Esta página ainda não está disponível no idioma selecionado. Estamos trabalhando para adicionar mais opções de idiomas. Agradecemos sua compreensão.
- What's New
- Function Overview
- Service Overview
- Billing
- Getting Started
-
User Guide
- Before You Start
- Permissions Management
-
Environment Management
- Environment Overview
- Creating an Environment
- Managing CCE Resources
- Managing Basic Resources
- Removing Managed Basic Resources
- Managing VM Agents
- Modifying an Environment
- Deleting an Environment
- Application Management
-
Component Management
- Component Overview
- Creating and Deploying a Component
- Viewing Component Details
- Managing Component Labels
- Changing the Component Description
- Managing Component Instances
- Upgrading a Single Component
- Upgrading Components in Batches
- Cloning Components in Batches
- Synchronizing Component Configurations in Batches
- Rolling Back a Component
- Redeploying a Component
- Configuring the Component Access Mode
- Changing the Component Access Domain Name
- Configuring a Scaling Policy of a Component Instance
- Component O&M
- Viewing the Component Running Environment
- Starting and Stopping a Component Instance
- Manually Synchronizing the Component Status
- Managing Cloud Service Settings of a Container-Deployed Component
- Managing Container Settings of a Container-Deployed Component
- Managing Application Settings of a Container-Deployed Component
- Managing Advanced Settings of a Container-Deployed Component
- Managing VM-Deployed Component Configurations
- Deleting a Component
- Configuration Management
- Release Management (OBT)
- Tech Stack Management
- Deployment Source Management
- Continuous Delivery
-
Microservice Engine
- Cloud Service Engine Overview
- Creating a Microservice Engine
-
Managing Microservice Engines
- Viewing Microservice Engine Information
- Obtaining the Service Center Address of a Microservice Engine
- Obtaining the Configuration Center Address of a Microservice Engine
- Viewing the Instance Quota of a Microservice Engine
- Viewing the Configuration Item Quota of a Microservice Engine
- Configuring Backup and Restoration of a Microservice Engine
- Managing Public Network Access for a Microservice Engine
- Viewing Microservice Engine Operation Logs
- Upgrading a Microservice Engine Version
- Deleting a Microservice Engine
- Managing Security Authentication for a Microservice Engine
- Using Microservice Engines
- Key Operations Recorded by CTS
- Viewing Monitoring Metrics and Alarms
-
Developer Guide
-
Microservice Developer Guide
- Overview
- Developing Microservice Applications
- Preparing the Environment
- Connecting Microservice Applications
- Deploying Microservice Applications
- Using Microservice Engine Functions
- Appendix
-
Microservice Developer Guide
-
Best Practices
- ServiceStage Best Practices
- Hosting and Managing a Weather Forecast Microservice Application on ServiceStage
- Enabling Security Authentication for an Exclusive ServiceComb Engine
- Connecting ServiceComb Engine Dashboard Data to AOM through ServiceStage
- Migrating the Registered Microservice Engine Using ServiceStage Without Code Modification
- Hosting a Spring Boot Application on ServiceStage
- Using GitLab to Interconnect with Jenkins to Automatically Build and Upgrade Components Deployed on ServiceStage
- Using ServiceStage to Migrate Components Across AZs and Upgrade Components in Sequence Based on Release Management
-
API Reference
- Before You Start
- API Overview
- Calling APIs
-
Application Management V3 APIs
-
Environment
- Creating an Environment
- Obtaining All Environments
- Deleting an Environment Based on the Environment ID
- Modifying an Environment Based on the Environment ID
- Obtaining Environment Details Based on the Environment ID
- Modifying an Environment Resource Based on the Environment ID
- Enabling an Environment Resource Based on the Environment ID
- Querying a Managed Resource Based on the Environment ID
- Querying a Created Resource Based on the Environment ID
- Adding an Environment Resource Based on the Environment ID
- Updating an Environment Resource Based on the Environment ID
- Deleting an Environment Resource Based on the Environment ID
- Querying Resource Enabling Records Based on the Environment ID
- Querying the Details of a Resource Enabling Record Based on the Environment ID
- Querying the Events of a Resource Enabling Record Based on the Environment ID
-
Application
- Creating an Application
- Obtaining All Applications
- Modifying Application Information Based on the Application ID
- Deleting an Application Based on the Application ID
- Obtaining Application Details Based on the Application ID
- Obtaining Application Configurations Based on the Application ID
- Modifying Application Configurations Based on the Application ID
- Deleting Application Configurations Based on the Application ID
-
Component
- Creating an Application Component
- Importing a CCE Workload to an Application to Create a Component
- Obtaining All Components of an Application
- Obtaining All Components
- Modifying Component Information Based on the Component ID
- Deleting a Component Based on the Component ID
- Obtaining Component Information Based on the Component ID
- Delivering a Component Task Based on the Component ID
- Obtaining Records Based on the Component ID
- Refreshing Component Information Based on the Component ID
- Obtaining Component Configuration Information
-
Technology Stack
- Querying a Runtime System Stack
- Querying a Built-in Image
- Creating a Technology Stack
- Querying a Technology Stack Based on the Technology Stack ID
- Modifying a Technology Stack Based on the Technology Stack ID
- Deleting a Technology Stack Based on the Technology Stack ID
- Releasing or Canceling the Release of a Technology Stack
-
Configuration Management
- Creating a Configuration Group
- Obtaining a Configuration Group
- Creating a Configuration File
- Importing a Configuration File
- Obtaining Configuration File Information
- Obtaining Configuration File Information Based on the Configuration File ID
- Deleting a Configuration File Based on the Configuration File ID
- Modifying a Configuration File Based on the Configuration File ID
- Obtaining the Configuration File Record Based on the Configuration File ID
- Obtaining the Configuration File Record Information Based on the Record ID
- Deleting a Configuration File Record Based on the Record ID
- Obtaining Configuration Group Details Based on the Group ID
- Deleting a Configuration Group Based on the Group ID
- Deployment Job
- Add-on Management
-
Environment
-
Git Repository Access APIs
- Obtaining a Git Repository Authorization List
- Obtaining an Authorization Redirection URL
- Creating OAuth Authorization
- Creating Private Token Authorization
- Creating Password Authorization
- Deleting Repository Authorization
- Obtaining a Repository Namespace
- Obtaining Repository Information Based on the Clone URL
- Obtaining All Projects in a Namespace
- Creating a Software Repository Project
- Obtaining a Project Branch
- Obtaining a Project Tag
- Creating a Project Tag
- Deleting a Project Tag
- Obtaining Project Commits
- Obtaining a Project Hook
- Creating a Project Hook
- Deleting a Project Hook
- Obtaining a Repository File Directory
- Obtaining Repository File Contents
- Creating a Repository File
- Modifying Repository File Contents
- Deleting a Repository File
-
CSE APIs
- API Calling
- Dynamic Configuration
-
Engine Management
- Querying Flavors Supported by an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Querying the Exclusive Microservice Engine List
- Creating an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Querying Details About an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Deleting an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Querying Details About an Exclusive Microservice Engine Job
-
ServiceComb APIs
- API Calling
- Authentication
-
Microservice
- Querying Information About a Microservice
- Deleting Definition Information About a Microservice
- Querying Information About All Microservices
- Creating Static Information for a Microservice
- Deleting Static Information About Microservices in Batches
- Modifying Extended Attributes of a Microservice
- Querying the Unique Service or Schema ID of a Microservice
- Schema
-
Microservice Instance
- Registering a Microservice Instance
- Querying a Microservice Instance Based on service_id
- Deregistering a Microservice Instance
- Querying Details About a Microservice Instance
- Modifying the Extended Information About a Microservice Instance
- Modifying Status of a Microservice Instance
- Sending Heartbeat Information
- Querying a Microservice Instance by Filter Criteria
- Querying Microservice Instances in Batches
- Dependency
- Configuration Management
- Examples
- Data Structure
- Permissions and Supported Actions
- Appendix
-
Historical APIs
-
Application Management V2 APIs
- Meta
- Environment
-
Application
- Creating an Application
- Obtaining All Applications
- Modifying Application Information
- Deleting an Application Based on the Application ID
- Obtaining Application Details Based on the Application ID
- Modifying Application Configurations
- Deleting Application Configurations
- Obtaining Application Configurations
- Component
- Instance
- Deployment Jobs
- Build APIs
- Querying Configurations
- Creating a Dependency Between Services
- Reporting Service Metrics
-
Application Management V2 APIs
- SDK Reference
-
FAQs
- Application Development FAQs
- Environment Management
-
Application Management
- How Do I View the Causes of Application Component Deployment Failures?
- What If an Instance Is Being Created for a Long Time?
- How Do I Solve the Dependency Problem When a Node Program Runs in Docker?
- How Do I Customize a Tomcat Context Path?
- How Do I Use a Fixed Application Component IP?
- What Should I Do If an ECS Error Occurs When I Create and Deploy a Component on a VM?
- What Should I Do If I Cannot Access the Port When I Create and Deploy a Component on a VM?
- Which Directories Do I Use to Write Files for VM-Deployed Application Components?
- What Should I Do If "host status is not active" Is Reported When a VM-Deployed Component Fails to Be Deleted?
- How Do I Use the ServiceStage Source Code Deployment Function?
- What Should I Do If Components Fail to Be Upgraded in ServiceStage Dark Launch?
- How Do I Mount Items to Modify the Configuration File of a Container-based Component?
- What Should I Do If the Application Name Displayed on Microservice Governance Is Different from That Displayed on ServiceStage Application Management After an Application Component Is Connected to a Microservice Engine?
-
Continuous Delivery
- How Does ServiceStage Manage Code on IDEA?
- How Do I Add the Build Server Address to the GitLab Server Security Group?
- How Do I Add the Build Server Address to the Maven Server Security Group?
- What Do I Do If ServiceStage Failed to Build a Job?
- How Can I Access Dependent Services Through VPC Endpoints When Building Images?
- Software Center
-
Infrastructure
- Are Existing Programs Affected If I Unsubscribe Servers?
- How Can I Access Dependent Services Through VPC Endpoints When Installing VM Agents?
- What Should I Do If I Don't See the VM Agent After Installing It?
- What Should I Do If the VM Agent Is Offline?
- What Should I Do If the Service Registration Fails After IPv6 Is Enabled for the Exclusive Microservice Engine with Security Authentication Enabled?
- What Should I Do If a Non-Microservice Engine Error Occurs When I Operate an Exclusive Microservice Engine?
- How Do I Switch a Cluster Used for Component Building from a Shared Cluster to a Private One?
- What Should I Do If the Access Address Fails to Be Processed During CSE Creation?
- What Do I Need to Know Before Upgrading an Exclusive Microservice Engine?
- Obtain Configurations Failed
- Application O&M
-
Application Development
- What Are the Differences Between the Microservice and Common Application?
- How Do I Handle a Microservice Registry Failure (Java Chassis)?
- How Do I Troubleshoot Microservices Deployed on the Cloud?
- Should I Use the SDK or ServiceMesh to Build a Microservice?
- What If I Fail to Obtain a Dependency?
- What Is Service Name Duplication Check?
- Why Do I Have to Define Service Contracts?
- Why Are Microservice Development Framework and Netty Versions Unmatched?
- How Do I Package a Java or Tomcat Application?
-
More Documents
-
User Guide (ME-Abu Dhabi Region)
- Service Overview
- Getting Started
-
User Guide
- Overview
- Permissions Management
- Application Management
- Environment Management
-
Application O&M
- Maintaining Application Component Instances
- Adding Labels for Application Component Instances
- Configuring Domain Name Mappings
- Configuring Alarm Thresholds for Resource Monitoring
- Configuring a Scaling Policy of an Application Component Instance
- Configuring a Scheduling Policy of an Application Component Instance
- Configuring an Upgrade Policy of an Application Component Instance
- Configuring Custom Monitoring of an Application Component
- Configuring a Log Policy of an Application
- Configuring Health Check
- Continuous Delivery
- Software Center
-
Infrastructure
-
Cloud Service Engine (CSE)
- Overview
- Creating an Exclusive Microservice Engine
-
Microservice Engine Management
- Configuring Backup and Restoration of an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Configuring Public Network Access of an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Viewing the Access Address of a Microservice Engine
- Viewing Operation Logs of an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Upgrading an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Deleting an Exclusive Microservice Engine
- Using the Microservice Dashboard
- Microservice Governance
- Configuring Microservices
- Maintaining Microservices
- Installing VM Agent on a Single VM
-
Cloud Service Engine (CSE)
-
FAQs
- How Do I Obtain an AK/SK Pair?
