Managing Costs
As you migrate more of your services to the cloud, managing cloud costs becomes more important. How to manage costs and reduce service loads when using MRS is also our concerns. The following describes how to manage costs in terms of cost composition, allocation, analysis, and optimization. Optimizing costs can help you maximize return on investment.
Cost Composition
Using MRS clusters incurs two types of costs:
- Resource costs: cost of resources and resource packages, depending on the billed items of MRS. For details, see Billing Items.
- O&M costs: labor costs incurred during the use of MRS clusters.
Huawei Cloud Cost Center helps you manage resource costs efficiently. You need to identify, manage, and optimize O&M costs on the page.
Cost Allocation
A good cost accountability system is the basis of cloud financial management. It ensures that departments, business teams, and owners are accountable for their respective cloud costs. Allocate costs to different teams or projects so that organizations have a clear picture of their respective costs.
Huawei Cloud provides multiple tools for you to optimize cost allocation in Cost Center.
- Allocate costs by linked account.
The enterprise master account can categorize the costs of its member accounts by linked account to manage the accounting of those member accounts. For details, see Viewing Costs by Linked Account.
- Allocate costs by enterprise project.
Before allocating costs, enable Enterprise Project Management Service (EPS) and plan your enterprise projects based on your organizational structure or businesses. Select an enterprise project for a newly purchased cloud resource so that the costs of that resource will be allocated to the selected enterprise project. For details, see Viewing Costs by Enterprise Project.
Figure 1 Selecting an enterprise project for the MRS cluster
- Allocate costs by cost tag.
Huawei Cloud assigns tags to your cloud resources so they can be sorted in different ways, for example, by purpose, owner, or environment. The following is the process of managing costs by predefined tags.
 Figure 2 Adding a tag to an MRS cluster
Figure 2 Adding a tag to an MRS cluster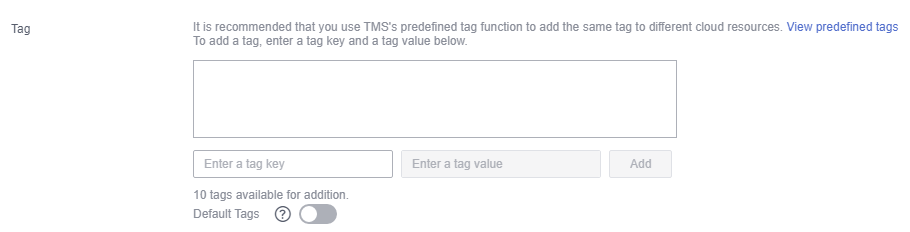
For details, see Viewing Costs by Cost Tag.
- Allocate costs by cost category.
You can use the Cost Categories in Cost Center to split shared costs. Shared costs include the costs for the resources (compute, network, storage, or resource packages) shared across departments or the costs that cannot be directly split by cost tag or enterprise project configured for the resources. These costs are not directly attributable to a singular owner, and hence cannot be categorized into a singular cost category. In this case, you can define cost splitting rules to fairly allocate these costs among teams or business units. For details, see Viewing Cost By Cost Category.
Cost Analysis
To accurately control and optimize your costs, you need a clear understanding of what parts of your enterprise incurred different costs. Cost Center visualizes original costs and amortized costs in various dimensions and through filters so that you can analyze service usage costs, trends, and factors from a variety of perspectives and scopes.
You can also use Cost Anomaly Detection to detect unexpected expenses in a timely manner. In this way, costs can be monitored, analyzed, and traced.
For details, see Performing Cost Analysis to Explore Costs and Usage and Enabling Cost Anomaly Detection to Identify Anomalies.
Cost Optimization
- Cost control
You can create different types of budgets on the Budgets page of Cost Center to track your costs against the budgeted amount you specified and send alerts to the recipients you configured if the thresholds you defined are reached. You can also create budget reports and we will periodically generate and send to the recipients you configured on a schedule you set.
