Developing a Go Event Function
For details about the syntax and SDK APIs of Go functions, see Function Development Overview.
Developing a Go Function
Log in to the Linux server where the Go 1.x SDK has been installed and perform the following steps to compile and package the Go function. (Currently, Ubuntu 14.04, Ubuntu 16.04, SUSE 11.3, SUSE 12.0, and SUSE 12.1 are supported.)
Go Versions Supporting go mod (1.11.1+)
- Create a temporary directory, for example, /home/fssgo, decompress the Go SDK of FunctionGraph to the created directory, and enable the go module function.
$ mkdir -p /home/fssgo $ unzip functiongraph-go-runtime-sdk-1.0.1.zip -d /home/fssgo $ export GO111MODULE="on"
- Generate the go.mod file in the /home/fssgo directory. Assume that the module name is test:
$ go mod init test
- Edit the go.mod file in the /home/fssgo directory as required (that is, add the content in bold).
module test go 1.24.5 require ( huaweicloud.com/go-runtime v0.0.0-00010101000000-000000000000 ) replace ( huaweicloud.com/go-runtime => ./go-runtime ) - Create a function file under the /home/fssgo directory and implement the following interface:
func Handler(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error)
In this interface, payload is the body of a client request, and ctx is the runtime context object provided for executing a function. For more information about the methods, see Table 13. The following uses test.go as an example.
package main import ( "fmt" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/go-api/context" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/pkg/runtime" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/apig" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/cts" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/dds" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/dis" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/kafka" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/lts" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/smn" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/timer" "encoding/json" ) func ApigTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var apigEvent apig.APIGTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &apigEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", apigEvent.String()) apigResp := apig.APIGTriggerResponse{ Body: apigEvent.String(), Headers: map[string]string { "content-type": "application/json", }, StatusCode: 200, } return apigResp, nil } func CtsTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var ctsEvent cts.CTSTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &ctsEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", ctsEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func DdsTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var ddsEvent dds.DDSTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &ddsEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", ddsEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func DisTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var disEvent dis.DISTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &disEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", disEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func KafkaTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var kafkaEvent kafka.KAFKATriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &kafkaEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", kafkaEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func LtsTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var ltsEvent lts.LTSTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, <sEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", ltsEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func SmnTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var smnEvent smn.SMNTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &smnEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", smnEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func TimerTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var timerEvent timer.TimerTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &timerEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } return timerEvent.String(), nil } func main() { runtime.Register(ApigTest) }Constraints:
- If the error parameter returned by a function is not nil, the function execution fails.
- If the error parameter returned by a function is nil, FunctionGraph supports only the following types of values:
nil: The HTTP response body is empty.
[]byte: The content in this byte array is the body of an HTTP response.
string: The content in this string is the body of an HTTP response.
Other: FunctionGraph returns a value for JSON encoding, and uses the encoded object as the body of an HTTP response. The Content-Type header of the HTTP response is set to application/json.
- The preceding example uses an APIG trigger as an example. For other trigger types, you need to modify the content of the main function. For example, change the CTS trigger to runtime.Register(CtsTest). Currently, only one entry can be registered.
- For details about the constraints for the APIG event source, see Base64 Decoding and Response Structure.
- Compile and package the function code.
After completing the function code, compile and package it as follows:
- Compile the code.
$ cd /home/fssgo $ go build -o handler test.go
The handler can be customized on the function details page on the FunctionGraph console.
- Package the code.
$ zip fss_examples_go1.x.zip handler
- Compile the code.
- Create a function.
Log in to the FunctionGraph console, create a Go 1.x function, and upload the code package fss_examples_go1.x.zip.
If you edit code in Go, package the compiled file into a ZIP file, and ensure that the name of the compiled file is consistent with the handler. For example, if the name of the binary file is handler, set the Handler to handler. The handler must be consistent with that defined in 3.b.
- Test the function.
- Create a test event.
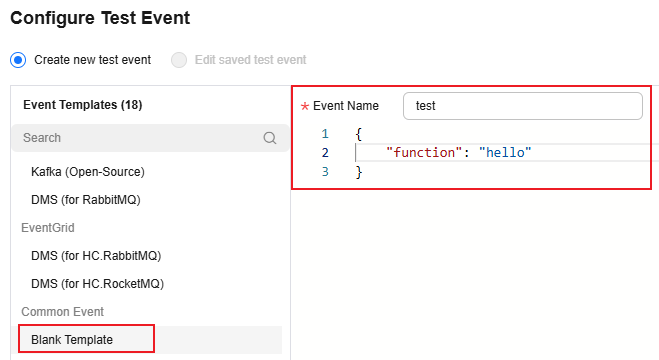
On the function details page that is displayed, click Configure Test Event. Configure the test event information, as shown in Figure 1, and then click Create.
- On the function details page, select the configured test event, click Test, and view the function execution result by referring to Function Execution Result.
- Create a test event.
Go Versions not Supporting go mod (<1.11.1)
- Create a temporary directory, for example, /home/fssgo/src/huaweicloud.com, and decompress the Go SDK to the created directory.
