Using DWS Query Filters to Intercept Slow SQL Statements
Functions
When using DWS, performance degradation or even complete unavailability of the cluster system can occur due to slow SQL queries. To address this, DWS offers a query filter function that allows you to intercept problematic statements by creating filtering rules.
The filter can block slow SQL queries based on their SQL ID. Additionally, if an exception rule is triggered a certain number of times, the corresponding SQL ID is automatically added to the blacklist for interception. For details, see exception rules. The query filter also supports more interception rules, such as SQL hash and regular expression matching. Interception rules can be associated with a specific user or database.
Notes and Constraints
The query filter is supported only by clusters of version 9.1.0.200 or later.
Creating a Query Filter
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster to go to the Cluster Information page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Resource Management.
- Click the Query Filter tab. On the displayed page, click Create and set the parameters listed in Table 1.
Figure 1 Adding a query filter
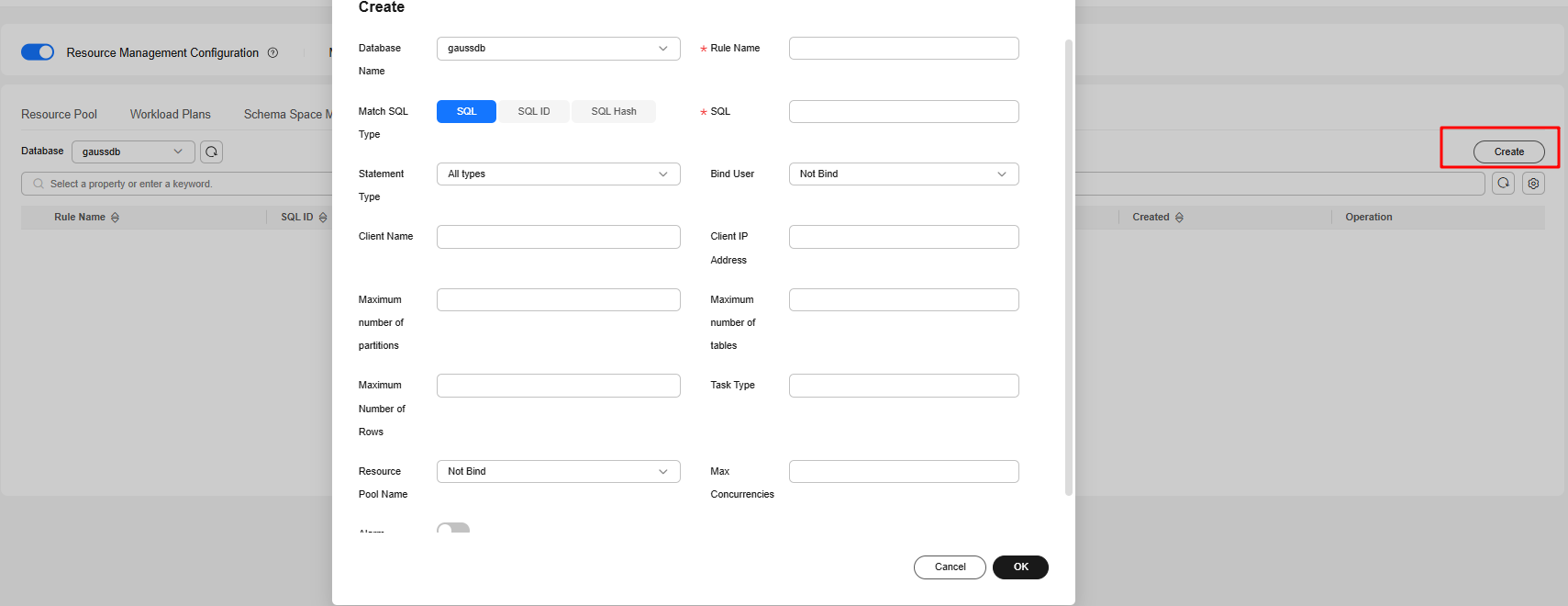
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Mandatory
Description
Database Name
Yes
Select a database from the drop-down list.
Rule Name
Yes
Name of the query filter. The value can contain 3 to 63 characters, including uppercase letters, lowercase letters, underscores (_), and dollar signs ($). The value must be unique.
Match SQL Type
Yes
You can select SQL, SQL ID, or QL Hash.
- SQL: Query the SQL statement that matches the filtering rule.
- SQL ID: Query the unique_sql_id value that matches the filtering rule.
- SQL Hash: Query the sql_hash value that matches the filtering rule.
Statement Type
No
You can select All types (default), SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE, and MERGE.
Bind User
No
The setting takes effect for a specified user.
Client Name
No
Name of the application that is connected to the database. You can assign a custom application name to each connection, such as gsql.
Client IP Address
No
The setting takes effect for a specified IP address.
Maximum number of partitions
No
Estimated maximum number of partitions on the node to be scanned.
Maximum number of tables
No
Estimated maximum number of tables to be scanned.
Maximum Number of Rows
No
Estimated maximum number of rows on a node to be scanned.
Task Type
No
Type of a task that is actively marked.
Resource Pool Name
No
Name of the resource pool that matches the filtering rule.
Max. Concurrencies
No
Maximum number of concurrent statements corresponding to the filtering rule.
Alarm
No
Whether to enable alarm reporting for filtering rules.
- Click OK.
Query Filter Management Operations
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster to go to the Cluster Information page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Resource Management.
- Click the Query Filter tab. You can edit or delete query filters. The following table lists the operations.
Table 2 Query filter management operations Operation
Description
Edit
Locate a query filter and click Edit in the Operation column to modify the filter parameters listed in Table 1.
Delete
Locate a query filter and click Delete in the Operation column to delete the filter.
- Click OK.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





