Asynchronous Command Delivery
Introduction
Asynchronous command delivery is used for IoTDA or applications to deliver commands to devices using LwM2M over CoAP to access IoTDA. Two modes are available.
Type |
Description |
Application |
Process |
|---|---|---|---|
Immediate delivery of asynchronous commands |
IoTDA delivers commands to a device upon receiving a command regardless of whether the device is online. If the device is offline or the device does not receive the command, the delivery fails. |
It is used in scenarios that have high requirements for timeliness. |
|
Delayed delivery of asynchronous commands |
The IoT platform caches a command and delivers it to a device when the device goes online or reports properties. If a device has multiple cached commands, the IoT platform delivers the commands in sequence. |
Delayed delivery applies to commands that do not need to be executed immediately, for example, configuring water meter parameters. |
Immediate Delivery of Asynchronous Commands
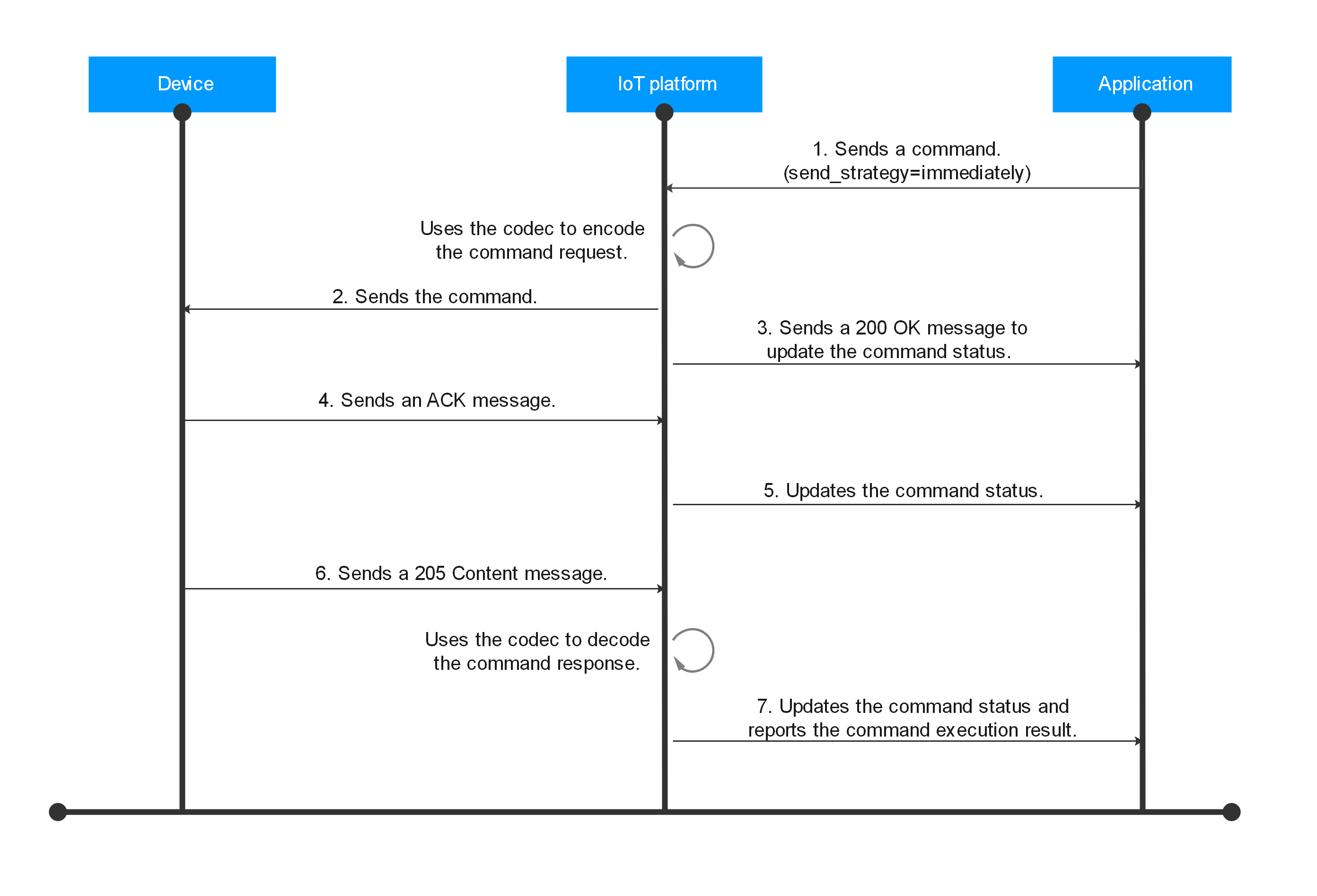
An example of the corresponding steps is as follows:
- An application calls the API Deliver an Asynchronous Command to send a command to the platform. The send_strategy parameter in the command request is set to immediately. Example message:
POST https://{endpoint}/v5/iot/{project_id}/devices/{device_id}/async-commands Content-Type: application/json X-Auth-Token: ******** { "service_id" : "WaterMeter", "command_name" : "ON_OFF", "paras" : { "value" : "ON" }, "expire_time": 0, "send_strategy": immediately } - The platform uses the codec to encode the command request, and sends the command through the Execute operation of the device management and service implementation interface defined in the LwM2M protocol. The message body is in binary format.
- The platform sends a 200 OK message carrying the command status SENT to the application. (If the device is offline or the device does not receive the command, the delivery fails and the command status is FAILED.)
- The device returns an ACK message after receiving the command.
- If the application has subscribed to command status change notifications, the platform pushes a message to the application by calling the API Pushing a Command Status Change Notification. The command status carried in the message is DELIVERED. Example message:
Method: POST request: Body: { "resource": "device.commmad.status", "event": "update", "event_time": "20200811T080745Z", "notify_data": { "header": { "app_id": "8d4a34e5363a49bfa809c6bd788e6ffa", "device_id": "5f111a5a29c62ac7edc88828_test0001", "node_id": "test0001", "product_id": "5f111a5a29c62ac7edc88828", "gateway_id": "5f111a5a29c62ac7edc88828_test0001", "tags": [] }, "body": { "command_id": "49ca40af-7e14-4f7b-b97b-78cdd347a6b9", "created_time": "20200811T080738Z", "sent_time": "20200811T080738Z", "delivered_time": "20200811T080745Z", "response_time": "", "status": "DELIVERED", "result": null } } } - After the command is executed, the device returns the command execution result in a 205 Content message.
- If the application has subscribed to command status change notifications, the platform uses the codec to decode the command response and sends a push message to the application by calling the API Pushing a Command Status Change Notification. The command status carried in the message is SUCCESSFUL. Example message:
