Restoring a DB Instance to a Point in Time (PITR)
Scenarios
You can restore instance data to a specified point in time. Data can be restored to a new, the original, or an existing DB instance.
The most recent full backup will be downloaded from OBS for restoration. After the restoration is complete, incremental backups will be replayed to the specified point in time. The time required depends on the amount of data to be restored.
Precautions
- Data can be restored to a new, the original, or an existing DB instance.
- Keep your account balance above zero so that backups can be restored to a new DB instance. You will be billed for the new DB instance.
- Do not run the reset master command on DB instances within their lifecycle. Otherwise, an exception may occur when restoring a DB instance to a specified point in time.
- Data on the original DB instance will be overwritten and the original DB instance will be unavailable during the restoration.
- Restoring to an existing DB instance will overwrite its data and root password. The existing DB instance is unavailable during the restoration. DB instances will not be displayed unless they have the same DB engine type, version, and table name case sensitivity as the original DB instance.
- If the original password of the existing DB instance cannot be used to connect to the database after the restoration, you can reset the password.
- Once encrypted backup is enabled for your DB instance, data cannot be restored to an existing DB instance, even if encrypted backup is disabled later.
- Ensure that the storage space of the selected DB instance is at least that of the original DB instance. Otherwise, data will not be restored.
Restoring a DB Instance to a Point in Time
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Backups. On the displayed page, click Restore to Point in Time.
Figure 1 Restoring to a point in time
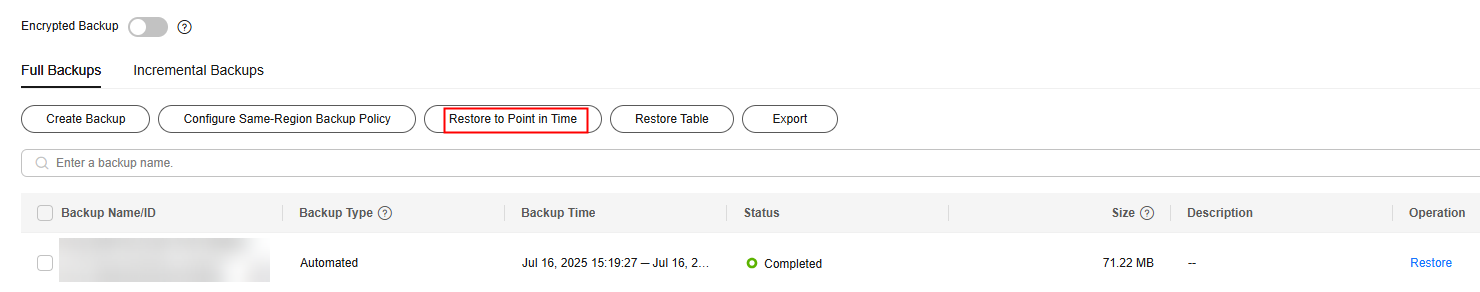
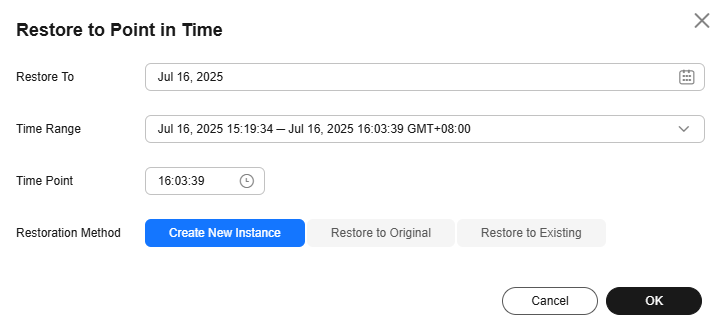
- Select the restoration date and time range, enter a time point within the selected time range, and set Restoration Method to Create New Instance. Then, click OK.
Figure 2 Restoring to a new DB instance
- On the displayed page, select a billing mode.
- Yearly/Monthly: a prepaid billing mode in which you pay for resources before using them. Bills are settled based on the subscription period. The longer the subscription, the bigger the discount. This mode is a good option for long-term, stable workloads.
- Pay-per-use: a postpaid billing mode. You pay as you go and just pay for what you use. The DB instance usage is calculated by the second but billed every hour. This mode allows you to adjust resource usage easily. You neither need to prepare for resources in advance, nor end up with excessive or insufficient preset resources.
- Serverless: The instance capacity automatically changes based on application requirements. You can start using the DB instance first and then pay as you go.
- Configure the DB instance. The region and DB engine version of the new DB instance are the same as those of the original DB instance and cannot be changed.
- Resource selection
Figure 3 Resource selection

Table 1 Resource selection Parameter
Description
DB Engine Version
Only TaurusDB V2.0 is supported.
Kernel Version
DB kernel version. For details about the updates in each kernel version, see TaurusDB Kernel Version Release History.
NOTE:Specifying the kernel version when buying an instance is in the OBT phase. To use this function, submit a service ticket.
Creation Method
Select Create new.
DB Instance Type
Select Cluster or Single.
- Cluster: A cluster instance can contain one primary node and 1 to 15 read replicas. The primary node processes read and write requests, and the read replicas process only read requests. If the primary node becomes unavailable, TaurusDB automatically fails over to a read replica.
- Single: A single-node instance only contains one primary node. There are no read replicas.
AZ Type
An AZ is a physical region where resources have their own independent power supply and networks. AZs are physically isolated but interconnected through an internal network. Some regions support both single-AZ and multi-AZ deployment and some only support single-AZ deployment.
Storage Type
- DL6
The original shared storage. The default storage type of TaurusDB instances created before July 2024 is shared storage, while that of TaurusDB instances created in July 2024 and beyond is DL6.
DL6-based instances achieve zero RPO with a 3-AZ deployment and deliver better performance and higher peak throughput. They are suitable for core application systems that are sensitive to performance and have demanding requirements on storage I/O during peak hours, such as those in finance, e-commerce, government, and gaming.
- DL5
A new type of storage. With Huawei Cloud's hardware and network infrastructure technologies, DL5-based instances maintain the same high availability (zero RPO in the 3-AZ deployment) as DL6-based instances.
