Reserved Instances
Overview
FunctionGraph provides on-demand and reserved instances.
- On-demand instances are created and released by FunctionGraph based on actual function usage. When receiving requests to invoke functions, FunctionGraph automatically allocates execution resources to the requests.
- Reserved instances are created and released by yourself. If a reserved instance is created for a function, FunctionGraph will forward invocation requests to the reserved instance. If the request peak exceeds the processing capability of the reserved instances, FunctionGraph sends the excess requests to on-demand instances and automatically allocates the required environments.
After reserved instances are created for a function, the code, dependencies, and initializer of the function are automatically loaded. Reserved instances are always alive in the execution environment, eliminating the influence of cold starts on your services. Do not execute one-time services using the initializer of reserved instances.
FunctionGraph supports Configuring a Fixed Number of Reserved Instances, Configuring a Scheduled Scaling Policy, and Configuring an Intelligent Recommendation Policy.
By default, you do not have permission to use the metric and intelligent recommendation policies. To use them, submit a service ticket.
Video Tutorial
This video introduces the background, application scenarios, and functions of intelligent recommendation of reserved instances.
As product functions evolve, the GUI may vary. This tutorial is for reference only.
Notes and Constraints
- Reserved instances cannot be configured for both a function alias and the corresponding version. For example, if the alias of the latest version is 1.0 and reserved instances have been configured for this version, no more instances can be configured for alias 1.0.
- After the idle mode is enabled, reserved instances are initialized and the mode change needs some time to take effect. You will still be billed at the price of reserved instances for non-idle mode in this period.
- If the function concurrency is greater than the number of reserved instances, the excess requests will be allocated to on-demand instances, which involve a cold start.
Billing Description
You will be billed for reserved instances on a pay-per-use basis. For details about the billing rules and items, see FunctionGraph Billing Items.
Prerequisites
You have configured an agency with permissions for querying AOM metrics and function configurations for the function. For details, see Configuring Agency Permissions.
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console. In the navigation pane, choose Functions > Function List.
- Click the name of a function.
- Choose Configuration > Concurrency.
- Click Add and configure the reserved instance policy.
The number of reserved instances cannot exceed the concurrency quota and Max. Instances per Function.Figure 1 Basic settings
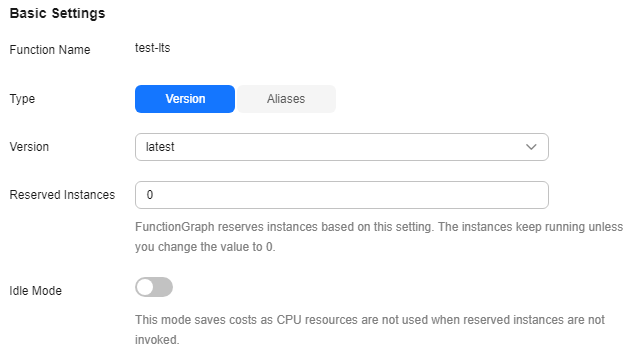
Table 1 Basic settings Parameter
Description
Function Name
Name of the current function.
Type
Whether to configure reserved instances for a function version or alias.
Version
This parameter is mandatory only when Type is set to Version.
Select the version of the function for which you want to configure reserved instances.
Alias
This parameter is mandatory only when Type is set to Aliases.
Select the alias of the function for which you want to configure reserved instances. Aliases of additional versions are supported.
Reserved Instances
Number of reserved instances. The value is an integer ranging from 1 to 1000. After it is configured, FunctionGraph creates a fixed number of function instances for the function and keeps them running.
Idle Mode
This mode saves costs as CPU resources are not used when reserved instances are not invoked.
Auto Scaling Policies
If the number of reserved instances is fixed, you do not need to configure this parameter.
- Click OK.
You can configure a scheduled policy for reserved instances. The number of reserved instances can be updated within a specified period. After this period, the number of reserved instances is restored to the Reserved Instances specified in the basic settings.
- For details about how to configure the basic settings of a reserved instance policy, see Configuring a Fixed Number of Reserved Instances.
- In the dialog box for adding reserved instance policies, click Add Policy and add an auto scaling policy by referring to Table 2.
Table 2 Parameters for configuring a scheduled policy Parameter
Description
Policy Type
Select Scheduled.
Policy Name
Name of a custom policy. The name can contain a maximum of 60 characters and must start with a letter and end with a letter or digit. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed.
Cron Expression (UTC)
Use a Cron expression to set the time when the number of reserved instances in the scheduled policy takes effect. For details about how to set a Cron expression, see Cron Expression Rules.
Validity
Time window when the scheduled policy takes effect. The scheduled policy takes effect only when the time is within the time window. If no scaling policy in the reserved instance policy takes effect, the number of reserved instances is restored to the value in the Basic Settings.
Reserved Instances
Number of reserved instances that need to be created when the scheduled policy takes effect. The value must be greater than or equal to the number of reserved instances configured in Configuring a Fixed Number of Reserved Instances.
- Click OK. The scheduled policy is added.
