Overview
You can discover, record, and resolve product function defects and poor performance during software product use. This function is to reduce the number of product or service faults on the live network, improve the quality of services, products, or applications, and prevent problems from recurring. In this module, the whole lifecycle of issues tickets is managed, including ticket creation, acceptance, rejection, transferring, handling, and closure. Issue tickets can be created manually or through northbound APIs.
You can also configure SLA rules. For details about how to configure SLA rules, see SLA Management.
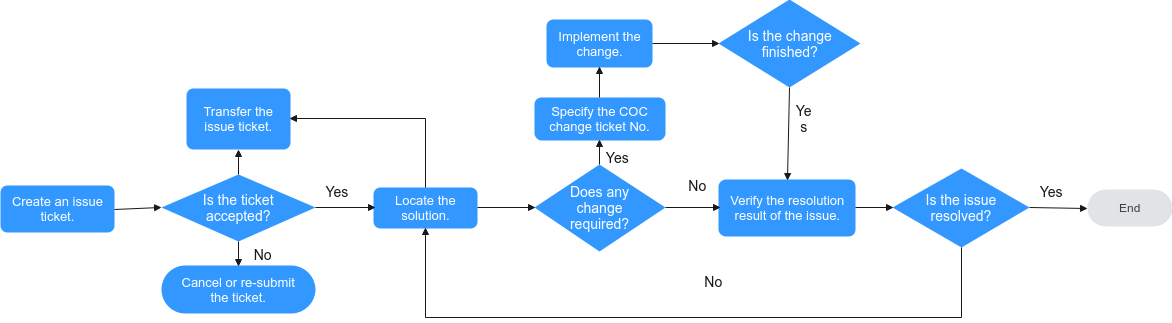
Issue Management Process
- After the issue ticket is created, the status is Not accepted. You can accept or reject the ticket, or transfer it to the owner.
- After the issue ticket is accepted, its status becomes Locate the solution. You can enter the issue locating result, transfer the ticket to the owner, escalate or de-escalate the ticket, or suspend it.
- After an issue ticket is suspended, it needs to be reviewed by the creator. After the ticket is approved, the status of the issue ticket changes to Suspend. You can manually cancel the suspension or the suspension is automatically canceled when the specified time arrives.
- When you enter the locating result, if you select change-required, the ticket status is To be implemented on the live network. You need to associate it with a change ticket and the change ticket has the backfilling result. In this way, the issue ticket can be transferred to the next step.
- If an issue ticket does not require change or the issue ticket has a change result, the ticket status is To be verified. The creator confirms whether the issue is resolved or not. If the issue is not resolved, the creator can reject the ticket.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