For example, an enterprise needs to create a monthly cost budget for MRS. The monthly budget is ¥2,000. The system should send an alarm when the forecast amount is greater than 80% of the budget amount. Then, the created budget is as follows:
Figure 3 Basic budget information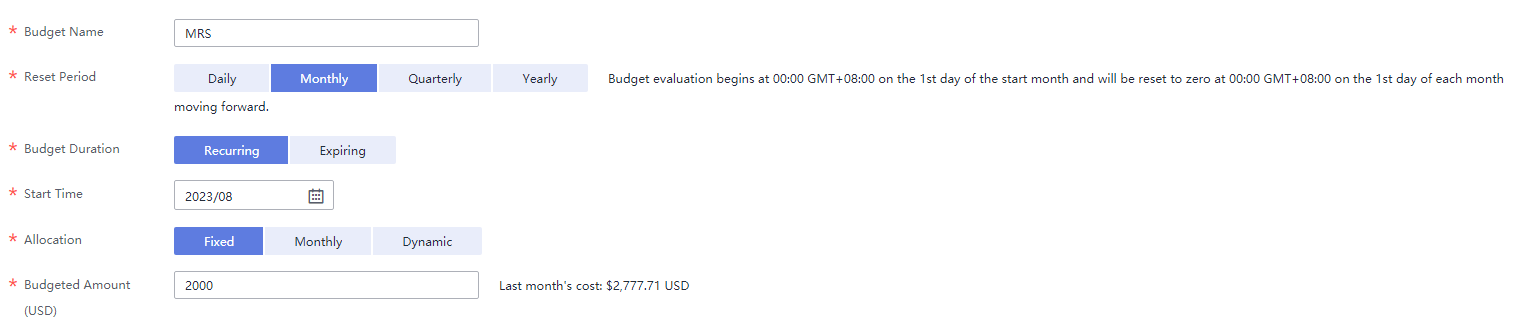 Figure 4 Budget scope
Figure 4 Budget scope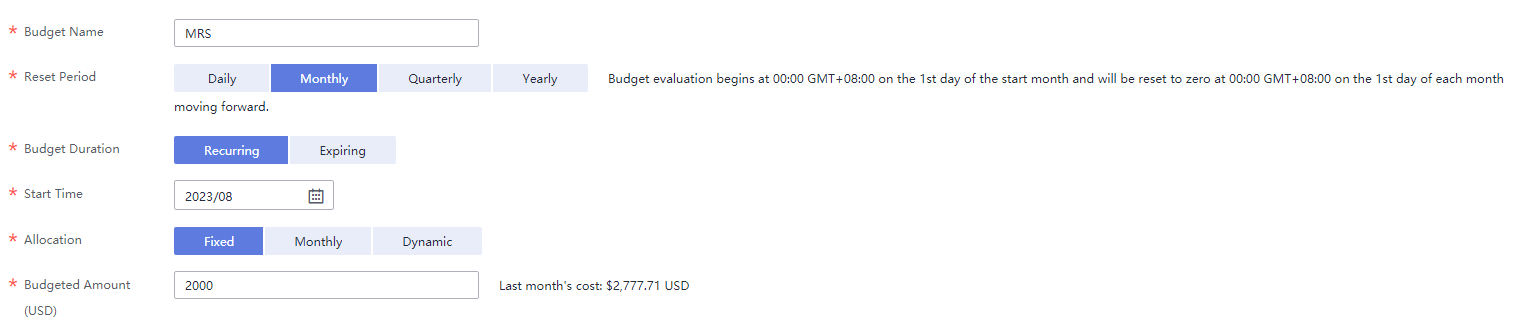 Figure 5 Budget alerts
Figure 5 Budget alerts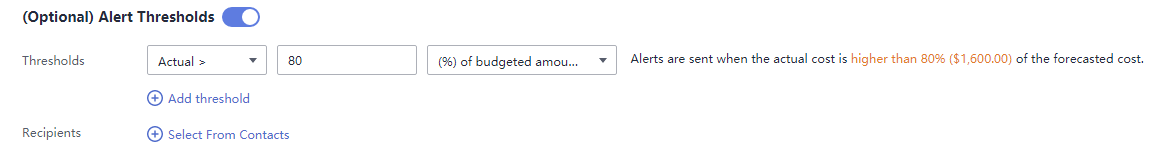
For details, see Enabling Forecasting and Creating Budgets to Track Cost and Usage.
- Resource optimization
Cloud Eye helps you monitor resource usage, identify idle resources, and find opportunities to save costs. You can also identify resources with high costs based on the analysis result in the cost analysis phase, and then take optimization measures accordingly.
- Monitor resource usage (including the usage of CPU, memory, EVS disks, and bandwidth) and evaluate whether the current configuration is too high.
- Detect idle resources (unattached EVS disks and unbound EIPs) to avoid waste.
- Billing mode selection
Different types of services have different requirements on resource usage periods and therefore require different billing modes to achieve the optimal outcome.
- For mature services that are stable for a long time, use the yearly/monthly billing mode.
- For short-term, unpredictable services that experience traffic bursts and cannot be interrupted, use pay-per-use billing.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