Method: POST request: Body: { "resource": "device.commmad.status", "event": "update", "event_time": "20200811T080745Z", "notify_data": { "header": { "app_id": "8d4a34e5363a49bfa809c6bd788e6ffa", "device_id": "5f111a5a29c62ac7edc88828_test0001", "node_id": "test0001", "product_id": "5f111a5a29c62ac7edc88828", "gateway_id": "5f111a5a29c62ac7edc88828_test0001", "tags": [] }, "body": { "command_id": "49ca40af-7e14-4f7b-b97b-78cdd347a6b9", "created_time": "20200811T080738Z", "sent_time": "20200811T080738Z", "delivered_time": "20200811T080745Z", "response_time": "20200811T081745Z", "status": "SUCCESSFUL", "result": { "resultCode":"SUCCESSFUL", "resultDetail": { "value": "ON" } } } } }
Delayed Delivery of Asynchronous Commands
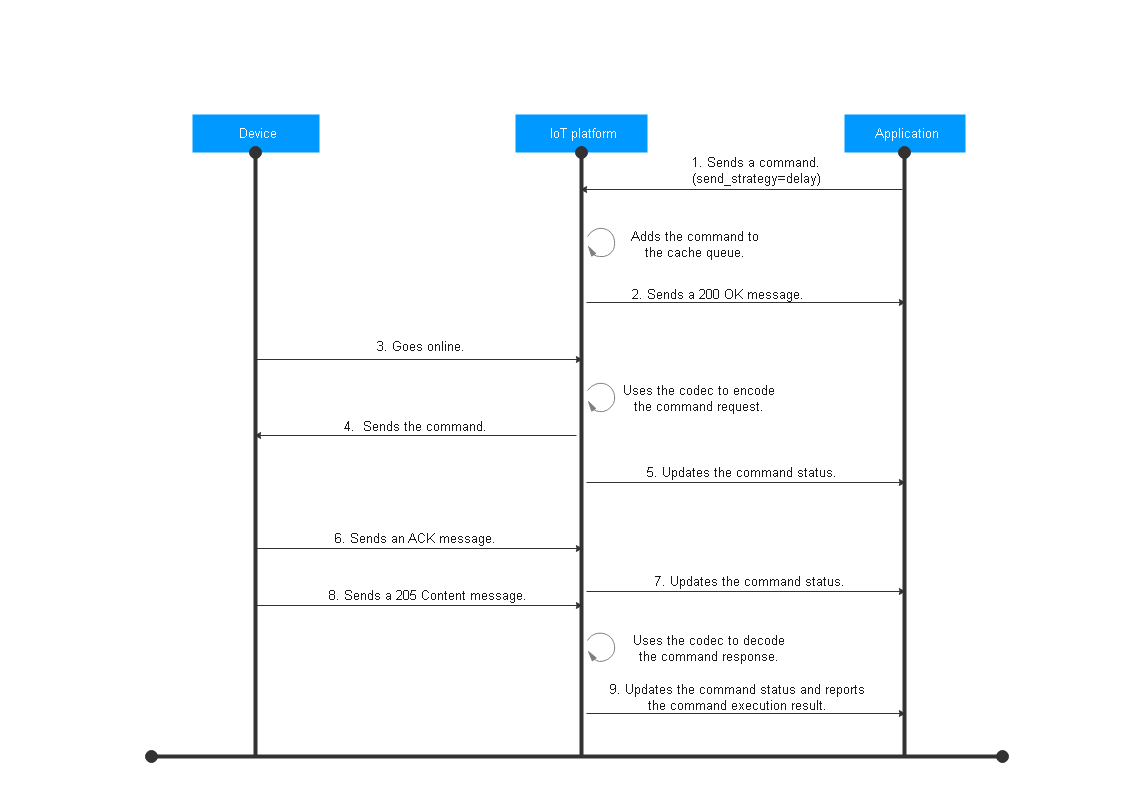
- An application calls the API Deliver an Asynchronous Command to send a command to the platform. The send_strategy parameter in the command request is set to delay.
- The platform adds the command to the cache queue and reports a 200 OK message. The command status is PENDING.
- The device goes online or reports data to the platform.
- The platform uses the codec to encode the command request and sends the command to the device according to the protocol specifications.
- If the application has subscribed to command status change notifications, the platform pushes a message to the application by calling the API Pushing a Command Status Change Notification. The command status carried in the message is SENT.
- The subsequent flow is the same as 4 to 7 described in the immediate delivery scenario.
LwM2M/CoAP Device Command Execution Status
The figure below illustrates the command execution status and the table below describes the status change mechanism.
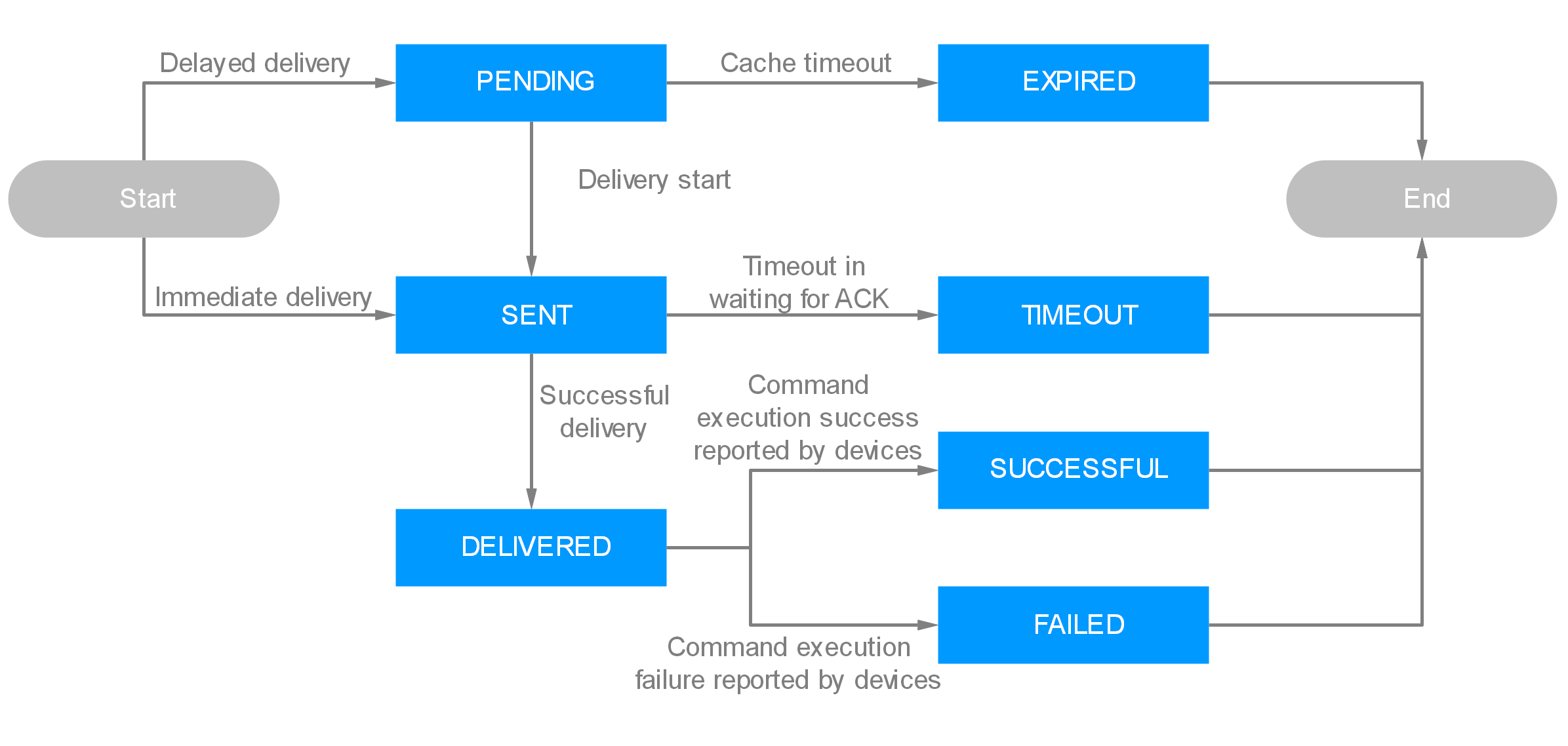
Status |
Description |
|---|---|
PENDING |
|
EXPIRED |
|
SENT |
|
TIMEOUT |
If the platform does not receive a response within 180 seconds after delivering a command to a device using LwM2M over CoAP, the command status is TIMEOUT. |
DELIVERED |
If the platform receives a response from a device, the command status is DELIVERED. |
SUCCESSFUL |
If the platform receives a result indicating that the command is executed, the command status is SUCCESSFUL. |
FAILED |
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





