Connecting to a DB Instance Through DAS (Recommended)
Data Admin Service (DAS) is a one-stop management platform that allows you to manage Huawei Cloud databases on a web console. It offers database development, O&M, and intelligent diagnosis, making it easy to use and maintain databases.
This section describes how to connect to a DB instance through DAS.
Prerequisites
You have purchased a DB instance. If you have not, purchase one by referring to Buying a DB Instance.
Procedure
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, locate a DB instance and click Log In in the Operation column.
Alternatively, on the Instances page, click the instance name. On the displayed Basic Information page, click Log In in the upper right corner.
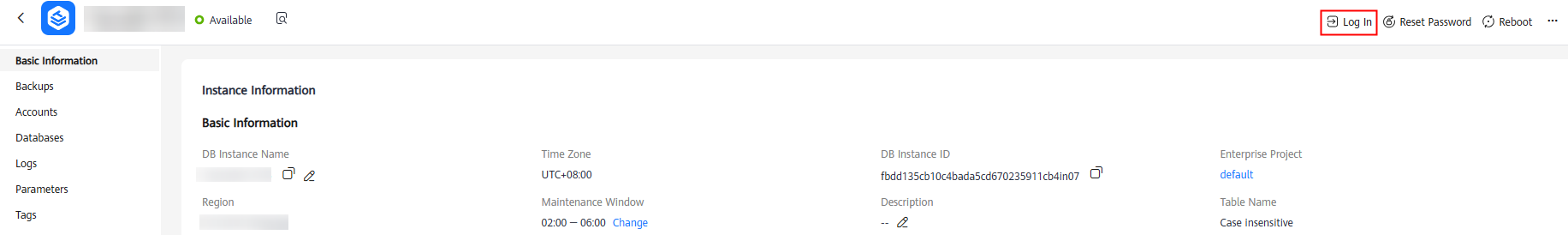
- Enter the login username and password and click Test Connection.
Figure 1 Login page

Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Login Username
The default administrator is root.
Password
Enter the password you specified for the root user during instance creation. If you forget the password, reset it. For details, see Resetting the Administrator Password.
Show Executed SQL Statements
You are advised to enable Show Executed SQL Statements. If enabled, you can view the executed SQL statements under SQL Operations > SQL History and execute them again without entering the SQL statements.
- After the connection test is successful, click Log In. Then you can access and manage your databases.
Other Methods for Connecting to a DB Instance
FAQs
Follow-up Operations
After logging in to a TaurusDB instance through DAS, you can manage your databases.
- Create a database.
After logging in to a TaurusDB instance, click Create Database on the home page, enter database information, and click OK.
Figure 2 Creating a database
Database test is used as an example. After the database is created, you can view it in the database list.
Figure 3 Viewing the created database
- Create a table.
Locate the database and click Create Table in the Operation column.
Figure 4 Creating a table
On the Basic Information tab, set the required parameters.
Figure 5 Entering basic table information
Click Next and enter column information.
Figure 6 Entering column information
Click Create. In the SQL preview window, view the SQL statements for creating a table and click Execute.
Figure 7 Previewing the SQL statements for creating a table
After the SQL statements are executed successfully, you can view the created table in the table list.
Figure 8 Viewing the created table
- Create a user and grant all permissions on the database created in 1 to the user.
On the top menu bar, choose Account Management > User Management.
Figure 9 User management
Click Create User and enter user information and authorization information.
Figure 10 Creating a user Figure 11 Entering user information and authorization information
Figure 11 Entering user information and authorization information
For example, in the Object Permissions area, all permissions on the table (table1) in the database (test) are granted to the user (user).
Figure 12 Previewing the SQL statements for creating a user Figure 13 Viewing the created user
Figure 13 Viewing the created user
- Log in to the database as the created user and write data into the database.
On the DAS development tool page, add a database login as user user. Click Log In in the Operation column to log in to the TaurusDB instance.
Figure 14 Adding a login as user
In the row containing the test database, click Query SQL Statements in the Operation column. The SQL execution window is displayed.
Figure 15 Accessing the SQL execution window
Run the following SQL statement in the SQL input box to query data in table1:
SELECT * FROM table1;
Figure 16 Viewing table data
There is no data in table1.
Run the following SQL statements to write several data records to table1:
insert into table1(id, name, age) values(1, 'sam', 30);
insert into table1(id, name, age) values(2, 'cidy', 25);
insert into table1(id, name, age) values(3, 'lily', 27);
Figure 17 Writing data to the table
Data has been written into the table.
Run the following SQL statement again to check whether there is data in table1:
SELECT * FROM table1;
Figure 18 Verifying the written data
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot