Streaming Response
Overview
To meet the requirements of web and AI applications for real-time data transmission and large packet transmission, you can configure the streaming response for the function to return response packets to the client in HTTP streaming mode.
Advantages:
- Supports larger response packets (up to 200 MB).
- Reduces memory usage by processing and transmitting data in batches instead of transferring the entire packets at once.
- Enables faster time to first byte through streaming transmission.
Scenarios:
- Processing large files or big data sets (such as images and videos)
- Real-time data processing (for example, AI applications using Server-Sent Events (SSE) for data transmission)
Notes and Constraints
- Currently, streaming response is supported only in the CN Southwest-Guiyang1 and CN North-Beijing4 regions.
- Streaming response is supported only for container image-based functions, custom runtime functions, and HTTP functions.
- The maximum size of a streaming response is 200 MB.
- Streaming responses support only synchronous invocation, and the maximum execution timeout is 300s.
Configuring Streaming Response
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console. In the navigation pane, choose Functions > Function List.
- Click the name of a function. Choose Configuration > Advanced Settings.
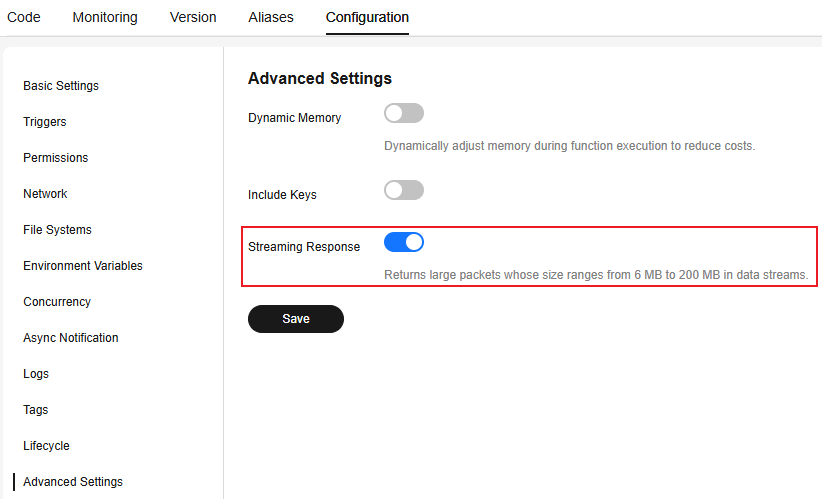
- Enable Streaming Response and click Save.
Figure 1 Enabling streaming response
Compiling Code for a Function with Streaming Response Enabled
The following are code examples of container image-based functions, HTTP functions, and custom runtime functions.
Create a container image-based function by referring to Creating a Function with an Image and enable streaming response. Note that the function execution timeout must be less than 300s. Otherwise, the function will fail to be saved.
To ensure that the function can correctly return streaming data, write streaming data in batches during the generation of the function response body to avoid memory waste. The following is an example of a simple Java Spring Boot application returning streaming data:
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class SpringBootDemoHelloworldApplication {
private ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoHelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
/**
* Stream Response
* @return
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/invoke")
public ResponseEntity<ResponseBodyEmitter> invoke(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> body) {
ResponseBodyEmitter emitter = new ResponseBodyEmitter();
executor.submit(() -> {
try {
emitter.send("hello \n", MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM);
emitter.send("world \n", MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM);
emitter.complete();
} catch (Exception ex) {
emitter.completeWithError(ex);
}
});
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
responseHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM);
return new ResponseEntity(emitter, responseHeaders, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
Create an HTTP function by referring to Creating an HTTP Function and enable streaming response. Note that the function execution timeout must be less than 300s. Otherwise, the function will fail to be saved.
For details about the sample code of an HTTP function, see Sample Code of a Container Image-based Function.
To return streaming data, the custom runtime function needs to call the POST method at http://$RUNTIME_API_ADDR/v1/runtime/invocation/response/$REQUEST_ID. Below is a simple Shell bootstrap example.
#!/bin/sh
set -o pipefail
#Processing requests loop
while true
do
HEADERS="$(mktemp)"
# Get an event
EVENT_DATA=$(curl -sS -LD "$HEADERS" -X GET "http://$RUNTIME_API_ADDR/v1/runtime/invocation/request")
# Get request id from response header
REQUEST_ID=$(grep -Fi x-cff-request-id "$HEADERS" | tr -d '[:space:]' | cut -d: -f2)
if [ -z "$REQUEST_ID" ]; then
continue
fi
# Send streamdata file content back to client
curl -X POST "http://$RUNTIME_API_ADDR/v1/runtime/invocation/response/$REQUEST_ID" -H "Content-Type:application/octet-stream" --data-binary "@code/streamdata.txt"
done
Testing Streaming Response Functions
- On the Code tab page of the function details page, click Test. The Configure Test Event dialog box is displayed.
- Select Blank Template, and click Create.
- Select the test event created in 2 and click Test again.
- After the function is executed, the download is automatically started. The download file name is the request ID, and the file content is the return value of the request.
Figure 2 File download
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