Although the peak performance of DL5-based instances may be a bit less than what you get with DL6-based instances, the cost per unit of capacity is a lot less. DL5-based instances are suitable for CPU-intensive sub-core business systems, or application modules that need to minimize costs.
For more information about storage types, see Storage Types.
- Instance options
Figure 4 Specifications and storage
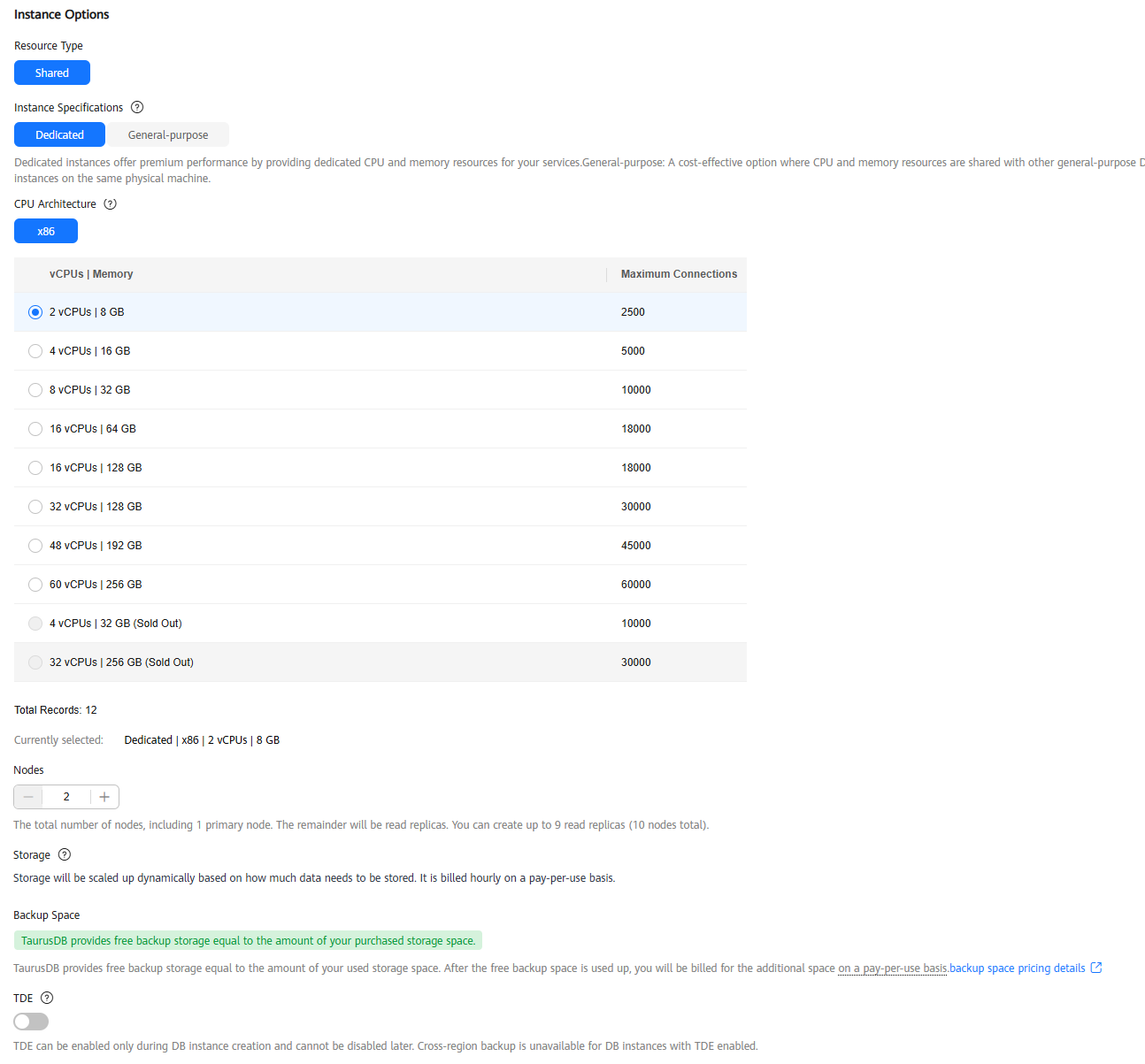
Table 2 Specifications and storage Parameter
Description
Resource Type
Select Shared.
Instance Specifications
TaurusDB is a cloud-native database that uses shared storage. To ensure that instances run stably under high read/write pressure, TaurusDB controls the read/write peaks of instances based on instance specifications. For details about how to select instance specifications, see Performance White Paper.
For more information about instance specifications, see Instance Specifications.
After an instance is created, you can change its vCPUs and memory.
CPU Architecture
Select x86 or Kunpeng.
- x86: x86 instances use Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors and feature robust and stable computing performance. When working on high-performance networks, the instances provide the additional performance and stability that enterprise-class applications demand.
- Kunpeng: Kunpeng instances use Kunpeng 920 processors and 25GE high-speed intelligent NICs for powerful compute and high-performance networks, making them an excellent choice for enterprises needing cost-effective, secure, and reliable cloud services.
Nodes
This parameter is mandatory for cluster instances.
- By default, each instance can contain one primary node and multiple read replicas.
- You can create up to 9 read replicas for a pay-per-use instance at once.
- You can also add read replicas after an instance is created. Each instance can contain up to 15 read replicas. For details, see Adding Read Replicas to a DB Instance.
Storage
It contains the file system overhead required for inodes, reserved blocks, and database operations.
Storage of a pay-per-use instance will be scaled up dynamically based on the amount of data that needs to be stored, and is billed hourly on a pay-per-use basis.
Backup Space
TaurusDB provides free backup space equal to the amount of your used storage. After the free backup space is used up, you will be billed for the additional space on a pay-per-use basis.
TDE
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) encrypts data files and backup files using certificates to implement real-time I/O encryption and decryption. This function effectively protects your databases and data files.
After TDE is enabled, you need to select the cryptographic algorithm AES256 or SM4 as needed.
For details about TDE constraints, see Enabling TDE for a DB Instance.
To enable TDE, submit a service ticket.
Figure 5 Network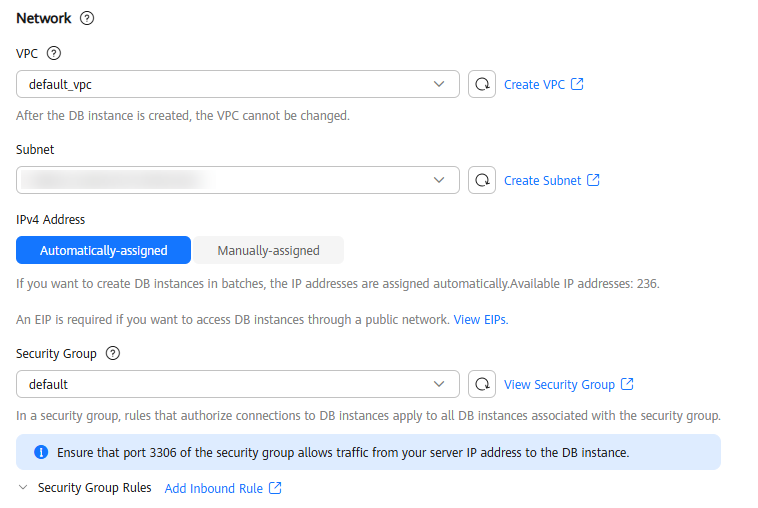
Table 3 Network Parameter
Description
VPC
A dedicated virtual network where your instance is located. It isolates networks for different workloads to enhance security.
TaurusDB allocates a default VPC (default_vpc) for your instance. You can also use an existing, new, or shared VPC.
After an instance is created, the VPC cannot be changed.
Subnet
A subnet provides dedicated network resources that are logically isolated from other networks for network security. Subnets are only valid within a specific AZ. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is enabled by default for subnets where you plan to create DB instances and cannot be disabled.
Security Group
A security group enhances security by controlling access to TaurusDB from other services. When you select a security group, you must ensure that it allows the client to access DB instances.
If no security group is available or has been created, TaurusDB allocates a security group to your DB instance by default.
To ensure subsequent database connection and access, you need to allow all IP addresses to access your DB instance through port 3306 and over ICMP. If the port and protocol are not enabled for the selected security group, click Add Inbound Rule as prompted and complete the configuration in the displayed dialog box.
For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules.
Figure 6 Setting an administrator password
Table 4 Database configuration Parameter
Description
DB Instance Name
The name must start with a letter and consist of 4 to 64 characters. Only letters (case-sensitive), digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed.
Administrator Password
The default administrator account is root.
The administrator password must consist of 8 to 32 characters and contain at least three of the following: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters (~!@#%^*-_=+?,()&$|.). Enter a strong password and periodically change it for security reasons.
If you select a custom parameter template during instance creation, the administrator password must comply with the values of validate_password parameters in the custom parameter template. Otherwise, the instance creation will fail.
To check the parameter values, go to the Parameter Templates page, find the target parameter template and click its name. In the upper right corner of the page, search for validate_password.
Keep this password secure. The system cannot retrieve it.
After a DB instance is created, you can reset this password. For details, see Resetting the Administrator Password.
Confirm Password
Enter the administrator password again.