- What Should I Do If an Error Occurs When I Change the Name of a Project ?
- What Are the Differences Between Microservices and Common Applications?
- How Do I View the Causes for Application Component Deployment Failures?
- What Should I Do If a VM Component Fails to Be Deployed or Updated?
- What Are the Constraints on Packaging a Node.js 8 Software Package?
- What Should I Do If the Agent Fails to Be Installed?
- What Should I Do If the Agent Is Offline?
- Which Directories Do I Use to Write Files for VM-based Application Components?
- What Should I Do If "host status is not active" Is Reported When a VM-based Component Fails to Be Deleted?
- How Do I Handle Docker Application Dependency?
- What Should I Do If Docker Client Fails to Push Images?
- How Do I Obtain a Project Name?
- What Should I Do If the Service Registration Fails After IPv6 Is Enabled for the Exclusive Microservice Engine with Security Authentication Enabled?
- What Should I Do If a Non-Microservice Engine Error Occurs When I Operate an Exclusive Microservice Engine?
- What Should I Do I Get an ECS Error When Deploying VM-based Components?
- What Should I Do If an ECS Error Occurs During VM-based Component Deployment?
- What Should I Do If I Cannot Access the Port During VM-based Deployment?
- What Should I Do If the Microservice Application Name Is Different from the Component Application Name?
- Why the Microservice Name Is Different from the Component Name?
- Failed to Restore Data of an Exclusive Microservice Engine
-
API Reference (ME-Abu Dhabi Region)
- Before You Start
- API Overview
- Calling APIs
-
Application Management APIs
- Meta
- Environment
-
Application
- Creating an Application
- Obtaining All Applications
- Modifying Application Information
- Deleting an Application Based on the Application ID
- Obtaining Application Details Based on the Application ID
- Adding or Modifying Application Configurations
- Deleting Application Configurations
- Obtaining Application Configurations
- Component
-
Instance
- Creating an Application Component Instance
- Obtaining All Instances of a Component
- Querying the Operations Performed on a Component Instance
- Modifying an Application Component Instance
- Deleting an Application Component Instance
- Querying Instance Details Based on the Instance ID
- Obtaining Component Instance Snapshots
- Job
-
Git Repository Access APIs
- Obtaining a Git Repository Authorization List
- Obtaining an Authorization Redirection URL
- Creating OAuth Authorization
- Creating Private Token Authorization
- Creating Password Authorization
- Deleting Repository Authorization
- Obtaining a Repository Namespace
- Obtaining Repository Information Based on the Clone URL
- Obtaining All Projects in a Namespace
- Creating a Software Repository Project
- Obtaining a Project Branch
- Obtaining a Project Tag
- Creating a Project Tag
- Deleting a Project Tag
- Obtaining Project Commits
- Obtaining a Project Hook
- Creating a Project Hook
- Deleting a Project Hook
- Obtaining a Repository File Directory
- Obtaining Repository File Contents
- Creating a Repository File
- Modifying Repository File Contents
- Deleting a Repository File
-
CSE API
- API Calling
- Querying Static Information About a Microservice
- Querying Static Information About All Microservices
- Creating Static Information for a Microservice
- Modifying Static Information About a Microservice
- Querying a Microservice Schema
- Modifying a Microservice Schema
- Creating a Dependency Between Services
- Querying All Providers of a Microservice
- Querying the Unique Service or Schema ID of a Microservice
- Registering a Microservice Instance
- Querying All Instances of a Microservice Based on the Service ID
- Deregistering a Microservice Instance
- Querying Details About a Microservice Instance
- Modifying the Extended Information About a Microservice Instance
- Changing the Status of a Microservice Instance
- Sending Heartbeat Information
- Querying a Microservice Instance by Filter Criteria
- Querying Configurations
- Deleting Static Information About a Microservice
- Deleting Static Information About Microservices in Batches
- Querying Microservice Instances in Batches
- Querying All Schema Information About a Microservice
- Data Structure
- Permissions Policies and Supported Actions
- Appendix
-
User Guide (Kuala Lumpur Region)
- Service Overview
- Getting Started
- Overview
- Permissions Management
- Environment Management
- Application Management
-
Component Management
- Component Overview
- Creating and Deploying a Component
- Viewing Component Details
- Managing Component Labels
- Managing Component Instances
- Upgrading a Single Component
- Upgrading Components in Batches
- Rolling Back a Component
- Redeploying a Component
- Setting the Access Mode of Components
- Changing the Component Access Domain Name
- Configuring a Scaling Policy of a Component Instance
- Component O&M
- Viewing the Component Running Environment
- Component Instance Start and Stop
- Deleting a Component
-
Component Advanced Setting
- Setting Component Environment Variables
- Configuring the Lifecycle of a Component
- Configuring Data Storage
- Configuring a Distributed Cache
- Configuring Relational Databases
- Configuring a Scheduling Policy of a Component Instance
- Configuring a Log Policy of an Application
- Configuring Custom Monitoring of a Component
- Configuring Health Check
- Deployment Source Management
- Continuous Delivery
-
Microservice Engine
- Cloud Service Engine Overview
- Creating a Microservice Engine
-
Managing Microservice Engines
- Viewing Microservice Engine Information
- Obtaining the Service Center Address of a Microservice Engine
- Obtaining the Configuration Center Address of a Microservice Engine
- Viewing the Quota of Microservice Engine Instances
- Viewing the Quota of Microservice Engine Configuration Items
- Configuring Backup and Restoration of a Microservice Engine
- Managing Public Network Access for a Microservice Engine
- Viewing Microservice Engine Operation Logs
- Upgrading a Microservice Engine Version
- Deleting a Microservice Engine
- Managing Security Authentication of a Microservice Engine
- Using Microservice Engines
- Key Operations Recorded by CTS
- Viewing Monitoring Metrics and Alarms
-
FAQs
- Application Development FAQs
- Environment Management
-
Application Management
- How Do I View the Causes of Application Component Deployment Failures?
- What If an Instance Is Being Created for a Long Time?
- How Do I Solve the Dependency Problem When a Node Program Runs in Docker?
- How Do I Customize a Tomcat Context Path?
- How Do I Use a Fixed Application Component IP?
- How Do I Use the ServiceStage Source Code Deployment Function?
- Continuous Delivery
- Infrastructure
- Application O&M
-
API Reference (Kuala Lumpur Region)
- Before You Start
- API Overview
- Calling APIs
-
Application Management APIs
- Meta
- Environment
-
Application
- Creating an Application
- Obtaining All Applications
- Modifying Application Information
- Deleting an Application Based on the Application ID
- Obtaining Application Details Based on the Application ID
- Adding or Modifying Application Configurations
- Deleting Application Configurations
- Obtaining Application Configurations
- Component
-
Instance
- Creating an Application Component Instance
- Obtaining All Instances of a Component
- Querying the Operations Performed on a Component Instance
- Modifying an Application Component Instance
- Deleting an Application Component Instance
- Querying Instance Details Based on the Instance ID
- Obtaining Component Instance Snapshots
- Job
-
CSE API
- API Calling
- Querying Static Information About a Microservice
- Querying Static Information About All Microservices
- Creating Static Information for a Microservice
- Modifying Static Information About a Microservice
- Querying a Microservice Schema
- Modifying a Microservice Schema
- Creating a Dependency Between Services
- Querying All Providers of a Microservice
- Querying the Unique Service or Schema ID of a Microservice
- Registering a Microservice Instance
- Querying All Instances of a Microservice Based on the Service ID
- Deregistering a Microservice Instance
- Querying Details About a Microservice Instance
- Modifying the Extended Information About a Microservice Instance
- Changing the Status of a Microservice Instance
- Sending Heartbeat Information
- Querying a Microservice Instance by Filter Criteria
- Querying Configurations
- Deleting Static Information About a Microservice
- Deleting Static Information About Microservices in Batches
- Querying Microservice Instances in Batches
- Querying All Schema Information About a Microservice
- Data Structure
- Permissions Policies and Supported Actions
- Appendix
-
User Guide (ME-Abu Dhabi Region)
- Videos
- General Reference
Copied.