$ mkdir -p /home/fssgo/src/huaweicloud.com
$ unzip functiongraph-go-runtime-sdk-1.0.1.zip -d /home/fssgo/src/huaweicloud.com
- Create a function file under the /home/fssgo/src directory and implement the following interface:
func Handler(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error)
In this interface, payload is the body of a client request, and ctx is the runtime context object provided for executing a function. For more information about the methods, see the SDK APIs. The following uses test.go as an example.
package main import ( "fmt" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/go-api/context" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/pkg/runtime" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/apig" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/cts" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/dds" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/dis" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/kafka" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/lts" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/smn" "huaweicloud.com/go-runtime/events/timer" "encoding/json" ) func ApigTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var apigEvent apig.APIGTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &apigEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", apigEvent.String()) apigResp := apig.APIGTriggerResponse{ Body: apigEvent.String(), Headers: map[string]string { "content-type": "application/json", }, StatusCode: 200, } return apigResp, nil } func CtsTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var ctsEvent cts.CTSTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &ctsEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", ctsEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func DdsTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var ddsEvent dds.DDSTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &ddsEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", ddsEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func DisTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var disEvent dis.DISTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &disEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", disEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func KafkaTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var kafkaEvent kafka.KAFKATriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &kafkaEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", kafkaEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func LtsTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var ltsEvent lts.LTSTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, <sEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", ltsEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func SmnTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var smnEvent smn.SMNTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &smnEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } ctx.GetLogger().Logf("payload:%s", smnEvent.String()) return "ok", nil } func TimerTest(payload []byte, ctx context.RuntimeContext) (interface{}, error) { var timerEvent timer.TimerTriggerEvent err := json.Unmarshal(payload, &timerEvent) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Unmarshal failed") return "invalid data", err } return timerEvent.String(), nil } func main() { runtime.Register(ApigTest) }Constraints:
- If the error parameter returned by a function is not nil, the function execution fails.
- If the error parameter returned by a function is nil, FunctionGraph supports only the following types of values:
nil: The HTTP response body is empty.
[]byte: The content in this byte array is the body of an HTTP response.
string: The content in this string is the body of an HTTP response.
Other: FunctionGraph returns a value for JSON encoding, and uses the encoded object as the body of an HTTP response. The Content-Type header of the HTTP response is set to application/json.
- The preceding example uses an APIG trigger as an example. For other trigger types, you need to modify the content of the main function. For example, change the CTS trigger to runtime.Register(CtsTest). Currently, only one entry can be registered.
- For details about the constraints for the APIG event source, see Base64 Decoding and Response Structure.
- Compile and package the function code.
After completing the function code, compile and package it as follows:
- Set environment variables GOROOT and GOPATH.
$ export GOROOT=/usr/local/go (Assume that the Go SDK is installed under the /usr/local/go directory.) $ export PATH=$GOROOT/bin:$PATH $ export GOPATH=/home/fssgo
- Compile the function code.
$ cd /home/fssgo $ go build -o handler test.go
The handler can be customized on the function details page on the FunctionGraph console.
- Package the code.
$ zip fss_examples_go1.x.zip handler
- Set environment variables GOROOT and GOPATH.
- Creating a function
Log in to the FunctionGraph console, create a Go 1.x function, and upload the code package fss_examples_go1.x.zip.
If you edit code in Go, package the compiled file into a ZIP file, and ensure that the name of the compiled file is consistent with the handler name. For example, if the name of the binary file is handler, set the Handler to handler. The handler must be consistent with that defined in 3.b.
- Test the function.
- Create a test event.
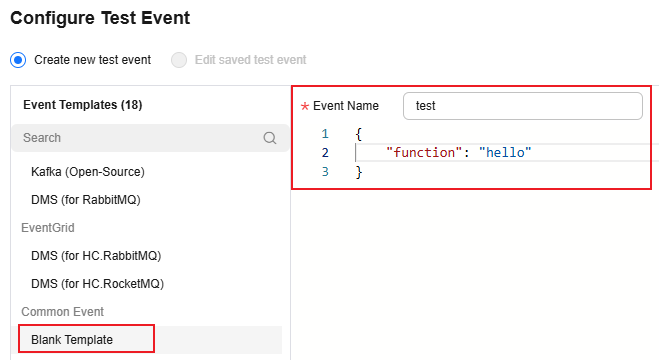
On the function details page that is displayed, click Configure Test Event. Configure the test event information, as shown in Figure 2, and then click Create.
- On the function details page, select the configured test event, click Test, and view the function execution result by referring to Function Execution Result.
- Create a test event.
Function Execution Result
The execution result consists of the function output, summary, and log output.
|
Parameter |
Successful Execution |
Failed Execution |
|---|---|---|
|
Function Output |
The defined function output information is returned. |
A JSON file that contains errorMessage and errorType is returned. The format is as follows: {
"errorMessage": "",
"errorType":"",
}
errorMessage: Error message returned by the runtime. errorType: Error type. |
|
Summary |
Request ID, Memory Configured, Execution Duration, Memory Used, and Billed Duration are displayed. |
Request ID, Memory Configured, Execution Duration, Memory Used, and Billed Duration are displayed. |
|
Log Output |
Function logs are printed. A maximum of 4 KB logs can be displayed. |
Error information is printed. A maximum of 4 KB logs can be displayed. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot