Anomaly Detection
IoTDA provides device anomaly detection functions, including security checks and disconnection analysis.
Security Checks
IoTDA continuously detects device security threats. This section describes security check items and how to view and handle detected security risks.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Connection mode |
No encryption protocol is used to establish secure connections between devices and IoTDA. This may cause man-in-the-middle and replay attacks and affect services. |
|
TLS version |
Insecure TLS protocol versions (TLS v1.0 and v1.1) have security vulnerabilities, which may cause security risks such as device data leakage. |
|
Cryptographic algorithm suite |
Currently, IoTDA checks the following insecure cryptographic algorithm suites: TLS_ECDHE_PSK_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_PSK_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA, TLS_PSK_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_PSK_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA Insecure cryptographic algorithm suites have security vulnerabilities, which may cause security risks such as device data leakage. |
|
Device connection |
If a device attempts to establish connections with IoTDA multiple times within 1 second, the device may be cracked with brute force. As a result, identity information may be leaked, normal devices may be forced to go offline, and service data may be stolen. |
|
Device authentication |
Incorrect device identity authentication information causes device connection failures. This may affect services. |
The preceding common check items are enabled by default. You can manually enable other non-common check items as required.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Memory leak check |
Checks device memory leaks. |
|
Abnormal port |
Checks whether abnormal ports are enabled on the device. |
|
CPU usage |
Checks whether the CPU usage of the device is too high. |
|
Disk space |
Checks whether the disk space of the device is insufficient. |
|
Battery level |
Checks whether the battery level of the device is too low. |
|
Malicious IP address |
Checks whether the device communicates with malicious IP addresses. |
|
Local login |
Checks whether attackers log in to the device through non-SSH networks. |
|
Brute-force cracking login |
Checks whether attackers attempt to log in to the device through brute force cracking. |
|
Device file tampering |
Checks whether files in a specified directory of a device are tampered with. |
Disconnection Analysis
IoTDA help you analyze device disconnection causes by collecting statistics on the disconnection time range and characteristics of disconnected devices.
|
Disconnection Cause |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Disconnection requested by device |
The device sends an MQTT disconnect packet to IoTDA for disconnection. |
|
Device heartbeat timed out |
The device does not comply with the MQTT protocol. It sends MQTT heartbeat packets to IoTDA within 1.5 times the configured heartbeat interval. As a result, IoTDA considers that the device connection is invalid and cuts off the connection according to protocol requirements. (Note: The heartbeat interval is specified when the device establishes a connection with IoTDA.) |
|
Device-platform TCP connection cutoff |
IoTDA receives a TCP disconnection packet from the device. As a result, the TCP connection between the device and IoTDA is cut off. |
|
Device deleted |
The device is deleted from IoTDA, and IoTDA cuts off the connection with the device. |
|
Device frozen |
The device is frozen on IoTDA, and IoTDA cuts off the connection with the device. |
|
Connection cut off by IoTDA |
IoTDA cuts off the connection with the device during upgrade. |
|
Earlier connection cutoff |
The device establishes connections with IoTDA repeatedly. IoTDA cuts off the existing connection and retains the new connection. |
|
Device secret reset |
When the device secret is reset and the connection is manually cut off, IoTDA cuts off the connection with the device. |
Procedure
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose O&M > Anomaly Detection and click Authorize. To use anomaly detection, authorize IoTDA service to perform operations on LTS.
Figure 1 Anomaly detection - Access authorization
- After authorization, Security Checks and Disconnection Analysis pages are available. Click Enable to enable the two functions. Otherwise, they cannot be used.
Figure 2 Anomaly detection - Security checks
 Figure 3 Anomaly detection - Offline analysis
Figure 3 Anomaly detection - Offline analysis
- When this function is enabled, IoTDA automatically creates a log group, a log stream, and a data forwarding rule with the data source set to run logs of all resource spaces. The log group name is {domainName}-device-exception-group, the log stream name is {domainName}-device-exception-stream, and the forwarding rule name is {domainName}-device-exception-rule. If you delete the rule with the data source set to run logs, this function will be affected. If you disable this function, rules will not be deleted and will be reused when you enable this function again.
- Pay attention to the storage space occupied by anomaly detection logs. When the free quota (500 MB) is used up, LTS will discard data or continue collecting data after you purchase LTS. You can click Quota in the upper right corner to modify the quota.
- To enable Security Checks, perform the following steps. Otherwise, skip them.
