Adding and Setting the URL Request of an API Script
- After the operations described in Creating an Automated API Test Case Template are complete, choose and click the name of the test case to be edited.
- Choose Scripting > URL Request to generate a test step.
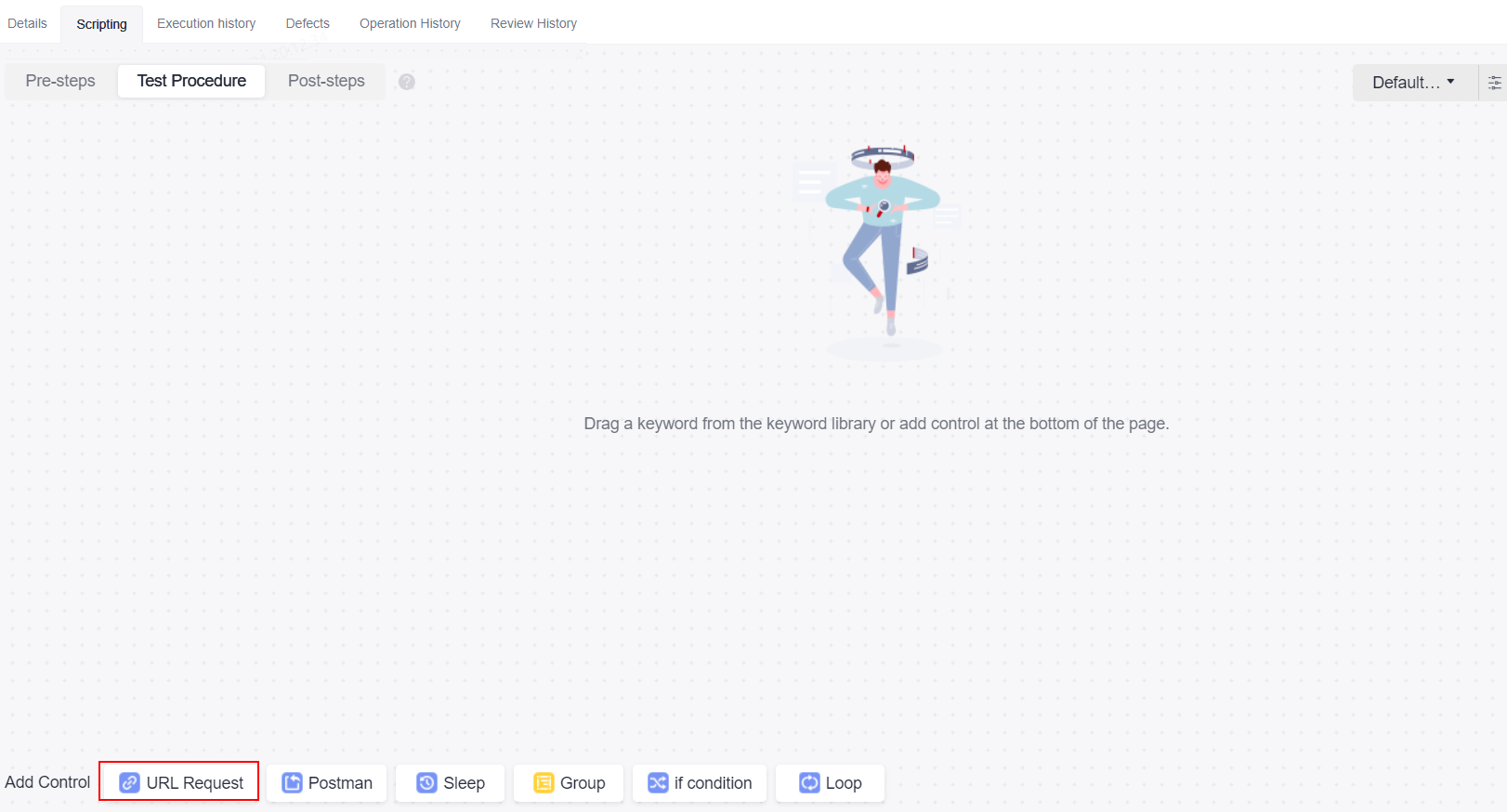
You can import a Swagger description file of the API to be tested to generate a script template and then orchestrate test cases. For details, see Saving Test Procedure as an API Keyword.
