Restoring Tables to a Point in Time (PITR)
Scenarios
To ensure data integrity and reduce impact on the original instance performance, the system restores the full and incremental data at the selected point in time to a temporary instance, exports the tables to be restored, and then restores the tables to the original instance. The time required depends on the amount of data to be backed up and restored on the instance. Restoring tables will not overwrite data in the instance.
Constraints
- Tables that have triggers cannot be restored.
- To prevent restoration failures and impact on original data, table-level restoration removes foreign key constraints.
- If a table you selected does not exist at the specified point in time, the table will not be restored.
- During table-level PITR, the instance cannot be rebooted or deleted, and the instance specifications cannot be changed.
- The number of tables to be restored must be no more than 20,000.
- If the number of tables to be restored exceeds 2,000, you are advised to restore the DB instance to a point in time. For details, see Restoring a DB Instance to a Point in Time (PITR).
- If the name of a table to be restored contains characters other than letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-), the restoration will fail.
- Modifying the kernel parameter rds_extended_partitions_enabled may cause compatibility issues during table-level PITR. Before modifying it, contact customer service for confirmation.
Restoring Tables to a Point in Time
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Backups. On the Full Backups tab, click Restore Table above the backup list.
Figure 1 Restoring tables to a point in time

- On the displayed page, set the restoration date, time range, time point, and tables to be restored.
Figure 2 Setting required parameters
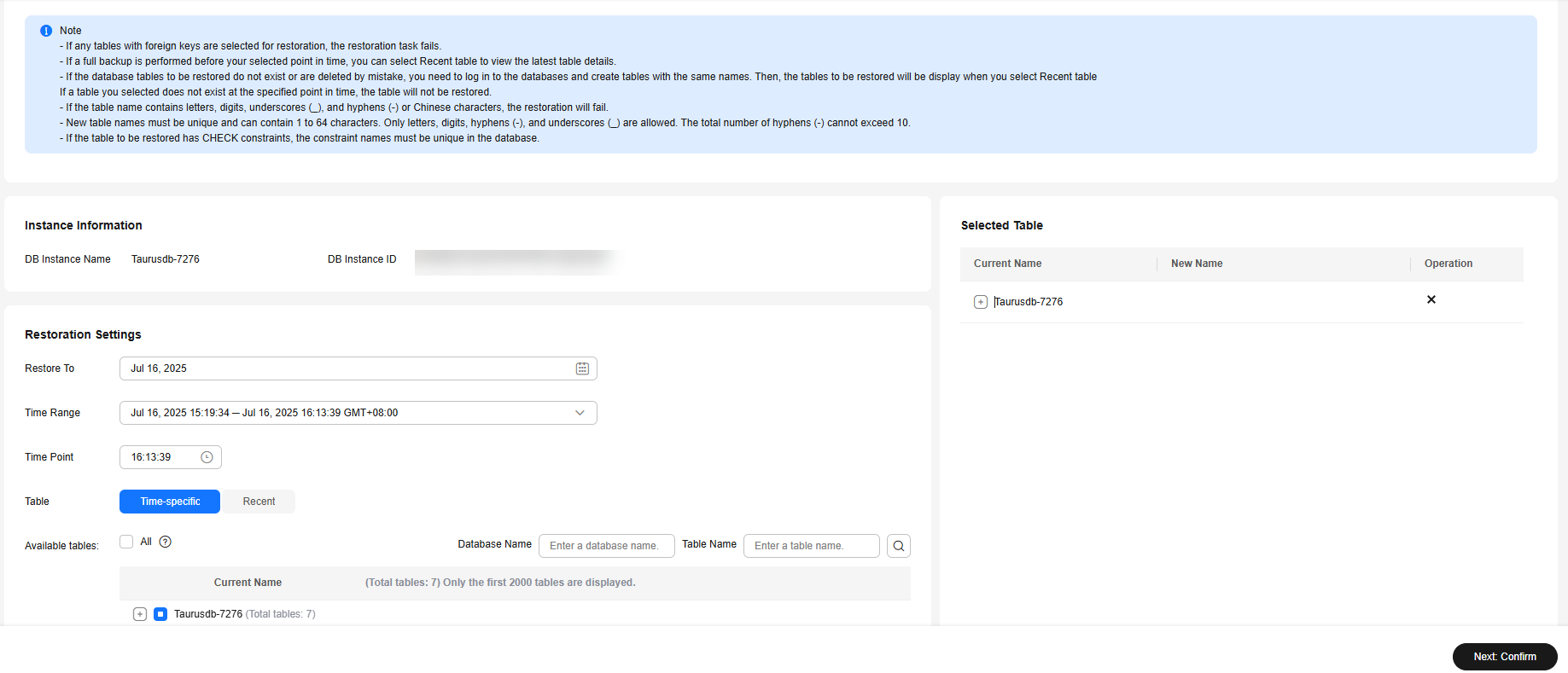
- To facilitate your operations, you can search for the tables and databases to be restored.
- After the restoration is complete, new tables with timestamps as suffixes are generated in the instance. You can rename the new tables. The new table name must be unique. It can contain up to 64 characters. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and dollar signs ($) are allowed.
- Time-specific table: The tables to be restored are read from the latest full backup before the selected time point. Recent table: The tables to be restored are read from the selected time point.
- Tables created after the latest full backup are not displayed in the time-specific table list. You can select Recent table to view the latest table details.
- If the tables to be restored are not found or are deleted by mistake, you need to log in to the databases and create tables with the same names. Then, the tables to be restored will be displayed when you select Recent table.
- Only specified tables are restored. Ensure that all tables to be restored are selected.
- Click Next: Confirm. On the displayed page, confirm the information about the tables to be restored and click Restore Now.
If you need to modify your settings, click Previous.
- On the Instances page, view the instance status, which is Restoring. During the restoration process, services are not interrupted.
You can also view the progress and result of restoring tables to a specified point in time on the Task Center page.
After the restoration is successful, you can manage data in the tables as required.
FAQs
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





