Developing an HTTP Function Using Go
This section describes how to develop an HTTP function using Go. For details about HTTP function, see Creating an HTTP Function.
Constraints
- HTTP functions can only use APIG or APIC triggers.
According to the forwarding protocol between FunctionGraph and APIG/APIC, a valid HTTP function response must contain body(String), statusCode(int), headers(Map), and isBase64Encoded(boolean). By default, the response is encoded using Base64. The default value of isBase64Encoded is true. The same applies to other frameworks. For details, see Base64 Decoding and Return Structure.
- By default, port 8000 is enabled for HTTP functions.
- Table 13 describes the context methods provided by FunctionGraph.
Example of Using Go to Develop an HTTP Function
Overview
Since HTTP functions do not directly support Go code deployment, this chapter provides an example of using binary conversion to deploy a Go program on FunctionGraph.
Procedure
For details, see Building an HTTP Function with Go.
Sample Code
The code of the source file main.go is as follows:
// main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/emicklei/go-restful"
)
func registerServer() {
fmt.Println("Running a Go Http server at localhost:8000/")
ws := new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/")
ws.Route(ws.GET("/hello").To(Hello))
c := restful.DefaultContainer
c.Add(ws)
fmt.Println(http.ListenAndServe(":8000", c))
}
func Hello(req *restful.Request, resp *restful.Response) {
resp.Write([]byte("nice to meet you"))
}
func main() {
registerServer()
}
# bootstrap /opt/function/code/go-http-demo
In main.go, an HTTP server is started using port 8000, and an API whose path is /hello is registered. When the API is invoked, "nice to meet you" is returned.
Compiling and Packaging
- On the Linux server, compile the preceding code using the go build -o go-http-demo main.go command.
- Compress go-http-demo and bootstrap into a ZIP package named xxx.zip.
Creating an HTTP Function
Create an HTTP function in FunctionGraph, and upload the xxx.zip code package.
Creating an APIG Trigger
Create an APIG trigger, select a proper group and environment, and click OK. (You can select None for Security Authentication in the test phase.)
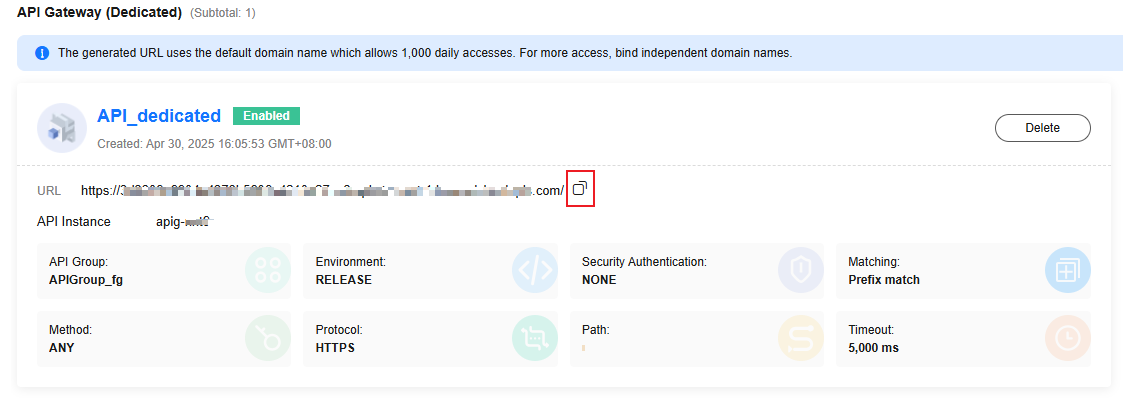
Invocation Test
Copy the URL generated in Creating an APIG Trigger + Path registered in the code + /hello to the address box of the browser. The following information is displayed:
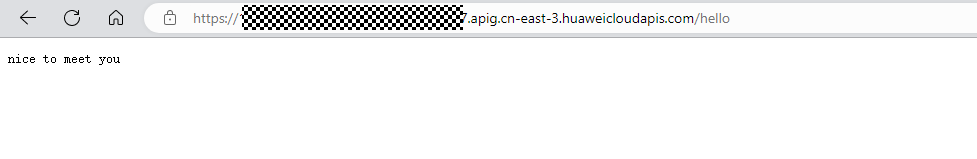
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