Select a script template and drag and drop the script template card or click
 on the card to add the script to the Test Procedure tab page.
on the card to add the script to the Test Procedure tab page.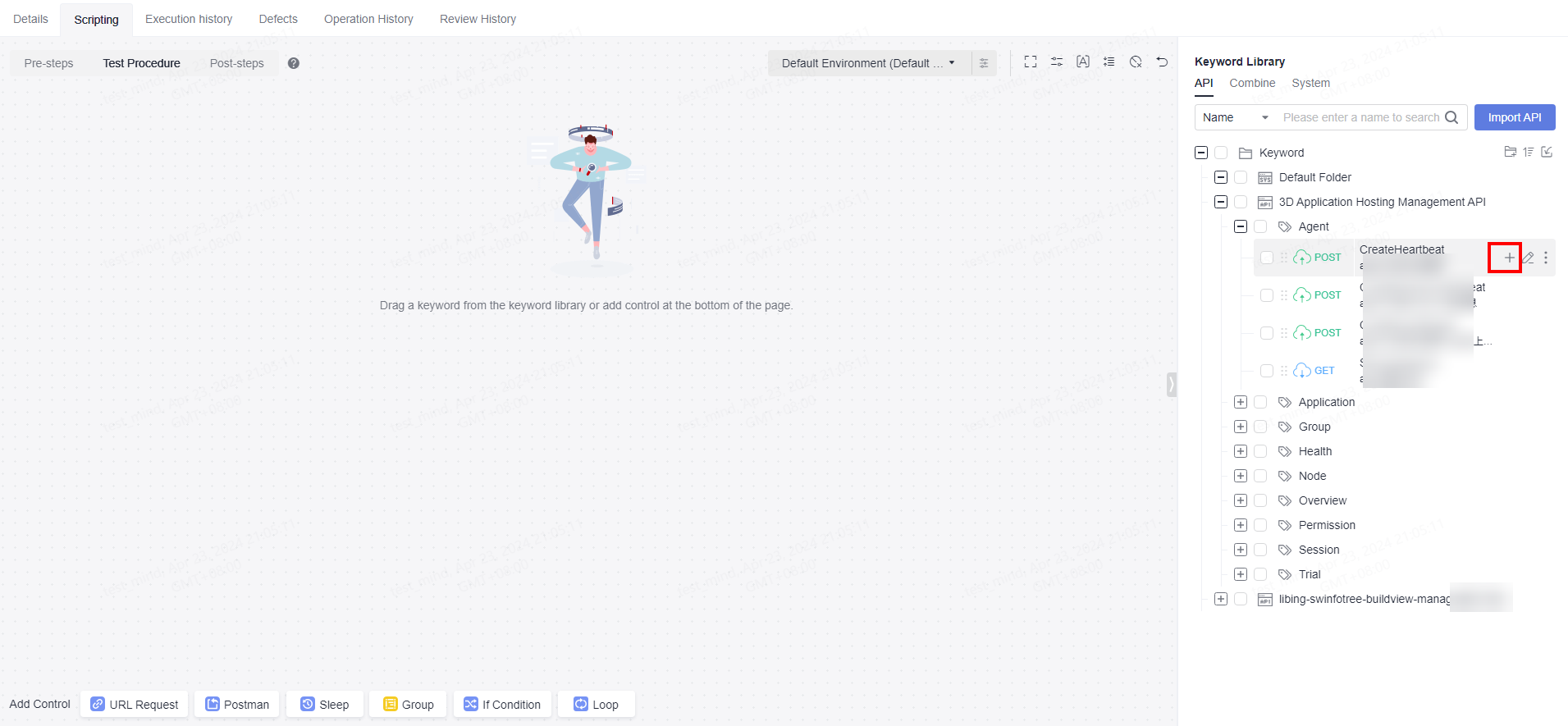
- Edit the URL request as required by referring to Adding and Setting the URL Request of an API Script, Setting Checkpoints for an API Script, and Setting the Response Extraction of an API Script. Enter a domain name or IP address as the environment address in the request. If you import a Swagger or Postman file, the address will be automatically generated to the request.
- (Optional) Repeat 2 to 3 to add pre-steps and post-steps.
- After the editing is complete, click Save in the upper right corner of the page to save the script.
- Automated API test cases support the use of built-in functions in the request URL path, request header, request body, checkpoint parameters, and URL response. For details about built-in functions, see Built-in Functions.
- When editing automated API test cases, you can right-click the title area of a test step to cut, copy, paste, and delete a test step. If there are multiple test steps, you can press Ctrl+left-click to select multiple test steps and right-click them in batches. After a test step is cut or copied, the test step can be pasted on the current tab page, across tab pages, or across test cases.
