Deploying and Using SVN
Overview
Subversion (SVN) is an open source version control system. It manages data that changes over time. The data is stored in a central repository. The library is like a common file server and records all file changes whenever they happen. In this way, you can restore the archive to an earlier version or browse the change history of a file.
This section uses CentOS 7.2 64-bit as an example to describe how to deploy and use SVN on CentOS 7.2.
Prerequisites
- You have purchased an ECS and bound an EIP to it.
- The rule listed in the following table has been added to the security group that the target ECS belongs to. For details, see Adding a Security Group Rule.
Table 1 Security group rules Direction
Priority
Action
Type
Protocol & Port
Source
Inbound
1
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 22
0.0.0.0/0
Inbound
1
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 80
0.0.0.0/0
Inbound
1
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 443
0.0.0.0/0
Inbound
1
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 3690
0.0.0.0/0
Deploying SVN
- Log in to the ECS.
- Install SVN.
- Run the following command to install SVN:
yum install subversion
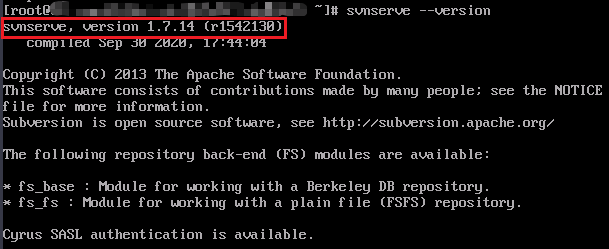
- Run the following command to check the SVN version:
svnserve --version
Information similar to the following is displayed.
- Run the following command to install SVN:
- Create an SVN version repository.
- Run the following command to create a directory:
mkdir /var/svn
- Run the following commands in sequence to create a version repository:
cd /var/svn svnadmin create /var/svn/svnrepos
- Run the following commands in sequence to view the version repository files generated automatically:
cd svnrepos ls
Information similar to the following is displayed.

The Subversion directory is described as follows:
- conf: stores the configuration files of the SVN version repository, including the access account and permissions of the version repository.
- db: stores all version control data files.
- format file: a text file that contains only one integer, indicating the version number of the current file repository.
- hooks: stores hook script files.
- locks: traces the clients that the file repository can be accessed.
- Run the following command to create a directory:
- Set the username and password of the SVN repository.
- Run the following commands to open the user configuration file:
cd conf/ vim passwd
- Press i to enter insert mode.
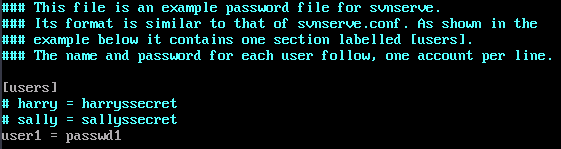
- Add the username and password to the [users] field.
The format of the username and password is Username = Password. As shown in the following figure, in user1 (username) = passwd1 (password), there must be a space before and after the equal sign (=).
- Press Esc to exit insert mode. Then, enter :wq to save the settings and exit the file.
- Run the following commands to open the user configuration file:
- Configure account permissions.
- Run the following command to open the permissions control file:
vim authz
- Press i to enter insert mode.
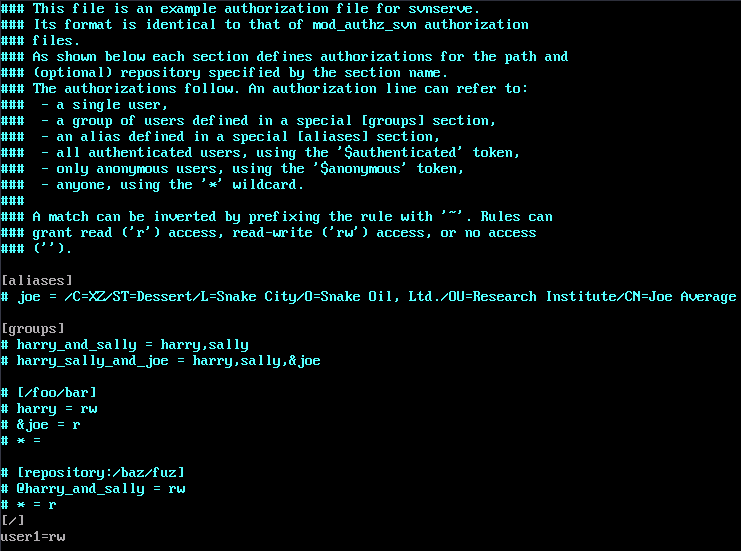
- Add the following content to the end of the file (user1 indicates the user added in 4, r indicates the read permissions, and w indicates the write permissions):
[/] user1=rw
- Press Esc to exit insert mode. Then, enter :wq to save the settings and exit the file.
- Run the following command to open the permissions control file:
- Modify the SVN service configuration file.
- Run the following command to open the SVN configuration file:
vim svnserve.conf
- Press i to enter insert mode.
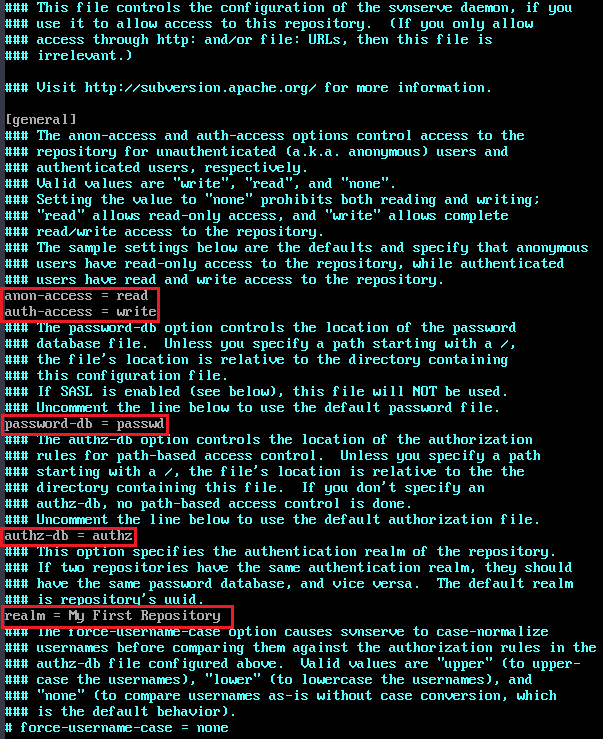
- Locate the following configuration lines and delete the comment tags (#) and spaces before the lines.
Note: Each line cannot start with a space. There must be a space before and after an equal sign (=).
anon-access = read # Read permissions of anonymous users. If anon-access is set to none, anonymous users are not allowed to access the file. If the value is set to none, the log date can be displayed normally. auth-access = write # Write permissions authorized to users. password-db = passwd # File to be used as the account file. authz-db = authz # File to be used as the permissions file. realm = /var/svn/svnrepos # Authentication space name, which is the directory where the version repository is located.
- Press Esc to exit insert mode. Then, enter :wq to save the settings and exit the file.
- Run the following command to open the SVN configuration file:
- Run the following command to start the SVN version library repository:
svnserve -d -r /var/svn/svnrepos
- Run the following command to check whether the SVN service is enabled:
ps -ef |grep svn
If information similar to the following is displayed, the SVN service is enabled.


Run the killall svnserve command to stop the SVN service.
Using SVN
The process of using SVN to manage code is as follows:
- Extract the source code to a local directory (Checkout).
- Other personnel modify and submit the source code to the repository.
- Obtain the latest code (Update).
- Modify and commission the source code.
- Submit the modified code to the repository so that others can view the modifications (Commit).
The procedure is as follows:
Extracting the source code to a local directory (Checkout)
- Download and install the TortoiseSVN client in the local Windows environment.
- Right-click the blank area in the local project folder.
- In the displayed menu, choose SVN Checkout...
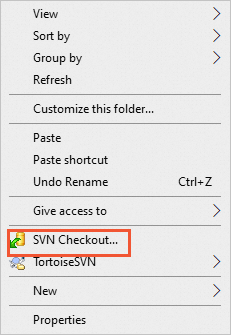
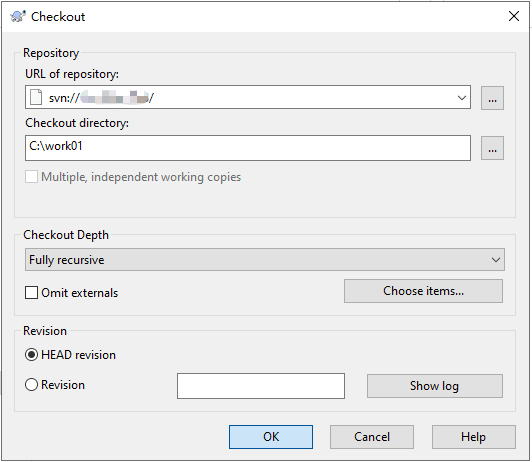
- Set the following parameters and click OK:
- URL of repository: version repository URL, which is the address for storing source code. The format is svn://Public IP address of the instance/.
- Checkout directory: local directory to which the source code is checked out. In this example, the directory is C:\work01.

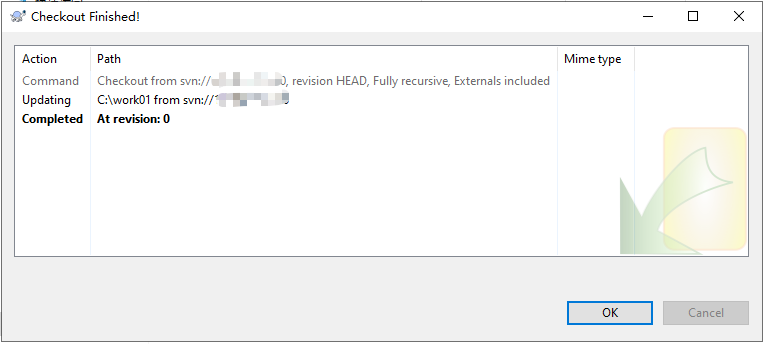
When you log in to the system for the first time, you need to enter the username and password set in the passwd file in 4.
The checkout result is as follows.
Obtaining updates (Update)
After a project in the system repository on the SVN server is updated, you can right-click the blank area in the local project file and choose SVN Update from the shortcut menu. The latest project is automatically downloaded and all updated content is displayed.
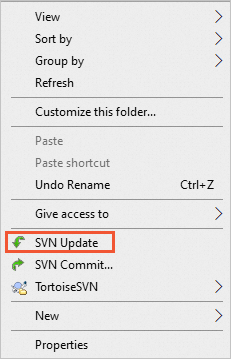

Right-click the original project folder to select SVN Update. The original content will be automatically overwritten. It is recommended that you back up the project before updating it to prevent data loss of your project.
Submitting the modification (Commit)
- Right-click the blank area of the project file and choose SVN Commit... from the shortcut menu.
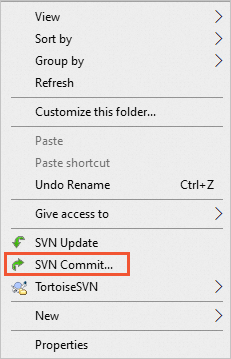
- Enter the version update information (modification comments), select the operation content to be submitted, and click OK.
You can submit the local project to the SVN server resource repository to overwrite the resource library project.
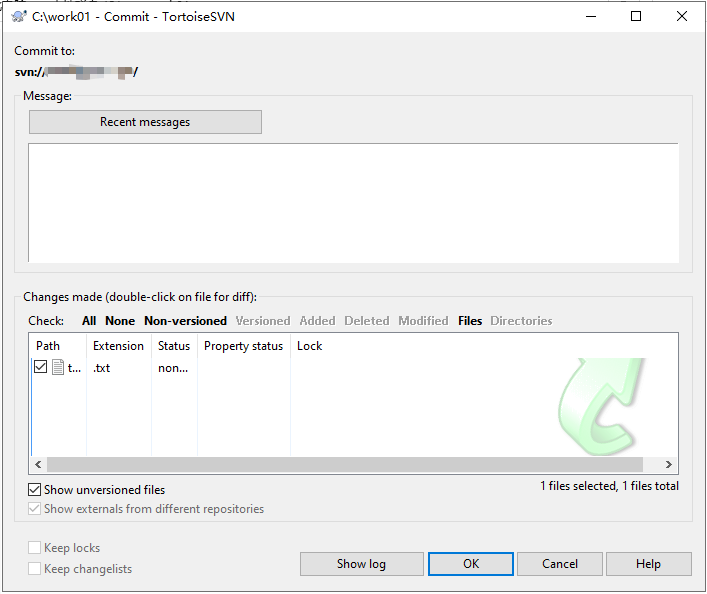

There may be conflicts if multiple users submit changes at the same time. In this case, you can back up your own project, download the latest project from the server, overwrite it with your own project, and then click SVN Commit.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