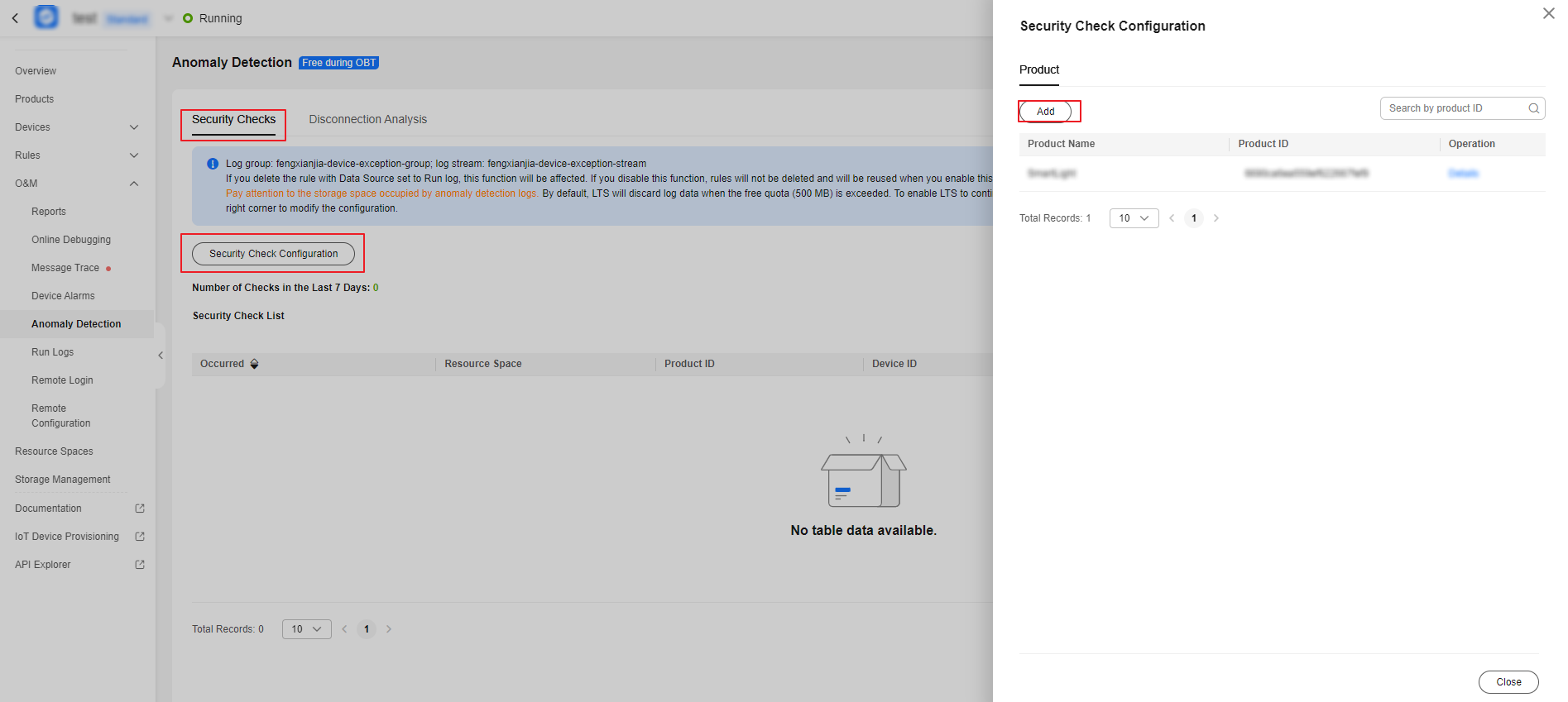
- On the Security Checks tab page, click Security Check Configuration. In the displayed dialog box, click Add.
Figure 4 Anomaly detection - Security check configuration
- On the configuration page, select the resource space and product name to be configured, and enable the corresponding check items as required.
Figure 5 Anomaly detection - Security check item configuration
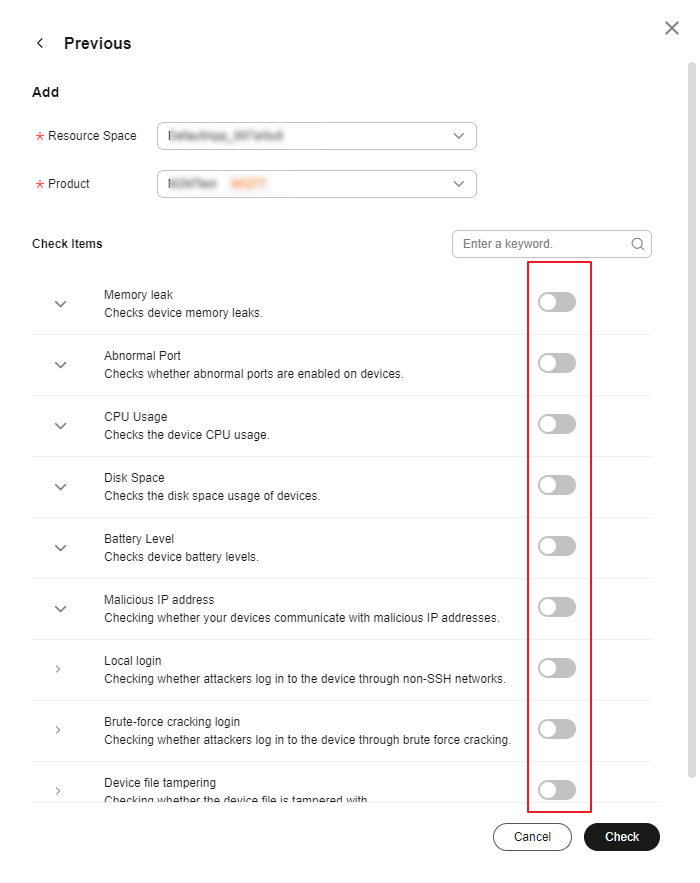
Memory/CPU usage/Disk space/Battery level checks: The system compares the values reported by the device with the thresholds configured in the check items to determine whether to generate alarms. Abnormal port/Malicious IP address checks: Enter whitelisted ports or IP addresses for checks. The system compares the parameters reported by the device and the configured whitelist members. You can add IP address segments to the whitelist, for example, 192.168.1.10/24.
- On the Security Checks tab page, click Security Check Configuration. In the displayed dialog box, click Add.
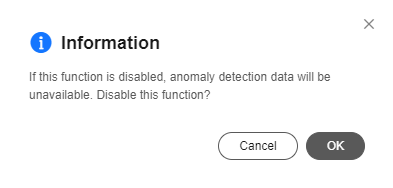
- You can click Disable on the corresponding pages to manually disable the security check and disconnection analysis functions, and click Enable to use them again.
Figure 6 Anomaly detection - Disabling the function
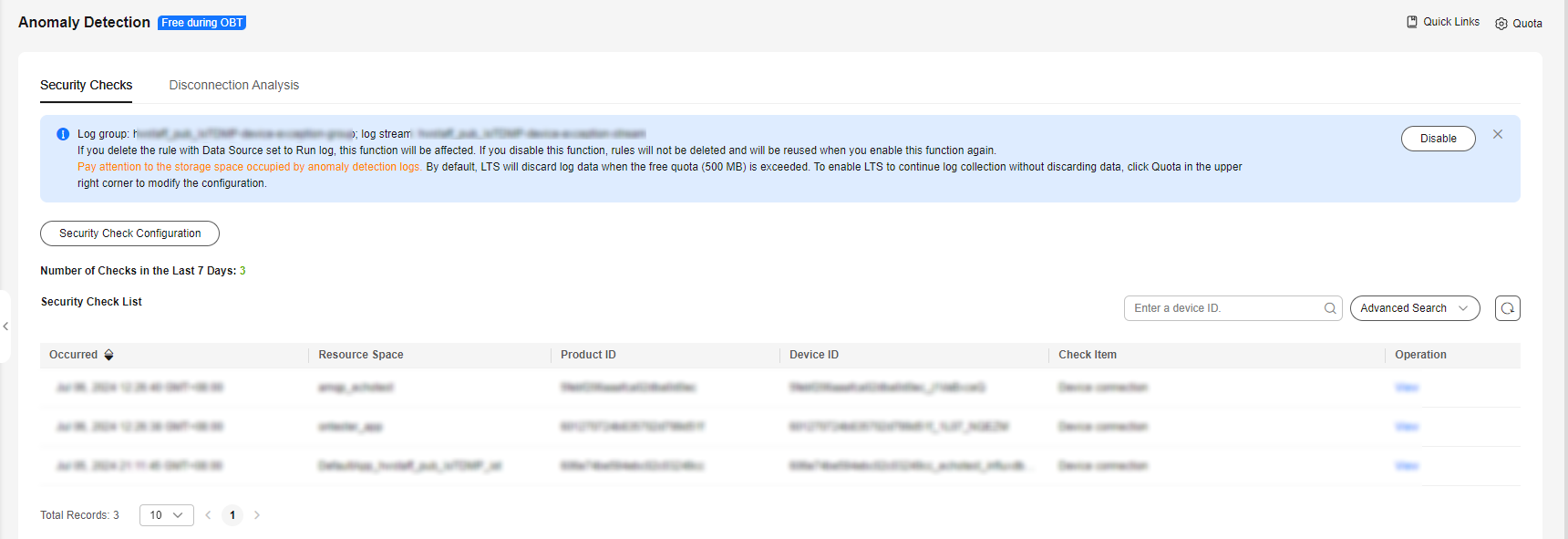
- After you enable security checks, IoTDA starts security checks on devices. Security check data of the last seven days can be stored at most. You can search for anomaly records by device ID, resource space, product, check item, and time range, and click the button to check record details.
Figure 7 Anomaly detection - Security check overview
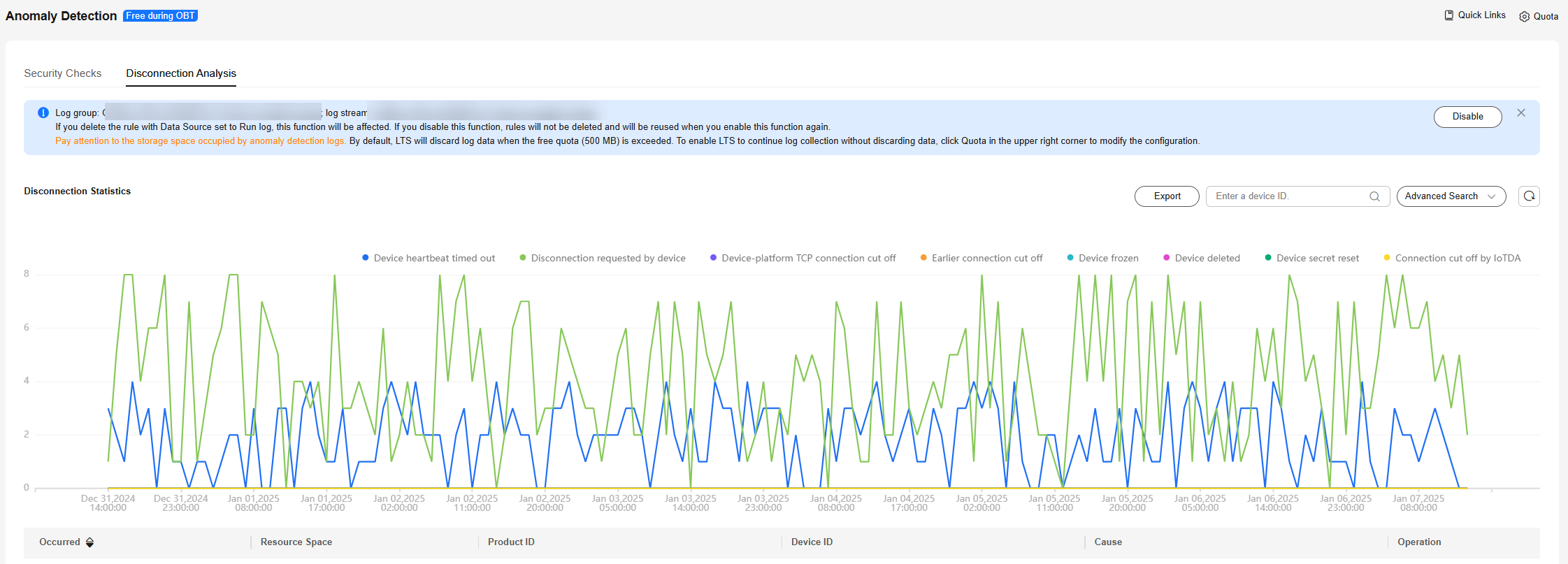
- After you enable disconnection analysis, IoTDA automatically analyzes the causes of device disconnections. Disconnection analysis data of the last seven days can be stored at most. You can search for disconnection data by device ID, resource space, product, cause, and time range, and click the button to check record details.
Figure 8 Anomaly detection - Offline analysis overview
- After you enable security checks, IoTDA starts security checks on devices. Security check data of the last seven days can be stored at most. You can search for anomaly records by device ID, resource space, product, check item, and time range, and click the button to check record details.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