- Note that the right-click response in the title area is the operation on the test step. So, when you edit the text box in the title area of the test step, the shortcut menu of the browser is overwritten by the shortcut menu of the system, and the shortcut menu of the browser does not take effect. To copy and paste text in the text box of the test step title area, press Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V.
Requesting URL and URL Parameters
On the Scripting tab page of the automated API test cases, enter the URL to be requested. HTTP and HTTPS requests are supported.
API automation supports the following URL request modes. By default, the request mode of a new URL is GET.
|
Request Mode |
Description |
|---|---|
|
GET |
Retrieves data from APIs. |
|
POST |
Uploads files and adds data. |
|
PUT |
Replaces the existing data. |
|
DELETE |
Deletes the existing data. |
|
HEAD |
Obtains the HTTP header of a response. |
|
OPTIONS |
Pre-checks requests. |
|
PATCH |
Updates the fields of some existing data. |
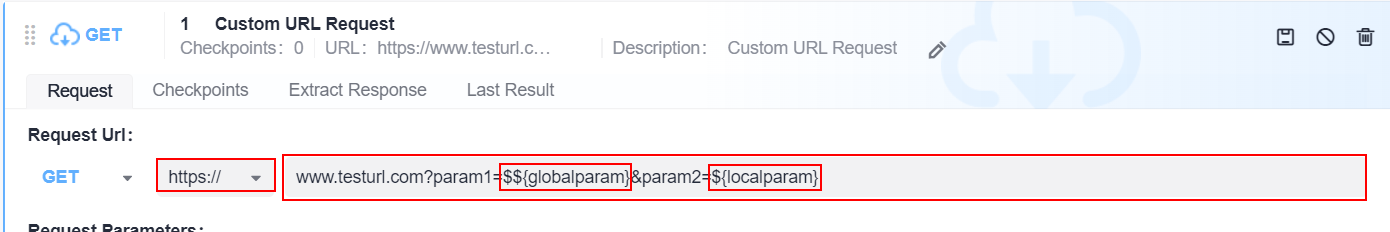
The request URL supports environment parameters, local parameters, and response extraction parameters. For details, see Setting Test Case Parameters of an API Script.
Request Header
Common HTTP request headers are preset for API automation. In the request header module, enter the request header information.
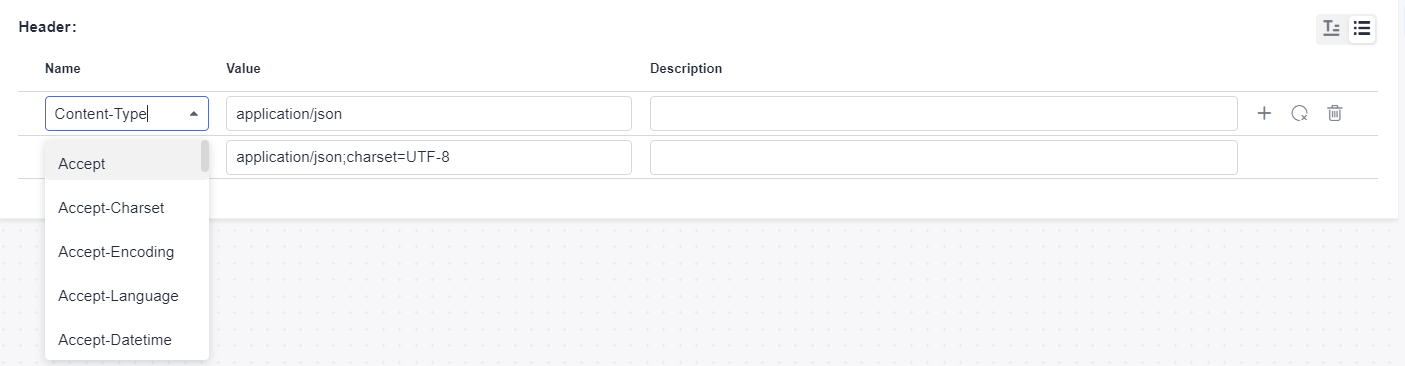
The request header can be in a form or text. By default, the form mode is used on the page. You can click  to switch between the form and text modes.
to switch between the form and text modes.
