MQTT Client Access
After configuring and activating rules by calling the platform APIs Creating a Rule Triggering Condition, Creating a Rule Action, and Modifying a Rule Triggering Condition, connect the MQTT client to IoTDA. Then run the MQTT client on your server to receive subscribed-to messages.
Configuring the Connection
The table below describes the connection address and connection authentication parameters for the MQTT client to connect to the platform.
- MQTT access domain name
It is automatically generated for each account. Log in to the IoTDA console to obtain it on the Access Details page.
Figure 1 Access information - MQTT access address on the application side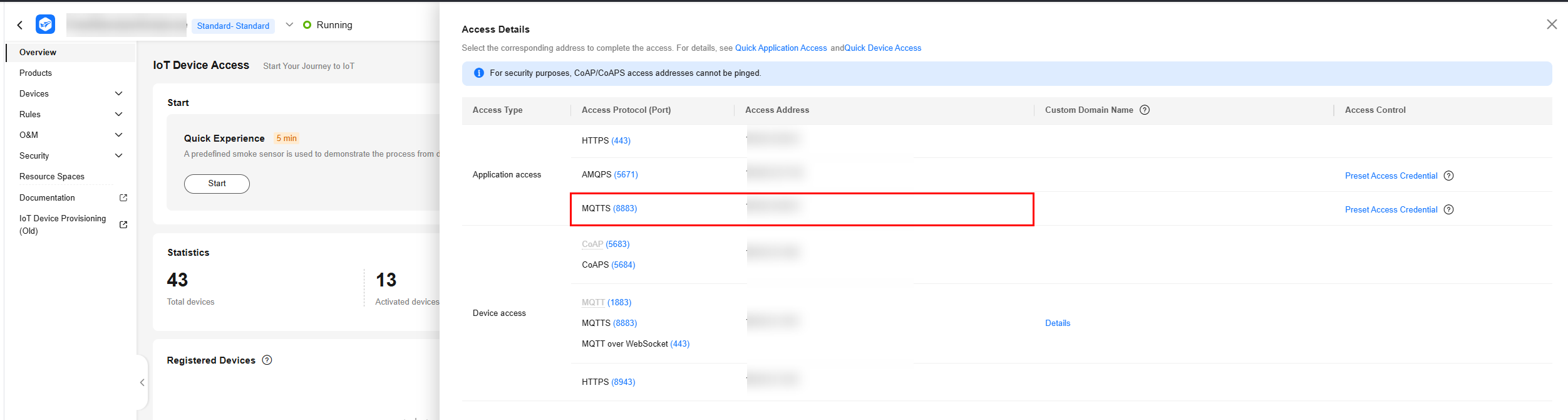
- Port: 8883
- Client identity authentication parameters
clientId: The value must be globally unique. You are advised to use username.
username ="accessKey=${accessKey}|timestamp=${timestamp}|instanceId=${instanceId}"
password ="${accessCode}"
Parameter
Mandatory
Description
${accessKey}
Yes
An accessKey can be used to establish a maximum of 10 concurrent connections. When establishing a connection for the first time, preset the parameter by following the instructions provided in Obtaining the AMQP Access Credential.
${timestamp}
Yes
Current time. The value is a 13-digit timestamp, accurate to milliseconds. The server verifies the client timestamp. There is a 5-minute difference between the client timestamp and server timestamp.
instanceId
No
Instance ID. This parameter is mandatory when multiple instances of the standard edition are purchased in the same region. For details, see Viewing Instance Details.
${accessCode}
Yes
The value can contain a maximum of 256 characters.
Obtaining the MQTT Access Credential
An access credential is required for an application that uses MQTT to connect to the platform for data forwarding. If you use an access credential for the first time or forget it, preset an access credential. You can call the API for generating an access credential or use the console to preset an access credential. The procedure for using the console to generate an access credential is as follows:
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- Choose . The Rule List page is displayed.
Figure 2 Rule details - Viewing rule details

- Click View. (If no rule exists, create one.) On the rule details page that is displayed, click the Set Forwarding Target tab.
Figure 3 Forwarding target - Setting a target

- Click Add. On the Add Forwarding Target page that is displayed, select MQTT message queue for Forwarding Target, and click Preset Access Credential to preset the access code and access key.
Figure 4 Creating a forwarding target - to an MQTT push message queue with preset credentials
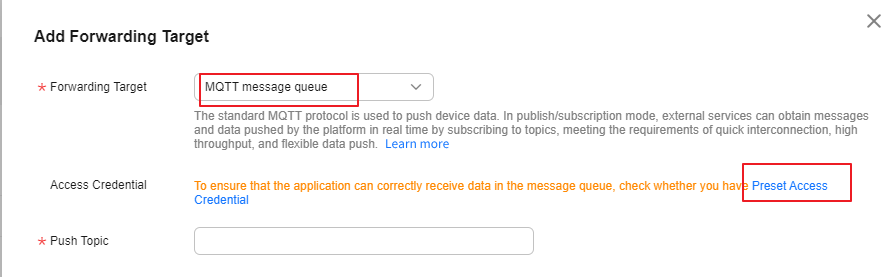
If you already have an access credential, the accessKey cannot be used after you preset the access credential again.
Receiving Push Messages
After a connection is established between the client and the platform, subscribe to the MQTT topic in the data forwarding rule. When a device reports data and the rule is triggered, the platform pushes the data to the MQTT client.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