Managing Namespace Quotas
By default, pods running in a CCE cluster can use the CPUs and memory of a node without restrictions. This means that pods in a namespace may exhaust all resources of the cluster.
Kubernetes provides namespaces for you to group workloads in a cluster. By setting resource quotas for each namespace, you can prevent resource exhaustion and ensure cluster reliability. You can configure quotas for resources such as CPU, memory, and the number of pods in a namespace. For more information, see Resource Quotas.
Prerequisites
- A CCE cluster has been bound to the environment. For details, see Binding a CCE Cluster.
- The CCE cluster bound to the environment has a user-created namespace or the cluster-created namespace default.
Managing Namespace Resource Quotas
- Log in to ServiceStage.
- Choose Environment Management. The Environment Management page is displayed.
- Click the target environment. The Overview page is displayed.
- Choose Cloud Container Engine from Compute.
- Go to the Namespace page.
- For an HA environment, click the cluster that has been bound in the environment and click the Namespace tab.
- For a non-HA environment, click the Namespace tab.
- Click Resource Quota Manager in the Operation column of the target namespace.
In the displayed Resource Quota Manager dialog box, view the resource types, total resource quotas, and accumulated quota usage in the namespace.Figure 1 Accessing the Resource Quota Manager page
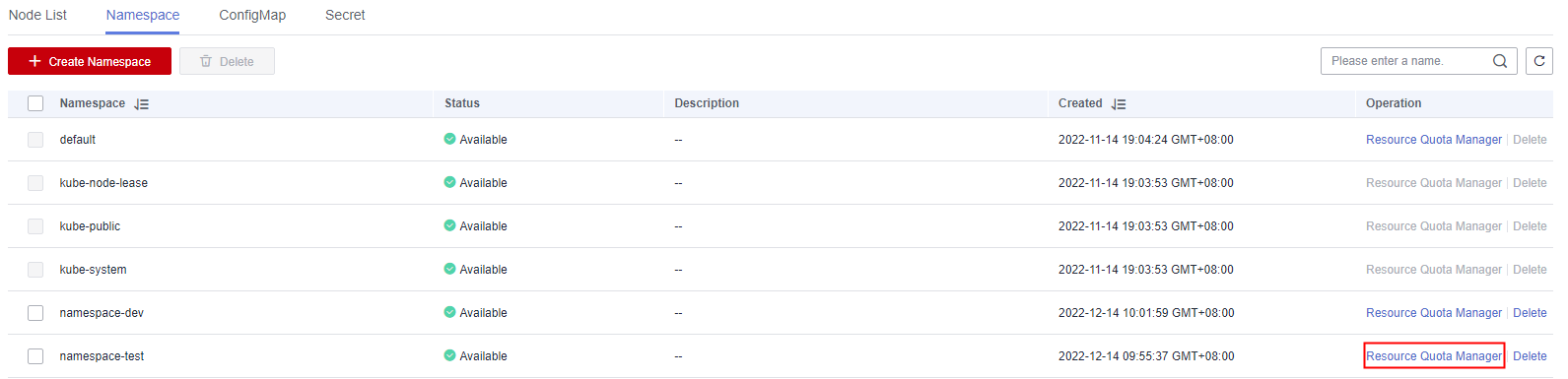
- Click Edit Quota and set the total quota of each resource type.
- If the usage of a resource type is not limited, leave it blank.
- If the usage of a resource type is limited, enter an expected integer ranging from 1 to 9,007,199,254,740,992.
NOTICE:
- Accumulated quota usage includes the default resources created by CCE, such as the Kubernetes service (which can be viewed using kubectl) created under the default namespace. Therefore, you are advised to set a resource quota slightly greater than expected.
- If the total CPU or memory quota in a namespace is limited, you must set the maximum and minimum number of CPU cores and memory (GiB) that can be used by the component when setting resources for the Kubernetes component of this namespace in Creating and Deploying a Component and Upgrading a Single Component. Otherwise, the operation will fail.
- If the total quota of other resource types in a namespace is limited and the remaining usage of this resource type does not meet requirements, the Kubernetes component of this namespace will fail to be deployed.
- Click OK.
On the Resource Quota Manager page, view the total resource quota and accumulated quota usage of the resource type whose quota has been reset.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot




