Disk Scaling
Context
As customer services evolve, disk space often becomes the initial bottleneck. In scenarios where other resources are ample, the conventional scale-out process is not only time-consuming but also resource-inefficient. Disk capacity expansion can quickly increase storage without service interruption. You can expand the disk capacity when no other services are running. If the disk space is insufficient after the expansion, you can continue to expand the disk capacity. If the expansion fails, you can expand the disk capacity again.

- Disk capacity expansion can be performed only for storage-compute coupled data warehouses with cloud SSDs. Only version 8.1.1.203 and later are supported.
- Disk capacity can be expanded only if the cluster is in Available, To be restarted, Read-only, or Node fault, Unbalanced state.
Precautions
- Hot storage disks cannot be scaled down.
- Scale up hot data storage during off-peak hours.
- If the cluster is in the read-only state, a message will be displayed after you click Change Disk Capacity. After you start expansion, wait until it is completed and the cluster changes to the available state.
- The added disks of a yearly/monthly cluster are billed in yearly/monthly mode by default.
Procedure
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters. All clusters are displayed by default.
- In the Operation column of the target cluster, choose More > Change Specifications and click Change disk capacity. The Change Disk Capacity page is displayed.
- Select the appropriate storage space based on the storage step of the corresponding flavor. The step refers to the interval for increasing or decreasing storage space. For details about the step of each flavor, see Data Warehouse Flavors. Click Resize Cluster Now.
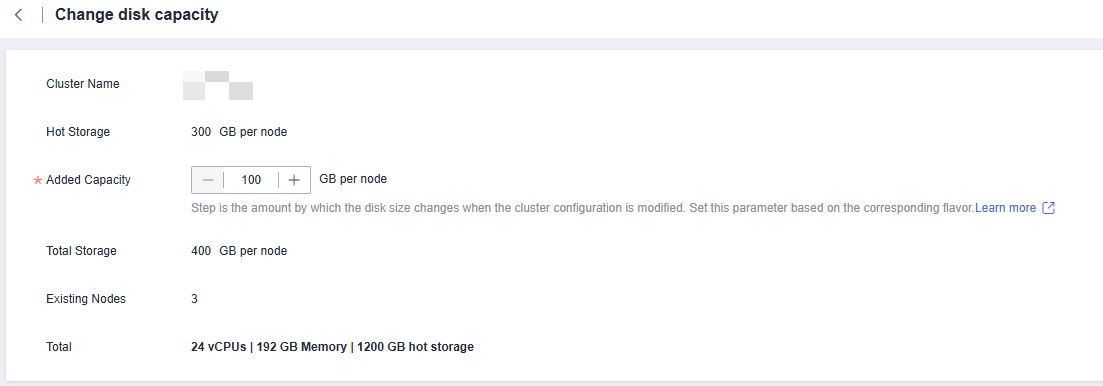

Hot Storage is changed to Hot Storage (with Cache) for storage-compute decoupled clusters.
- Confirm the settings and click Submit.
- Return to the cluster list and check the disk capacity expansion progress.
Hybrid Billing for Disk Capacity Expansion of a Yearly/Monthly Cluster
Prerequisites
To handle peak demand, nodes are added to a yearly/monthly cluster as per the schedule of logical clusters and are billed based on a pay-per-use basis. For details, see Elastically Adding or Deleting a Logical Cluster. After scale-out, the cluster uses the hybrid billing mode, that is, both the pay-per-use and yearly/monthly billing modes are used. Nodes created by creating addition or deletion plans are pay-per-use nodes, and nodes created by creating a yearly/monthly cluster are yearly/monthly nodes.

Only storage-compute decoupled clusters support hybrid billing.
Procedure
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters.
- Click Create DWS Cluster to create a storage-compute decoupled cluster if needed. For details, see Creating a Dedicated DWS Cluster.
- After the cluster is created, add an addition or deletion plan. After nodes are automatically added, if you need to expand the disk capacity, locate the row that contains the cluster and choose More > Change Specifications > Change disk capacity in the Operation column. The hybrid price page is displayed. The supplementary fee is the price that needs to be paid for the disk scale-out of yearly/monthly nodes. The configuration fee is the hourly price of pay-per-use nodes in the cluster after disk scale-out.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