Figure 2 Policy list
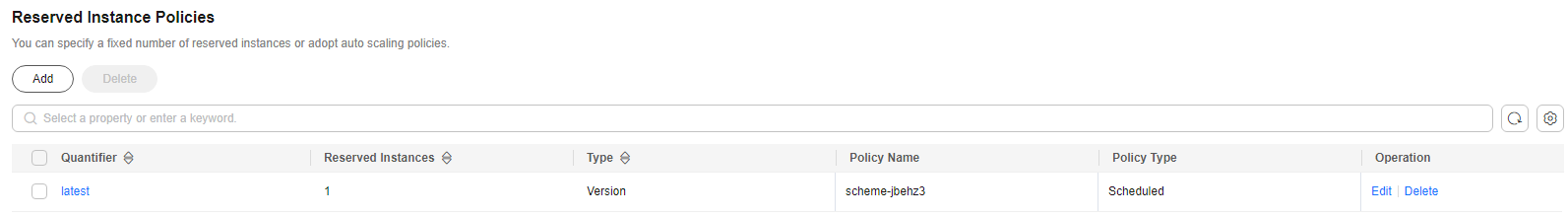
- Click OK. The reserved instance policy is configured.
- Multiple scheduled policies can be configured. For example, the number of reserved instances at 08:00 and 21:00 is updated to 100 and 10 respectively.
- After the configuration is complete, you can click the name of a reserved instance policy in the Reserved Instance Policies area, and click the name of an auto scaling policy to view the number of instances concurrently executed by the function.
Multiple scheduled policies can be configured. For example, the number of reserved instances at 08:00 and 21:00 is updated to 100 and 10 respectively.
Intelligent recommendation policies are based on feature profiling and load prediction technologies, dynamically adjusting reserved instances for peak and off-peak demands.
You can add an intelligent recommendation policy to reserved instances. FunctionGraph will update the number of reserved instances based on function load.
Intelligent recommendation policies are available in three options: high performance, balance, and low cost. The system dynamically adjusts the number of reserved instances based on load prediction to adapt to the peak and off-peak loads. The cost and performance of reserved instances are displayed. (Intelligent recommendation policies cannot coexist with other types of policies. A function version or alias can have only one such policy.)
- For details about how to configure the basic settings of a reserved instance policy, see Configuring a Fixed Number of Reserved Instances.
- In the dialog box for adding reserved instance policies, click Add Policy and add an auto scaling policy by referring to Table 3.
Figure 3 Intelligent recommendation
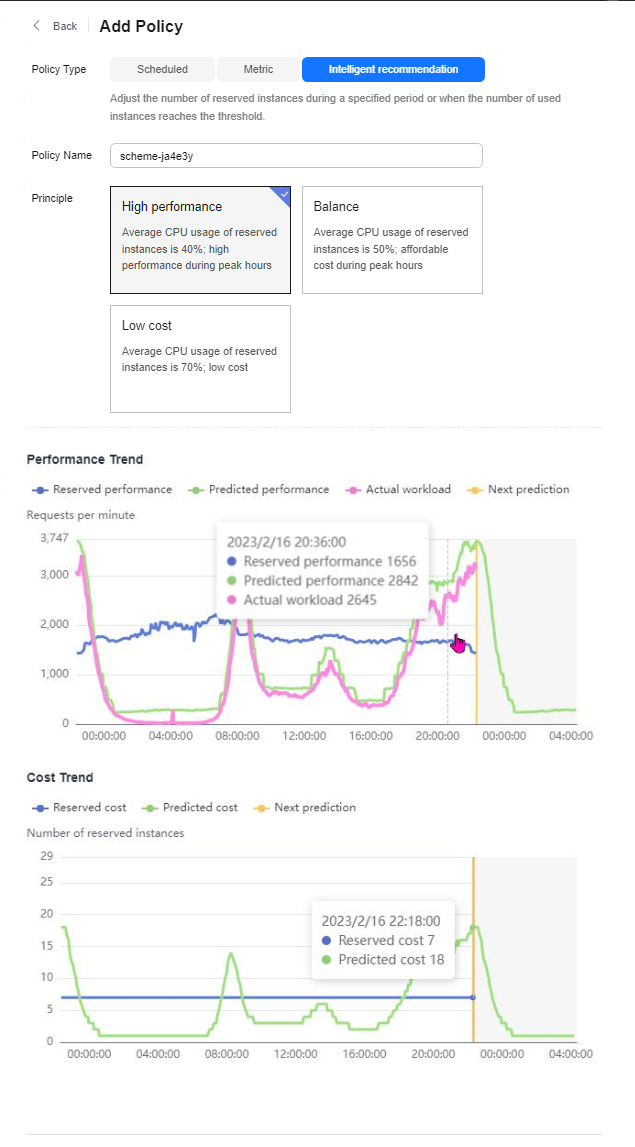
Table 3 Parameters for configuring an intelligent recommendation policy Parameter
Description
Policy Type
Select Intelligent recommendation.
Policy Name
Name of a custom policy. The name can contain a maximum of 60 characters and must start with a letter and end with a letter or digit. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed.
Principle
Select the execution mode of the intelligent policy based on service requirements. The options are High performance, Balance, and Low cost.
- High performance: Average CPU usage of 40%; high performance during peak hours
- Balance: Average CPU usage of 40%; affordable cost during peak hours
- Low cost: Average CPU usage of 70% and low cost
- Click OK. The intelligent recommendation policy is added.
Figure 4 Reserved Instance Policies

- Click OK. The reserved instance policy is configured.
After the configuration is complete, you can click the name of a reserved instance policy in the Reserved Instance Policies area, and click the name of an auto scaling policy to view the cost and performance statistics of reserved instances.
Helpful Links
- For details about function instance types and their usage modes, see Function Instance Types and Usage Modes.
- Manage reserved instances using APIs. For details, see Reserved Instances APIs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