- Advanced settings
Figure 7 Advanced settings
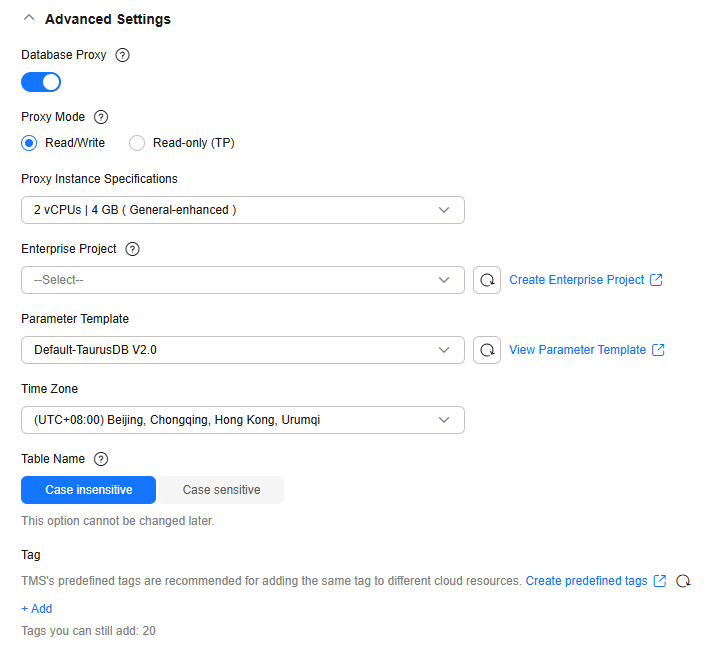
Table 5 Advanced settings Parameter
Description
Database Proxy
Enabled by default. After a proxy instance is created, you can use the proxy address to connect to your DB instance.
Proxy Mode
You can select Read/Write or Read-only (TP) as needed.
- Read/Write: All write requests are forwarded only to the primary node, and all read requests are forwarded to the selected nodes based on the read weights.
- Read-only (TP): The primary node does not process write or read requests, and all read requests are forwarded to the selected read replicas based on read weights.
Proxy Instance Specifications
You can select the proxy instance specifications as needed.
Enterprise Project
This parameter is only available for enterprise users. To use it, contact customer service.
An enterprise project provides a way to manage cloud resources and enterprise members on a project-by-project basis.
You can select an enterprise project from the drop-down list. The default project is default.
Parameter Template
Contains engine configuration values that can be applied to one or more instances.
In the drop-down list, you can select the original instance parameter template, the default parameter template (Default-TaurusDB V2.0), the high-performance parameter template (Default-TaurusDB V2.0-High Performance), or a custom parameter template in the current region as required.
- If you select the original instance parameter template, parameters of the original instance are automatically synchronized. If the original instance is deleted, its parameters cannot be synchronized using backups.
When you synchronize parameters of the original instance, the following parameters cannot be synchronized and you need to manually modify them after the instance is restored.
innodb_write_io_threads, innodb_read_io_threads, max_connections, innodb_log_buffer_size, innodb_parallel_read_threads, temptable_max_ram, threadpool_size, innodb_buffer_pool_size, and innodb_page_cleaners
- Default-TaurusDB V2.0 contains DB engine defaults and system defaults that are configured based on the engine, compute class, and allocated storage space of an instance. Parameter values in the default template cannot be changed, but you can create a custom template with whatever values you require.
- Default-TaurusDB V2.0-High Performance is a set of optimized configuration parameters that aim to enhance the performance and reliability of database servers. The parameter settings in the template can be adjusted based on different application scenarios and hardware configurations. For details, see Introducing the High-Performance Parameter Template.
- You can select a custom parameter template and change the parameter values as required. The changes to parameter values in a custom parameter template are not applied to your instance until you apply the template to the instance. For details, see Applying a Parameter Template. If you select a custom parameter template when creating an instance, the specification-related parameters in the custom template will not be applied. Instead, the default values are used. For details, see What Parameters Should I Pay Attention to When Creating a DB Instance?
Time Zone
You need to select a time zone for your instance based on the region hosting your instance. The time zone is selected during instance creation and cannot be changed after the instance is created.
Tag
Tags a TaurusDB instance. This parameter is optional. Adding tags helps you better identify and manage your instances. Each instance can have up to 20 tags.
- Resource selection
- View the restoration results.
A new DB instance is created, where data is restored based on the point in time when the backup was created. When the instance status changes from Creating to Available, the restoration is complete. The new DB instance is independent from the original one. If you want to offload the read load from the primary node, create one or more read replicas for the new DB instance.
After the restoration, a full backup will be automatically triggered.
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Backups. On the displayed page, click Restore to Point in Time.
Figure 8 Restoring to a point in time

- Select the restoration date and time range, enter a time point within the selected time range, set Restoration Method to Restore to Original, select the confirmation check box, and click Next.
Figure 9 Restoring to the original DB instance
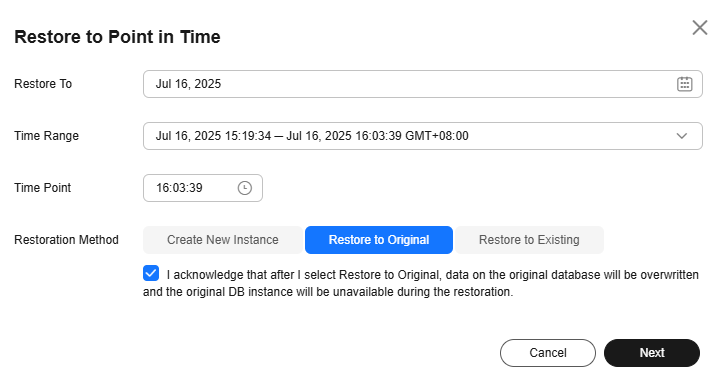
- Confirm the task details and click OK.
Data on the original DB instance will be overwritten and the original DB instance will be unavailable during the restoration.
- View the restoration results.
When the instance status changes from Restoring to Available, the restoration is complete.
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Backups. On the displayed page, click Restore to Point in Time.
Figure 10 Restoring to a point in time

- Select the restoration date and time range, and enter a time point within the selected time range.
- Set Restoration Method to Restore to Existing, select the confirmation check box, and click Next.
Figure 11 Restoring to an existing DB instance
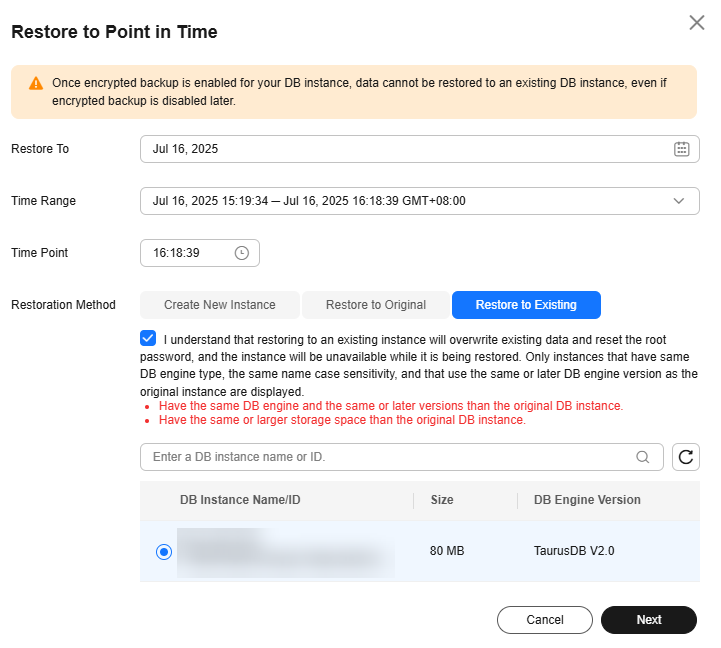
- Confirm the task details and click OK.
- Restoring to an existing DB instance will overwrite its data and root password. The existing DB instance is unavailable during the restoration. DB instances will not be displayed unless they have the same DB engine type, version, and table name case sensitivity as the original DB instance.
- The restored DB instance contains the data and account information of the original DB instance, but does not contain the parameter settings of the original DB instance.
- If the original password of the existing DB instance cannot be used to connect to the database after the restoration, you can reset the password.
- View the restoration results.
When the instance status changes from Restoring to Available, the restoration is complete.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