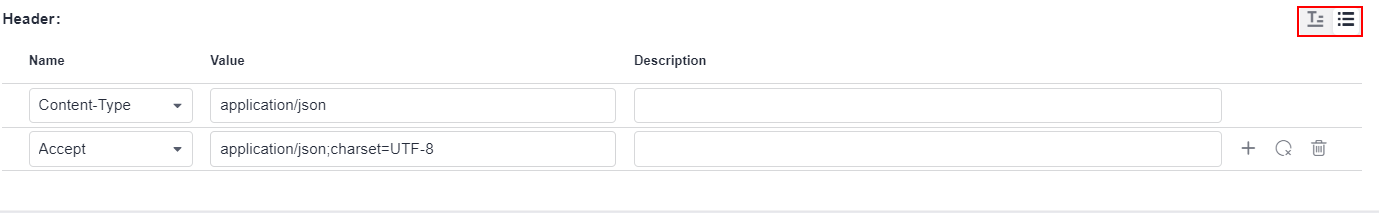
- Form: Select or enter a request header name in the Name column, and select or enter a value in the Value column.
- Text: The request header must be in the format of key:value.
Unlike the form mode, the text mode supports only the configuration of Request Header and Value, but not Description.
Pay attention to the following restrictions when setting request headers:
Multiple common HTTP request headers are preset in CodeArts TestPlan. For details, see the following table.
|
Request Header |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Accept |
Acceptable response content type (Content-Types), for example, text/plain. |
|
Accept-Charset |
Acceptable character set, for example, UTF-8. |
|
Accept-Encoding |
List of acceptable encoding modes, for example, compress | gzip | identity. |
|
Accept-Language |
Natural language list of acceptable response content, for example, en-US. |
|
Accept-Datetime |
Acceptable versions displayed by time. |
|
Access-Control-Request-Method |
Pre-checks requests so that the server knows which HTTP methods will be used when the actual requests are sent. |
|
Access-Control-Request-Headers |
Pre-checks requests so that the server knows which HTTP headers will be used when the actual requests are sent. |
|
Authorization |
Information used for HTTP authentication. |
|
Cache-Control |
Instructions that must be followed by all cache mechanisms for a request or response chain. |
|
Connection |
Preferred connection type used by the browser. |
|
Cookie |
HTTP cookie sent by servers through the Set-Cookie. |
|
Content-Length |
Length of the request body represented by 8-byte arrays. |
|
Content-MD5 |
Binary MD5 hash value of the content of the request body, which is encoded using Base64. |
|
Content-Type |
Multimedia types of the request body (used in POST and PUT requests), for example, application/json. |
|
Date |
Date and time when a message is sent. |
|
Expect |
Specific actions required by a client for a server. |
|
Forwarded |
Client-oriented information from the path proxy server that the proxy participates in the request when it is changed or lost. It is used for debugging, collecting statistics on, and generating location-dependent content, and is designed to display privacy-sensitive information, such as the IP address of the client. So, pay attention to user privacy when deploying this header. |
|
From |
Email address of the user who initiates the request. |
|
Host |
Domain name of the server (used for the virtual host) and the port number of the transmission control protocol listened to by the server. If the requested port is the standard port of the corresponding service, the port number can be omitted. This field is mandatory since HTTP/1.1. If the domain name in the URL is an IP address, this field is automatically added. Otherwise, enter the IP address and port number of the tested application in this field. |
|
If-Match |
The corresponding operation is performed only when the entity provided by the client matches the entity on the server. It is used in a method such as PUT to update a resource which has not been modified since the last update. |
|
If-Modified-Since |
Return 304 Not Modified is allowed when the corresponding content is not modified. |
|
If-None-Match |
Return 304 Not Modified is allowed when the corresponding content is not modified. Refer to the HTTP entity tag. In a typical use, when a URL is requested, the web server returns the resource and its corresponding ETag value, which is placed in the ETag field of the HTTP. The client can then decide whether to cache the resource and its ETag. If the client requests the same URL in the future, a request containing the saved ETag and the If-None-Match field is sent. |
|
If-Range |
If an entity is not modified, one or more parts that are missing are sent to the sender. Otherwise, the entire new entity is sent. |
|
If-Unmodified-Since |
A response is sent only when the entity has not been modified since a specific time. |
|
Max-Forwards |
Number of times a message can be forwarded by the proxy and gateway. |
|
Origin |
Initiates a request for cross-origin resource sharing. The server is mandatory to add an Access-Control-Allow-Origin field to the response. |
|
Pragma |
Related to specific implementations and may produce multiple effects at any time in the request or response chain. |
|
Proxy-Authorization |
Information used to authenticate a proxy. |
|
Range |
Requests only a part of an entity with the byte offset starting from 0. |
|
Referer |
Previous page accessed by a browser. A link on this page brings the browser to the currently requested page. |
|
TE |
Transmission coding mode expected by a browser. You can use a value of Transfer-Encoding in the response protocol header. In addition, the value trailers (related to the block transmission mode) indicates that the browser expects to receive additional fields if the size of the last block is 0. |
|
User-Agent |
String of the browser identity. |
|
Upgrade |
Asks the server to be upgraded to another protocol. |
|
Via |
Request-sending agents informed to the server. |
|
Warning |
General warning indicating that errors may exist in the body of an entity. |
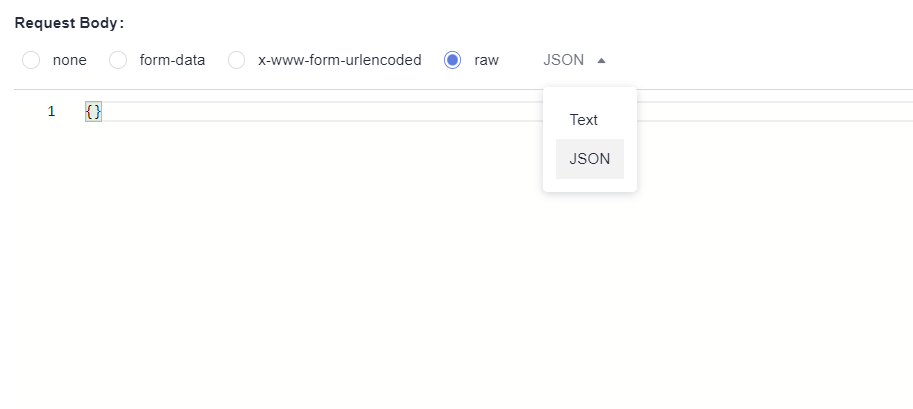
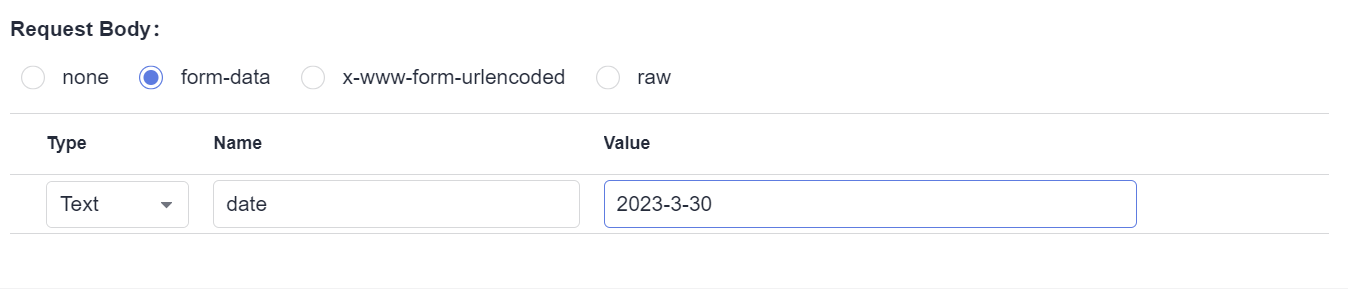
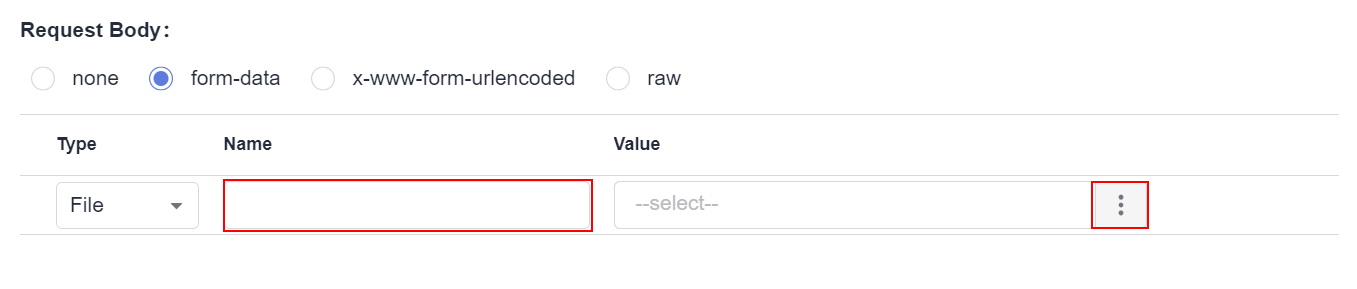
Request Body
A request body is a message (packet) to be transferred in an API request. The request body can be in text, JSON, or form format.
If the request method is POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS, PATCH, or HEAD, the request body is displayed on the page. If the request method is GET, the request body is not displayed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot