Importing Data to a Doris Cluster with Broker Load
Broker Load is an asynchronous import method, and the supported data sources depend on the data sources supported by the Broker process. This section describes the basic principles, basic operations, system configurations, and application examples of Broker Load import.
Application Scenarios
- The source data is in a storage system that the Broker can access, such as HDFS and OBS.
- The amount of data is at the level of tens to hundreds of GB.
Basic Principles
After an import job is submitted, the FE will generate a plan and distribute the plan to multiple BEs for execution based on the current number of BEs and file size, and each BE executes a part of the imported data.
A BE pulls data from the Broker during execution, and imports the data into the system after transforming the data. After all BEs complete the import, the FE determines whether the import is successful.
+
| 1. user create broker load
v
+----+----+
| |
| FE |
| |
+----+----+
|
| 2. BE etl and load the data
+--------------------------+
| | |
+---v---+ +--v----+ +---v---+
| | | | | |
| BE | | BE | | BE |
| | | | | |
+---+-^-+ +---+-^-+ +--+-^--+
| | | | | |
| | | | | | 3. pull data from broker
+---v-+-+ +---v-+-+ +--v-+--+
| | | | | |
|Broker | |Broker | |Broker |
| | | | | |
+---+-^-+ +---+-^-+ +---+-^-+
| | | | | |
+---v-+-----------v-+----------v-+-+
| HDFS/BOS/AFS cluster |
| |
+----------------------------------+
Starting the Import
The following are some examples of using Broker Load import.
Data sample:
'100','101','102','103','104','105',100.00,100.01,100.02,'100',200,100.08,2022-04-01
'101','102','103','104','105','105',100.00,100.01,100.02,'100',200,100.08,2022-04-02
'102','103','104','105','106','105',100.00,100.01,100.02,'100',200,100.08,2022-04-03
Preparations:
Create a sample data file source_text.txt on the local host and upload it to the /tmp/ directory of HDFS.
CREATE TABLE `ods_source`( `id` string, `store_id` string, `company_id` string, `tower_id` string, `commodity_id` string, `commodity_name` string, `commodity_price` double, `member_price` double, `cost_price` double, `unit` string, `quantity` string, `actual_price` double, `day ` string ) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' stored as textfile;
load data inpath '/tmp/source_text.txt' into table ods_source;
- Example 1: Import the data in textfile format.
- Create a partitioned table in Hive and write data to it.
- Create the ods_demo_detail table.
CREATE TABLE `ods_demo_detail`( `id` string, `store_id` string, `company_id` string, `tower_id` string, `commodity_id` string, `commodity_name` string, `commodity_price` double, `member_price` double, `cost_price` double, `unit` string, `quantity` string, `actual_price` double ) PARTITIONED BY (day string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' stored as textfile;
- Import data in the ods_source table to the ods_demo_detail table.
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict; set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true; insert overwrite table ods_demo_detail partition(day) select * from ods_source;
- Create the ods_demo_detail table.
- Check whether Hive table ods_demo_detail contains data.
select * from ods_demo_detail;
- Create a database in Doris.
create database doris_demo_db;
- Create Doris table doris_ods_test_detail.
If the ultra-high I/O specification is not selected for the cluster during cluster creation, delete 'storage_medium'='SSD'.
use doris_demo_db; CREATE TABLE `doris_ods_test_detail` ( `rq` date NULL, `id` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `store_id` varchar(32) NULL, `company_id` varchar(32) NULL, `tower_id` varchar(32) NULL, `commodity_id` varchar(32) NULL, `commodity_name` varchar(500) NULL, `commodity_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `member_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `cost_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `unit` varchar(50) NULL, `quantity` int(11) NULL, `actual_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL ) ENGINE=OLAP UNIQUE KEY(`rq`, `id`, `store_id`) PARTITION BY RANGE(`rq`) ( PARTITION P_202204 VALUES [('2022-04-01'),('2022-08-30'))) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`store_id`) BUCKETS 1 PROPERTIES ( 'replication_allocation' = 'tag.location.default: 3', 'dynamic_partition.enable' = 'true', 'dynamic_partition.time_unit' = 'MONTH', 'dynamic_partition.start' = '-2147483648', 'dynamic_partition.end' = '2', 'dynamic_partition.prefix' = 'P_', 'dynamic_partition.buckets' = '1', 'in_memory' = 'false', 'storage_format' = 'V2', 'storage_medium' = 'SSD' ); - Import data.
LOAD LABEL broker_name_test01 ( DATA INFILE('hdfs://{HDFS remote IP address}:{HDFS remote port number}/user/hive/warehouse/ods_demo_detail/*/*') INTO TABLE doris_ods_test_detail COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ',' (id,store_id,company_id,tower_id,commodity_id,commodity_name,commodity_price,member_price,cost_price,unit,quantity,actual_price) COLUMNS FROM PATH AS (`day`) SET (rq = str_to_date(`day`,'%Y-%m-%d'),id=id,store_id=store_id,company_id=company_id,tower_id=tower_id,commodity_id=commodity_id,commodity_name=commodity_name,commodity_price=commodity_price,member_price=member_price,cost_price=cost_price,unit=unit,quantity=quantity,actual_price=actual_price) ) WITH BROKER 'broker1' ( 'username' = 'hdfs', 'password' = '' ) PROPERTIES ( 'timeout'='1200', 'max_filter_ratio'='0.1' ); - Check the import status.
You can run the following command to view the status of the import job:
show load order by createtime desc limit 1\G;
 If the status information contains the "Scan bytes per file scanner exceed limit: 3221225472", the import fails. In this case, you need to modify the max_bytes_per_broker_scanner parameter. For details, see FE node parameters in Modifying Doris Parameters to Optimize Cluster Performance.Figure 1 Checking the import status
If the status information contains the "Scan bytes per file scanner exceed limit: 3221225472", the import fails. In this case, you need to modify the max_bytes_per_broker_scanner parameter. For details, see FE node parameters in Modifying Doris Parameters to Optimize Cluster Performance.Figure 1 Checking the import status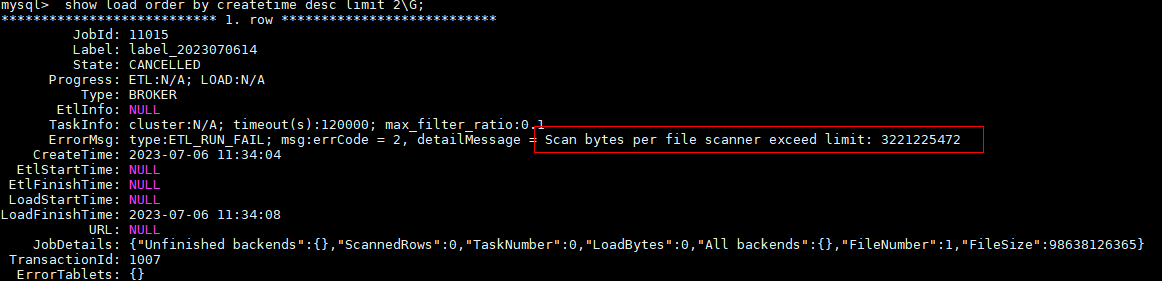
- Create a partitioned table in Hive and write data to it.
- Example 2: Import an ORC table.
- Create a Hive partitioned table in ORC format.
CREATE TABLE `ods_demo_orc_detail`( `id` string, `store_id` string, `company_id` string, `tower_id` string, `commodity_id` string, `commodity_name` string, `commodity_price` double, `member_price` double, `cost_price` double, `unit` string, `quantity` double, `actual_price` double ) PARTITIONED BY (day string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' STORED AS ORC;
- Query the source table and write it to the partitioned table.
insert overwrite table ods_demo_orc_detail partition(day) select * from ods_source;
- Create a Doris table.
CREATE TABLE `doris_ods_orc_detail` ( `rq` date NULL, `id` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `store_id` varchar(32) NULL, `company_id` varchar(32) NULL, `tower_id` varchar(32) NULL, `commodity_id` varchar(32) NULL, `commodity_name` varchar(500) NULL, `commodity_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `member_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `cost_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `unit` varchar(50) NULL, `quantity` int(11) NULL, `actual_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL ) ENGINE=OLAP UNIQUE KEY(`rq`, `id`, `store_id`) PARTITION BY RANGE(`rq`) ( PARTITION P_202204 VALUES [('2022-04-01'), ('2022-08-30'))) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`store_id`) BUCKETS 1 PROPERTIES ( 'replication_allocation' = 'tag.location.default: 3', 'dynamic_partition.enable' = 'true', 'dynamic_partition.time_unit' = 'MONTH', 'dynamic_partition.start' = "-2147483648", 'dynamic_partition.end' = '2', 'dynamic_partition.prefix' = 'P_', 'dynamic_partition.buckets' = '1', 'in_memory' = 'false', 'storage_format' = 'V2'); - Import data.
LOAD LABEL orc_2022_02_17 ( DATA INFILE("hdfs://{HDFS remote IP address}:{HDFS remote port number}/user/hive/warehouse/ods_demo_orc_detail/*/*") INTO TABLE doris_ods_orc_detail COLUMNS TERMINATED BY "," FORMAT AS 'orc' (id,store_id,company_id,tower_id,commodity_id,commodity_name,commodity_price,member_price,cost_price,unit,quantity,actual_price) COLUMNS FROM PATH AS (`day`) SET (rq = str_to_date(`day`,'%Y-%m-%d'),id=id,store_id=store_id,company_id=company_id,tower_id=tower_id,commodity_id=commodity_id,commodity_name=commodity_name,commodity_price=commodity_price,member_price=member_price,cost_price=cost_price,unit=unit,quantity=quantity,actual_price=actual_price) ) WITH BROKER 'broker1' ( 'username' = 'hdfs', 'password'= "" ) PROPERTIES ( 'timeout'="1200", 'max_filter_ratio'="0.1" ); - Query the imported data.
show load order by createtime desc limit 1\G;
- Create a Hive partitioned table in ORC format.
- Example 3: Import data in OBS format.
- Create a Doris table.
CREATE TABLE `obs_detail_test` ( `id` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `store_id` varchar(32) NULL, `company_id` varchar(32) NULL, `tower_id` varchar(32) NULL, `commodity_id` varchar(32) NULL, `commodity_name` varchar(500) NULL, `commodity_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `member_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `cost_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `unit` varchar(50) NULL, `quantity` int(11) NULL, `actual_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL ) ENGINE=OLAP UNIQUE KEY(`id`, `store_id`) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`store_id`) BUCKETS 1 PROPERTIES ( 'replication_allocation' = 'tag.location.default: 3', 'in_memory' = 'false', 'storage_format' = 'V2' );
- Import OBS data to the Doris table.
Construct 100 pieces of text data, which corresponds to the fields in the Doris table. Upload the data to OBS buckets.
LOAD LABEL label_2023021801 ( DATA INFILE("obs://xxx/source_text2.txt") INTO TABLE `obs_detail_test` COLUMNS TERMINATED BY "," (id,store_id,company_id,tower_id,commodity_id,commodity_name,commodity_price,member_price,cost_price,unit,quantity,actual_price) ) WITH BROKER 'broker1' ( 'fs.obs.access.key' = 'xxx', 'fs.obs.secret.key' = 'xxxxxx', 'fs.obs.endpoint' = 'xxxxxx' ) PROPERTIES ( 'timeout'="1200", 'max_filter_ratio'='0.1' );Methods for obtaining fs.obs.access.key, fs.obs.secret.key, and fs.obs.endpoint:
- For details about how to obtain fs.obs.access.key and fs.obs.secret.key, see Access Keys in the OBS documentation.
- For details about how to obtain fs.obs.endpoint, see How Do I Obtain an OBS Endpoint in the OBS documentation.
- Query data.
show load order by createtime desc limit 1\G;
- Create a Doris table.
- Example 4: Import HDFS data to a Doris table through With HDFS.
- Create a Doris table.
CREATE TABLE `ods_dish_detail_test` ( `id` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `store_id` varchar(32) NULL, `company_id` varchar(32) NULL, `tower_id` varchar(32) NULL, `commodity_id` varchar(32) NULL, `commodity_name` varchar(500) NULL, `commodity_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `member_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `cost_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL, `unit` varchar(50) NULL, `quantity` int(11) NULL, `actual_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL ) ENGINE=OLAP UNIQUE KEY(`id`, `store_id`) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`store_id`) BUCKETS 1 PROPERTIES ( 'replication_allocation' = 'tag.location.default: 3', 'in_memory' = 'false', 'storage_format' = 'V2' );
- Import data.
Construct 100 text data records, which correspond to fields in the Doris table.
LOAD LABEL label_2023021703 ( DATA INFILE("hdfs://{HDFS remote IP address}:{HDFS remote port number}/tmp/source_text2.txt") INTO TABLE `ods_dish_detail_test` COLUMNS TERMINATED BY "," (id,store_id,company_id,tower_id,commodity_id,commodity_name,commodity_price,member_price,cost_price,unit,quantity,actual_price) ) with HDFS ( 'fs.defaultFS'="hdfs://{HDFS remote IP address}:{HDFS remote port}", 'hadoop.username'="hdfs", 'password'="" ) PROPERTIES ( 'timeout'="1200", 'max_filter_ratio'='0.1' ); - Query data.
show load order by createtime desc limit 1\G;
- Create a Doris table.
Canceling Data Import
If a Broker Load job is not cancelled or finished, you can manually cancel it. When canceling an import job, you need to specify the label of the job.
System Configurations
Configure the FE. The following configurations belong to the system-level configuration of Broker Load, that is, the configurations that apply to all Broker Load import jobs. You can change the configuration values by modifying the FE configuration items.
max_bytes_per_broker_scanner/max_broker_concurrency
max_bytes_per_broker_scanner limits the maximum amount of data processed by a single BE node. max_broker_concurrency limits the maximum number of concurrent imports in a job. The minimum amount of data processed (64 MB by default), the maximum number of concurrent imports, source file size, and the number of BE nodes in the current cluster together determine the number of concurrent imports in a job.
Number of concurrent imports = Math.min(Source file size/Minimum amount of data processed (64 MB by default), Maximum concurrent imports, Current number of BE nodes) Amount of data processed by a single BE node = Source file size/Number of concurrent imports
Usually, the maximum amount of data supported by an import job is the product of the max_bytes_per_broker_scanner value and the number of BE nodes. If you need to import a larger amount of data, you need to adjust the value of the max_bytes_per_broker_scanner parameter appropriately.
Default configuration:
- max_broker_concurrency: The default value is 10.
- max_bytes_per_broker_scanner: The default value is 3 GB, which should be converted to the unit of bytes.
Application Examples
- Application scenarios
If raw data is stored in a file system (such as HDFS, BOS, or AFS), Broker Load is the most suitable solution. Broker Load is the only way of asynchronous import in a single import. Therefore, if you need to use asynchronous access when importing large files, you can also use Broker Load.
- Data volume
Only the case of a single BE node is discussed here. If you have multiple BE nodes in your cluster, the amount of data below should be multiplied by the number of BE nodes. For example, if you have three BE nodes, the value below 3 GB should be multiplied by 3, that is, 9 GB.
- Below 3 GB (included): You can directly submit a request to create a Broker Load import.
- Above 3 GB: Since the maximum amount of data processed by a single BE node is 3 GB in a single import job, you can import the files larger than 3 GB only by adjusting the import parameters of Broker Load.
- Change the maximum number of scans and the maximum number of concurrent imports of a single BE node based on the number of BE nodes and the source file size.
Modify FE configuration items. max_broker_concurrency = Number of BE nodes Maximum amount of data processed by a single BE node in the current import job = Source file size/max_broker_concurrency max_bytes_per_broker_scanner ≥ Maximum amount of data processed by a single BE node in the current import job For example, for a 100 GB file, the number of BE nodes in the cluster is 10. max_broker_concurrency = 10 max_bytes_per_broker_scanner ≥10 GB = 100 GB/10
After the modification, all BE nodes concurrently process the import job, and each BE node processes a part of the source file.
The configurations of two FE nodes above are all system-level configurations and their modifications apply to all Broker Load jobs.
- When creating an import job, customize its timeout period.
You are not advised to directly increase the maximum timeout period. If the time for a single import exceeds the default maximum import timeout period (4 hours), you are advised to split the file in a single import and then import the file fragments multiple times. If a single import exceeds 4 hours, it also takes a long time to retry upon an import failure.
You can use the following formula to calculate the expected maximum data volume of files to be imported in a Doris cluster:
Expected maximum data volume of files to be imported = 14,400s × 10 MB/s × Number of BE nodes Assume that the number of BE nodes in a cluster is 10. Expected maximum data volume of files to be imported = 14,400s × 10 MB/s × 10 = 1,440,000 MB ≈ 1,440 GB
Generally, a user's environment may not reach the speed of 10 MB/s, so it is recommended that files over 500 GB be split before being imported.
- Change the maximum number of scans and the maximum number of concurrent imports of a single BE node based on the number of BE nodes and the source file size.
Job Scheduling
The system limits the number of running Broker Load jobs in a cluster to prevent too many Load jobs from running at the same time.
First, the configuration parameter desired_max_waiting_jobs of the FE node will limit the number of Broker Load jobs that have not started or are running (jobs in the PENDING or LOADING state) in a cluster. The default value is 100. If the threshold is exceeded, newly submitted jobs will be rejected.
A Broker Load job has the pending task and loading task phases. The pending task phase is responsible for obtaining the information of the file to be imported, and the loading task phase will send the specific import job to the BE node to execute.
The FE configuration parameter async_pending_load_task_pool_size is used to limit the number of pending tasks running at the same time. In this way, the number of running import jobs is controlled. The default value is 10. Assume that 100 Load jobs are submitted. At the same time only 10 jobs will enter the LOADING state and start execution, while other jobs stay in the PENDING state.
The FE configuration parameter async_loading_load_task_pool_size is used to limit the number of loading tasks running at the same time. A Broker Load job will have one pending task and multiple loading tasks (equal to the number of DATA INFILE clauses in the LOAD statement). Therefore, the value of async_loading_load_task_pool_size must be greater than or equal to that of async_pending_load_task_pool_size.
Performance Analysis
You can run set enable_profile=true to enable session variables before submitting a Load job. Then, submit the import job. After the import job is complete, you can view the profile of the import job on the Queries page of the FE web UI.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





