When a bucket is accessed, OBS logs all the requests for the bucket. After logging is enabled for the bucket, OBS stores the logs either in the logged bucket or another bucket that belongs to the same account and region as the logged bucket. You can search and analyze these logs to trace and locate abnormal events. This section describes how to configure logging, verify the logging configuration, and disable logging for a bucket.
Configuring Logging for a Bucket
You can use OBS Console, APIs, or SDKs to configure logging for a bucket.
Using OBS Console
- In the navigation pane of OBS Console, choose Object Storage.
- In the bucket list, click the bucket you want to operate. The Objects page is displayed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Overview.
- In the Basic Configurations area, click Logging. The Logging dialog box is displayed.
- Select Enable. For details, see Figure 1.
Figure 1 Logging

- Configure parameters.
Table 1 Parameters for configuring logging for the bucket
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Save Logs To |
Specifies the target bucket for storing log files of the source bucket.
You can select the source bucket or another bucket as the log storage bucket. If you choose another bucket, it must belong to the same account and region as the source bucket.
Once a log storage bucket is specified, OBS automatically grants log delivery users the write and ACL read permissions for that bucket. |
|
Log File Name Prefix |
Specifies the prefix of the log file name. By default, OBS assigns the Bucket name-log/ prefix. This prefix represents a folder (for storing log files) in the root directory of the bucket.
After logging is enabled, generated log files are named in the following format:
<Log File Name Prefix>YYYY-mm-DD-HH-MM-SS-<UniqueString>
- <Log File Name Prefix> is the prefix of the log file name, which is the parameter to be set here.
- If <Log file name prefix> ends with a slash (/), the bucket's log files are stored in the folder named <Log file name prefix> in the target bucket. Each log file is named YYYY-mm-DD-HH-MM-SS-<UniqueString>, for example, 2025-06-03-07-18-11-WKK0T9O74VAWMHB7.
- If <Log file name prefix> does not end with a slash (/), the bucket's log files are stored in the root directory of the target bucket. Each log file is named <Log file name prefix>YYYY-mm-DD-HH-MM-SS-<UniqueString>, for example, example-bucket-a-log2025-06-03-07-18-11-WKK0T9O74VAWMHB7.
- YYYY-mm-DD-HH-MM-SS indicates when the log file was generated.
- <UniqueString> indicates a character string assigned by OBS.
|
|
IAM Agency |
An agency is required to grant OBS permissions to upload log files to the log storage bucket.
- By default, you only need to grant the agency the upload permission (obs:object:PutObject) for the log storage bucket.
- If the log storage bucket has Server-Side Encryption enabled, the agency also requires the KMS Administrator permission for the region where the bucket is located.
You can choose an existing IAM agency from the drop-down list or click Create Agency to create one.
To create an agency, see Creating an Agency for Uploading Logs. |
- Click OK.
After logging is configured for a bucket, its operation logs will appear in the log storage bucket in about fifteen minutes.
Verifying the Logging Configuration of a Bucket
After configuring logging for a bucket, you can use OBS Console, APIs, SDKs, or obsutil to verify the logging configuration. You can check whether OBS has generated log files and whether you have access to them.
Using OBS Console
- In the navigation pane of OBS Console, choose Object Storage.
- In the bucket list of OBS Console, click the log storage bucket to go to the Objects page.
- Check whether log files exist.
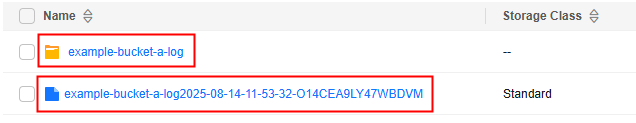
Check whether log files exist or whether the folder for storing log files exists in the object list based on the configured log file name prefix and log file naming rules.
Figure 2 Checking the log folder or log files
- Check whether you can access the log files.
- In the object list or in the log folder, click the name of a log file. The Basic Information page is displayed.
- Click
 next to the link to copy the link of the log file.
next to the link to copy the link of the log file.
- Open this link in a browser.
Using SDKs
- Check whether log files exist.
Use the following SDKs to list all objects in the bucket. Then, check whether log files exist in the list based on the log file name prefix and log file naming rules.
- Download log files.
Use the following SDKs to download log files.
Using the CLI Tool - obsutil
- Check whether log files exist.
List all objects in the bucket by referring to Listing Objects. Then, check whether log files exist in the list based on the log file name prefix and log file naming rules.
- Download log files.
Download log files by referring to Downloading an Object.
Disabling Logging for a Bucket
Uploading and storing bucket logs will incur costs for PUT requests and storage. If you no longer need to record logs, disable logging for the bucket. After logging is disabled, OBS stops recording new logs, but existing logs in the log storage bucket will be retained.
You can use OBS Console to disable logging for a bucket.
Using OBS Console
- In the navigation pane of OBS Console, choose Object Storage.
- In the bucket list, click the bucket you want to operate. The Objects page is displayed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Overview.
- In the Basic Configurations area, click Logging. The Logging dialog box is displayed.
- Select Disable and then click OK.
References
Creating an Agency for Uploading Logs
- In the Logging dialog box, click Create Agency to jump to the Agencies page on the Identity and Access Management console.
- Click Create Agency. On the displayed page, set the parameters related to the agency for uploading logs and retain the default settings for other parameters.
Table 2 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Agency Name |
Name of the agency to be created
The agency name cannot be left blank. |
|
Agency Type |
You can grant permissions to another account or cloud service for managing resources in your account.
Select Cloud service for Agency Type. |
|
Cloud Service |
You can grant permissions to a cloud service for managing resources in your account. This parameter is mandatory when Agency Type is set to Cloud service.
Select Object Storage Service (OBS) for Cloud Service. |
- Click OK. In the Agency Created dialog box that is displayed, click Cancel. If the newly created agency is displayed in the agency list, the agency is created successfully.
- Create a custom policy to grant OBS permissions to the agency. If a policy that meets the requirements already exists, skip this step.
- In the navigation pane of the IAM console, choose Permissions > Policies/Roles.
- On the Policies/Roles page, click Create Custom Policy in the upper right corner.
- On the Create Custom Policy page, set the parameters as follows and retain the default settings for other parameters.
Figure 3 Configuring a custom policy
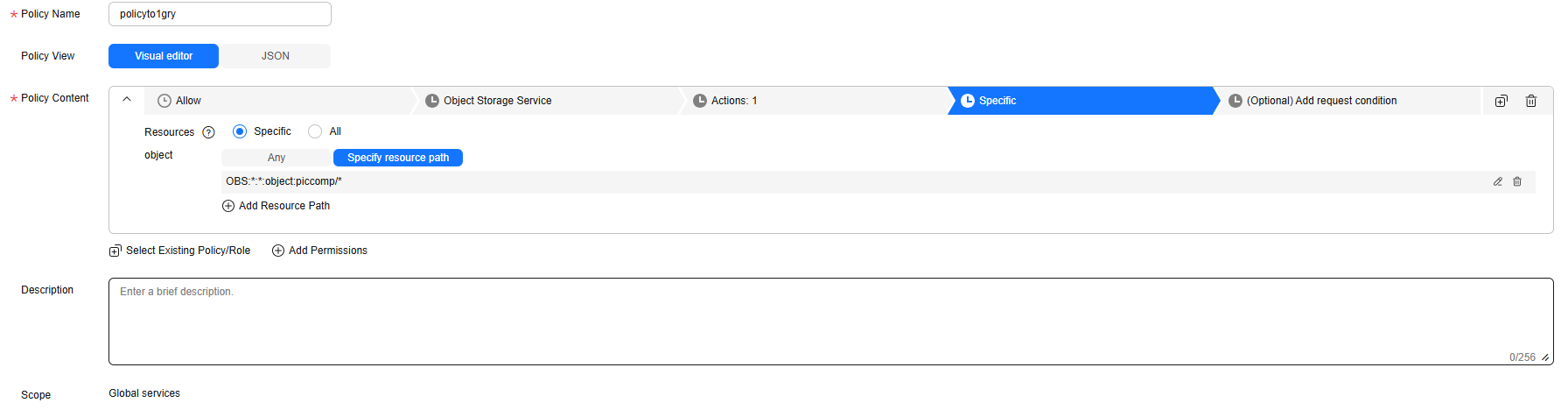
- Policy Name: Enter a name that is easy to remember.
- Select service: Select Object Storage Service (OBS).
- Actions: Select obs:object:PutObject.
- Resources: Select Specific.
object: Select Specify resource path. The resource path format is OBS:*:*:object:Bucket name/Object name.
Replace Bucket name with the name of the log storage bucket. For example, OBS:*:*:object:piccomp/* indicates all objects in the log storage bucket piccomp.
- Click OK. If the created custom policy is displayed in the policy list, the policy is created successfully.
- Grant OBS permissions to the created agency.
- In the navigation pane of the IAM console, choose Agencies.
- Click Authorize in the Operation column of the agency created in 2.
- On the Select Policy/Role page, select the custom policy created in 4 and click Next.
- On the Select Scope page, select All resources and click OK.
- In the Information dialog box that is displayed, click OK.
- On the Finish page, click Finish.
- (Optional) If the log storage bucket has server-side encryption enabled, the agency also requires the KMS Administrator permission for the region where the bucket is located.
- In the navigation pane of the IAM console, choose Agencies.
- Click Authorize in the Operation column of the agency created in 2.
- On the Select Policy/Role page, search for and select KMS Administrator. Then, click Next.
- Select Region-specific projects for Scope, and select the project in the region where the log bucket resides.
- Click OK.