Device Reporting Messages
Introduction
Message reporting is a method by which a device directly sends data to the cloud and forwards the data to applications or other Huawei Cloud services through data forwarding. The platform does not parse or store the messages reported by devices. In this case, a product model is not required.
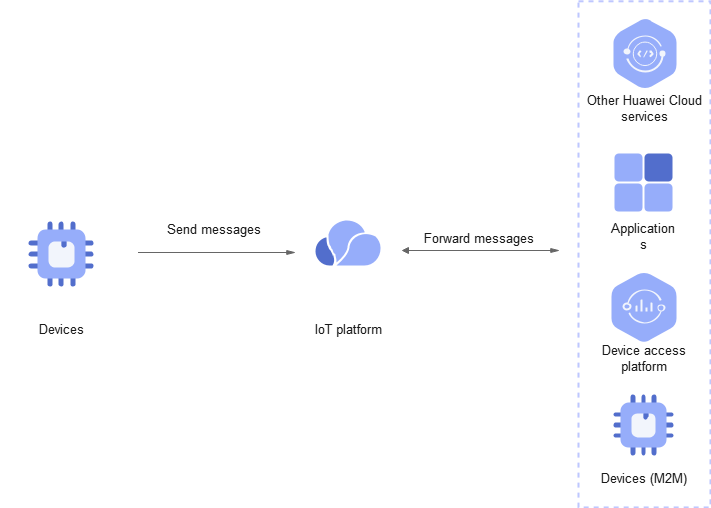
Scenarios
IoTDA does not parse or store the data reported by devices. Instead, it forwards the data to other Huawei Cloud services for storage and processing based on data forwarding rules.
Constraints
- Max. size of a single message: 1 MB.
- Max. bandwidth of a single MQTT connection: 1 Mbit/s.
- Max. upstream messages for a single MQTT connection per second: 50 (one request is considered as one message).
Process

- Product and device creation: For details, see Creating a Product and Registering an Individual Device.
- Device authentication: The platform checks whether the device has the access permission.
- Device message reporting: Devices report messages through protocols such as MQTT and HTTPS.
Use different APIs for different protocols.
MQTT: Use the message reporting APIs for MQTT devices.
- Example topic of MQTT message reporting:
$oc/devices/{device_id}/sys/messages/up - Example format of MQTT message reporting:
{ "content": {"hello":"123"} }
HTTPS: Use the message reporting APIs for HTTP devices. To obtain access_token for HTTP devices, see Authenticating a Device. The following is an example of HTTPS device message reporting.POST https://{endpoint}/v5/devices/{device_id}/sys/messages/up Content-Type: application/json access_token: ******** { "name": "name", "id": "id", "content": "messageUp" }
For details about devices using different protocols, see MQTT Device Reporting a Message and HTTP Device Reporting a Message.
- Example topic of MQTT message reporting:
- Data forwarding: With the data forwarding function, data can be forwarded to applications or other Huawei Cloud services for further processing.
Message Reporting Using Java SDK
This section describes how to use Java SDKs for the development of message reporting. JDK 1.8 or later is used.
Configure the SDK on the device side:
- Download an SDK.
- Configure the Maven dependency of the SDK on devices.
<dependency> <groupId>com.huaweicloud</groupId> <artifactId>iot-device-sdk-java</artifactId> <version>1.1.4</version> </dependency>
- Configure the SDK and device connection parameters on devices.
// Load the CA certificate of the IoT platform. For details about how to obtain the certificate, visit https://support.huaweicloud.com/intl/en-us/devg-iothub/iot_02_1004.html. URL resource = BroadcastMessageSample.class.getClassLoader().getResource("ca.jks"); File file = new File(resource.getPath()); // The format is ssl://Access address:Port number. // To obtain the access address, log in to the IoTDA console. In the navigation pane, choose Overview and click Access Details in the Instance Information area. Select the access address corresponding to port 8883. String serverUrl = "ssl://localhost:8883"; // Device ID created on the platform String deviceId = "deviceId"; // Secret corresponding to the device ID String deviceSecret = "secret"; // Create a device. IoTDevice device = new IoTDevice(serverUrl, deviceId, deviceSecret, file); if (device.init() != 0) { return; }
- Report a device message.
device.getClient().reportDeviceMessage(new DeviceMessage("hello"), new ActionListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Object context) { log.info("reportDeviceMessage success: "); } @Override public void onFailure(Object context, Throwable var2) { log.error("reportDeviceMessage fail: "+var2); } });
Verify the setting:
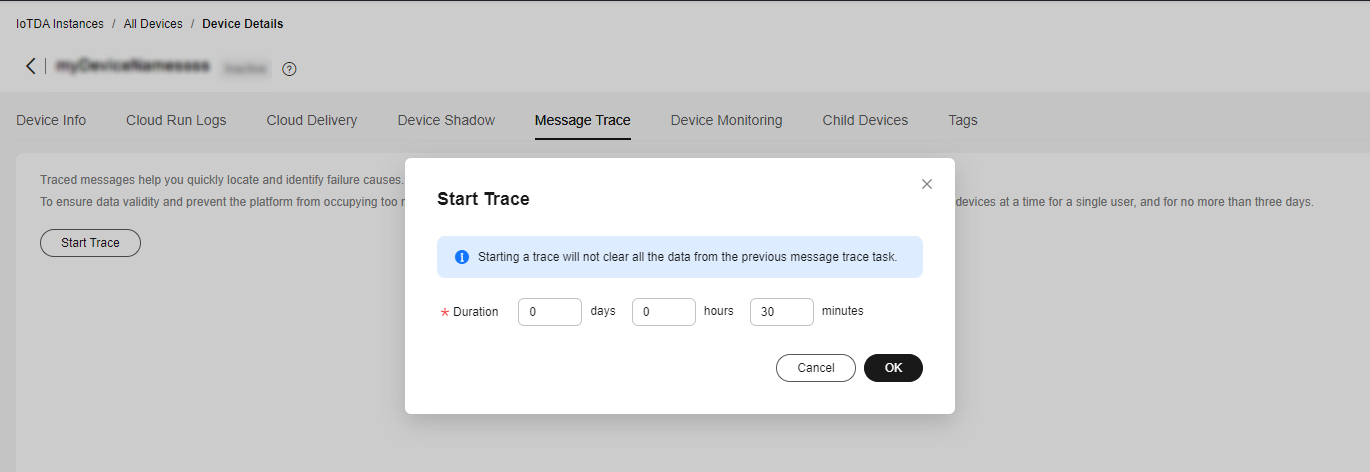
- On the IoTDA console, choose Devices > All Devices, select a device to access its details page, and click Start Trace on the Message Trace tab page.
Figure 3 Message tracing - Starting message tracing
- Run the SDK code on the device. The following is an example of the log format when the device reports properties.
Figure 4 Java SDK message reporting result log

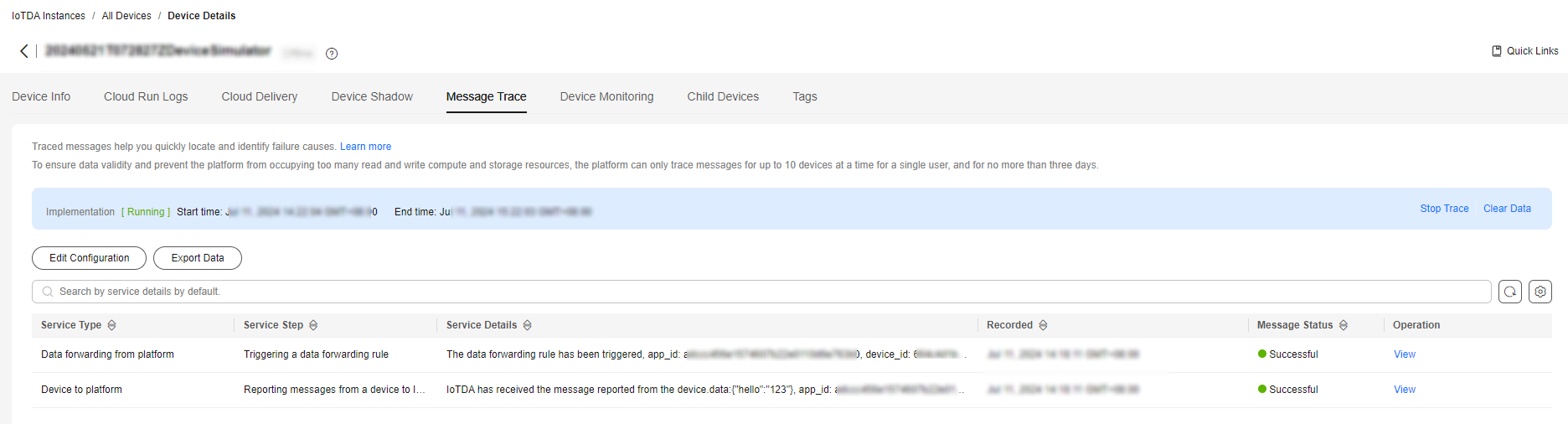
- Check the result on the Message Trace tab page. The platform has received messages from the device and the data forwarding rule has been triggered.
Figure 5 Message tracing - Message reporting triggering a forwarding rule
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





