Creating a Secret for Data Storage Rotation
Applications and business systems have a large number of secrets and are difficult to manage. Cloud Secret Management Service (CSMS) can store, retrieve, and use secrets in a unified manner throughout their lifecycles.
Procedure
This section uses a shared secret and a rotated secret as examples to describe how to create a secret and rotate data. The following figure shows the process.

|
Procedure |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Register a Huawei ID, enable Huawei Cloud services, top up the account, and grant CSMS permissions to the account. |
|
|
Create a secret and choose the secret type. |
|
|
After the secret is created, you can configure FunctionGraph to complete data rotation within the secret. |
Preparations
- Before creating a secret, register a Huawei Cloud account and enable Huawei Cloud services. For details, see Signing Up for a HUAWEI ID and Enabling Huawei Cloud Services.
If you have enabled Huawei Cloud, skip this step.
- Before purchasing an instance, ensure that your account balance is sufficient. For details, see Top-Up and Payment.
- Before using a rotated secret, you need to create a database instance and database account.
- RDS secret: Create an RDS instance. For details, see Buying an RDS for MySQL DB Instance.
- TaurusDB secret: Only TaurusDB instances are supported. For details, see Buying a DB Instance.
Step 1: Creating a Secret
The following describes how to create a shared secret and a rotated secret.
Full lifecycle management is supported for customized secrets in different scenarios. You can use CSMS to centrally manage, retrieve, and securely store various types of secrets, such as database account passwords, server passwords, SSH keys, and access keys. Multiple versions can be managed, so you can rotate secrets.
- Log in to the DEW console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Cloud Secret Management Service > Secrets. On the displayed page, click Create Secret in the upper left corner.
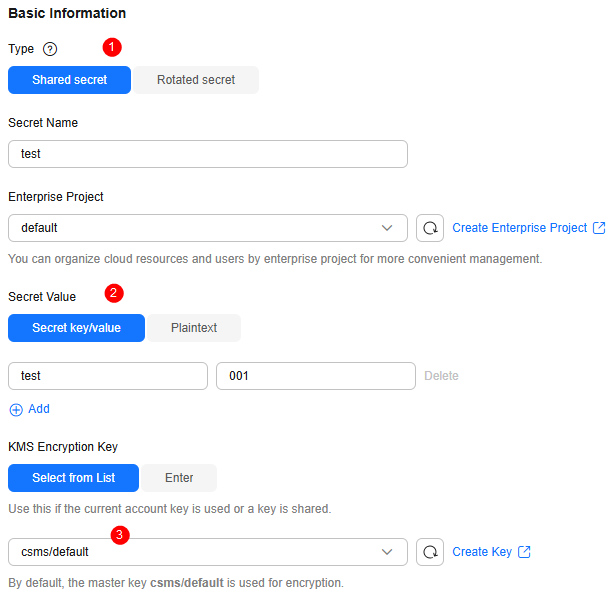
- On the displayed page, configure the parameters as shown in Figure 2.
- Click Next.
- Click Next and confirm the creation information.
- Click OK. In the secret list, you can view the created secrets, which are in the Enabled state by default.
Database secret leakage is the main cause of data leakage. CSMS supports RDS and TaurusDB secrets hosting, as well as automatic and manual rotation, meeting various database secret management scenarios and reducing security risks faced by service data.
- Log in to the DEW console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Cloud Secret Management Service > Secrets. On the displayed page, click Create Secret in the upper left corner.
- On the displayed page, configure the parameter as shown in the following and retain default settings for other parameters. For details about the parameters, see Table 1.
Figure 3 Creating a rotated secret
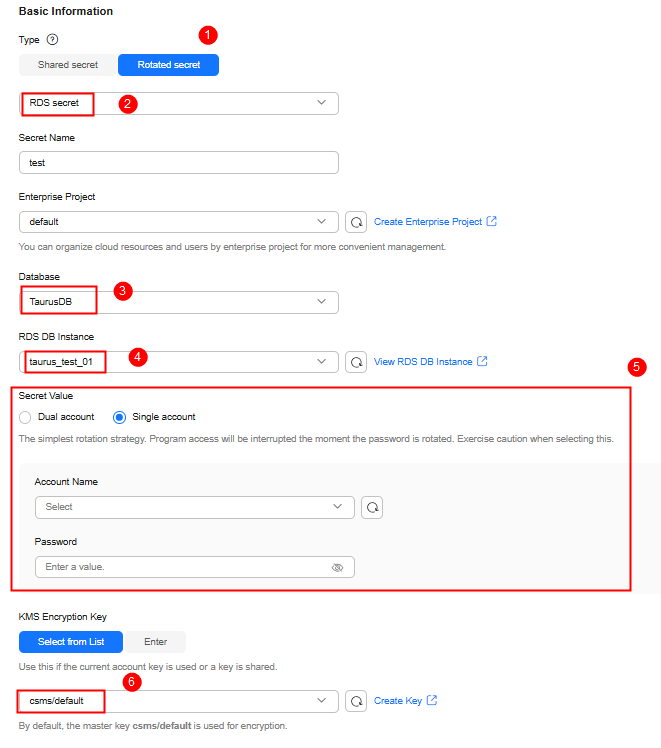
Table 1 Parameters for creating a rotated secret Parameter
Example Value
Description
Type
Rotated secret > RDS secret
CSMS supports the following secret types:
- Shared secret: Automatic secret rotation is not supported.
- Rotated secret: Automatic secret rotation is supported. The secret type can be RDS secret or TaurusDB secret.
Database
TaurusDB
RDS secrets support MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLServer, MariaDB, and TaurusDB databases.
RDS DB Instance
taurus_test_01
Select the RDS instance corresponding to the target database type.
Secret Value
Single account
Set Account Name and Password as required.
Account name and password to be encrypted.- If Single account is selected, you need to enter an available database account.
- If Dual account is selected, after you enter an available database account, a cloned account with the same permissions will be created. Select I understand the risks.
KMS Encryption Key
csms/default
The following modes are supported:- Select from list: Select this if you want to use the key used or shared by the current account. Select the default key csms/default or a custom key created on KMS.
- Enter: Enter the ID of the authorized key. Enter an encryption key if an authorized key is used. Only symmetric algorithm key IDs are supported. Do not enter an asymmetric key ID.
NOTE:- CSMS encrypts secret values using the encryption key provided by KMS. When you use the KMS encryption function, KMS creates a default key csms/default for you to use.
- For details about how to create a custom key on KMS, see Creating a Key.
- After a grant is created, you can switch to the manual input mode, and enter the key ID to use the granted key for encryption. For details, see Creating a Grant for a Custom Key.
- Click Next. On the displayed page, enable automatic rotation and set the rotation period as required.
- Under Rotation function, click Create one, enter the function name, select I understand the risks, and click Next.
- Click OK. In the secret list, you can view the created secrets, which are in the Enabled state by default.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot