More operations |
Click
|
|
Unfold/Fold |
Click |
|
Downloading logs |
You can download log files or log query and analysis results to your local PC. To avoid downloading empty files, ensure that raw logs have been uploaded to the current log stream.
|
|
Hiding/Expanding all |
Click |
|
JSON |
Move the cursor over Formatting is enabled by default. The default number of expanded levels is 2. If a log contains multiple backslashes, the first backslash will be lost when the log is displayed in JSON format because it will be processed as an escape character during JSON parsing.
|
|
Collapse configuration |
Move the cursor over If the number of characters in a log exceeds the maximum, the extra characters will be hidden. Click Expand to view all. Logs are collapsed by default, with a default character limit of 400. |
|
Log time display |
Move the cursor over |
|
Invisible fields ( |
This list displays the invisible fields configured in the layout settings.
|
Cross-Stream Search
On the log stream details page, you can search for logs across log streams. This meas you can search for logs in other log streams without exiting the current log search page.
- On the log stream details page, click
 .
Figure 9 Cross-stream search
.
Figure 9 Cross-stream search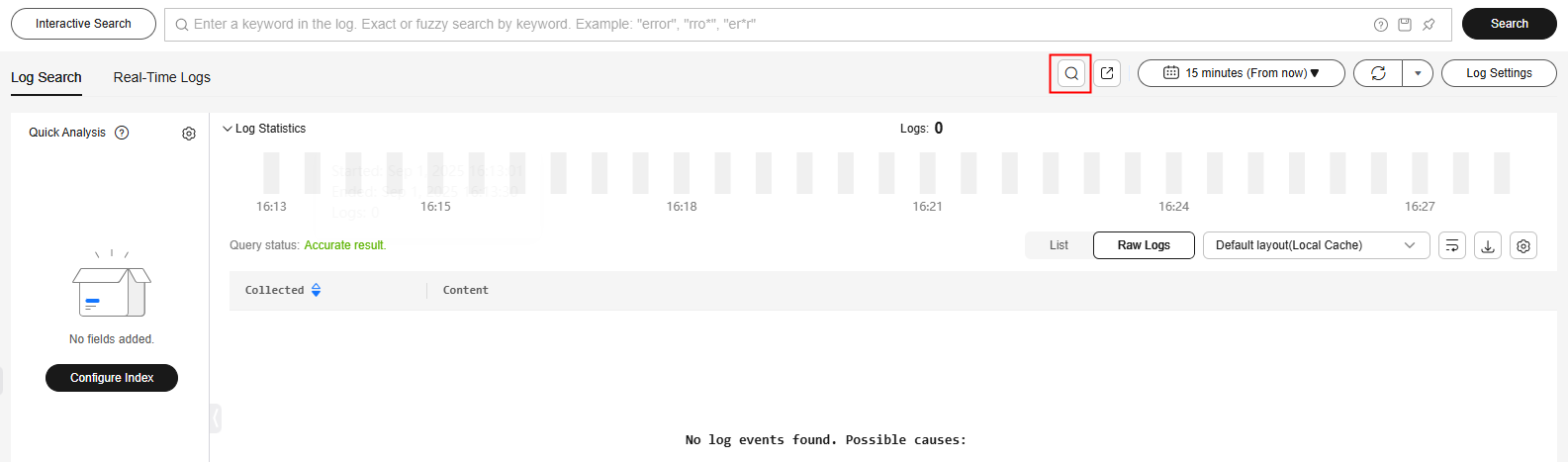
- On the displayed page, select one or more target log streams.
Figure 10 Target log stream
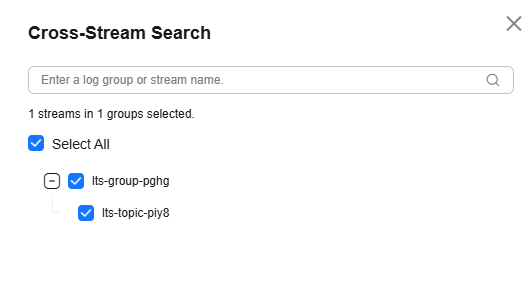
- Click OK.
- On the target log stream details page displayed, search for logs by referring to Using Search Syntax.
To change the log stream, click
 next to Cross-Stream Search in the upper left corner and select another log stream.Figure 11 Changing a log stream
next to Cross-Stream Search in the upper left corner and select another log stream.Figure 11 Changing a log stream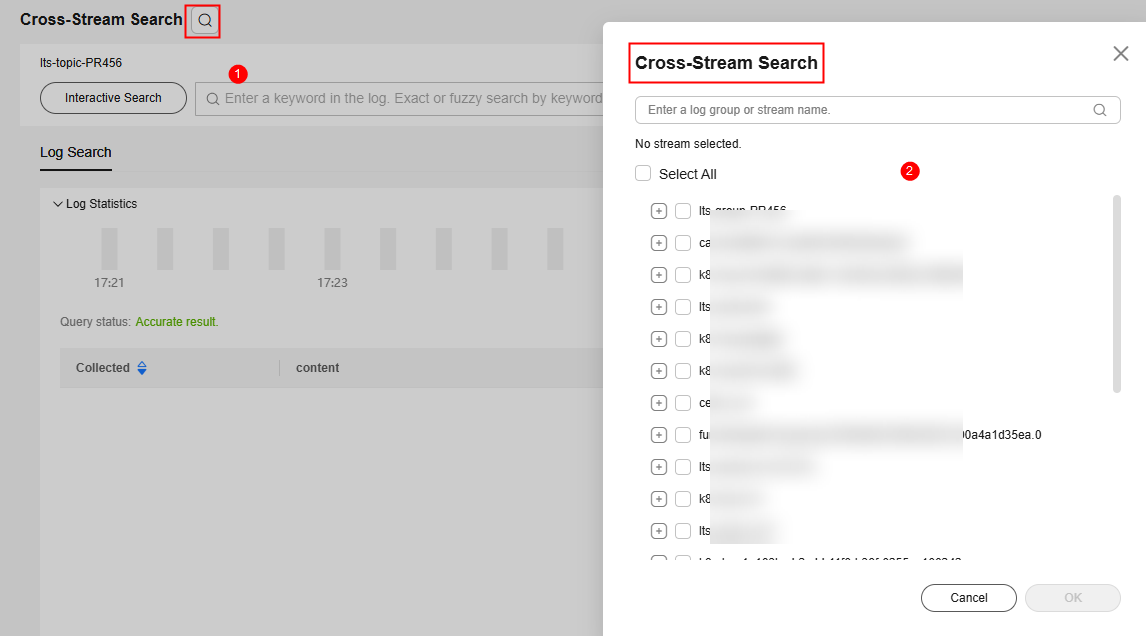
- After the search is complete, click Exit in the upper right corner to return to the current log stream search page.
- If the target log streams for cross-stream search use different delimiters, the log keywords in different streams will be highlighted differently.
- Up to 50 log streams can be searched at a time.
- Only raw logs can be searched. SQL statements cannot be used for statistical analysis.
- You can select log streams across log groups, but not across regions.
- If you select multiple log streams with different index configurations for cross-stream search, for example, indexing Key1 in stream A but not in stream B, searches for Key1:xxx will only return logs from stream A. Address the issue according to the error message and retry the log search.
Helpful Links
- You can use the log alarm function of LTS to set alarm rules to notify you of exceptions in the ingested logs. For details, see Configuring Log Alarm Rules.
- If you have any questions during log search, see Log Search and Analysis in the FAQ.
- For best practices of log search and analysis, see Log Search and Analysis in the Best Practices.
- You can analyze ingested WAF logs on the LTS console. For details, see Analyzing Huawei Cloud WAF Logs on LTS.
- You can embed the log query page of LTS into your system. For details, see Embedding the LTS Log Query Page into a User-built System.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot























